Pyramid. Correct pyramid
Polyhedra
This video tutorial will help users get an idea of the Pyramid theme. Correct pyramid. In this lesson we will get acquainted with the concept of a pyramid and give it a definition. Let's consider what a regular pyramid is and what properties it has. Then we prove the lateral surface theorem regular pyramid.
In this lesson we will get acquainted with the concept of a pyramid and give it a definition.
Consider a polygon A 1 A 2...A n, which lies in the α plane, and the point P, which does not lie in the α plane (Fig. 1). Let's connect the dots P with peaks A 1, A 2, A 3, … A n. We get n triangles: A 1 A 2 R, A 2 A 3 R and so on.
Definition. Polyhedron RA 1 A 2 ...A n, made up of n-square A 1 A 2...A n And n triangles RA 1 A 2, RA 2 A 3 …RA n A n-1 is called n-coal pyramid. Rice. 1.
Rice. 1
Consider a quadrangular pyramid PABCD(Fig. 2).
R- the top of the pyramid.
ABCD- the base of the pyramid.
RA - side rib.
AB- base rib.
From point R let's drop the perpendicular RN to the base plane ABCD. The perpendicular drawn is the height of the pyramid.
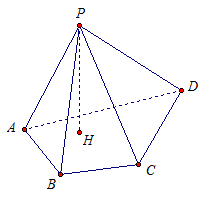
Rice. 2
Full surface The pyramid consists of a lateral surface, that is, the area of all lateral faces, and the area of the base:
S full = S side + S main
A pyramid is called correct if:
- its foundation - regular polygon;
- the segment connecting the top of the pyramid to the center of the base is its height.
Explanation using the example of a regular quadrangular pyramid
Consider a regular quadrangular pyramid PABCD(Fig. 3).
R- the top of the pyramid. Base of the pyramid ABCD- a regular quadrilateral, that is, a square. Dot ABOUT, the point of intersection of the diagonals, is the center of the square. Means, RO is the height of the pyramid.
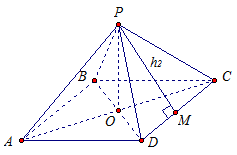
Rice. 3
Explanation: in the correct n In a triangle, the center of the inscribed circle and the center of the circumcircle coincide. This center is called the center of the polygon. Sometimes they say that the vertex is projected into the center.
The height of the side face of a regular pyramid drawn from its vertex is called apothem and is designated h a.
1. all lateral edges of a regular pyramid are equal;
2. side faces are congruent isosceles triangles.
We will give a proof of these properties using the example of a regular quadrangular pyramid.
Given: PABCD- regular quadrangular pyramid,
ABCD- square,
RO- height of the pyramid.
Prove:
1. RA = PB = RS = PD
2.∆ABP = ∆BCP =∆CDP =∆DAP See Fig. 4.
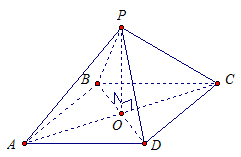
Rice. 4
Proof.
RO- height of the pyramid. That is, straight RO perpendicular to the plane ABC, and therefore direct JSC, VO, SO And DO lying in it. So triangles ROA, ROV, ROS, ROD- rectangular.
Consider a square ABCD. From the properties of a square it follows that AO = VO = CO = DO.
Then the right triangles ROA, ROV, ROS, ROD leg RO- general and legs JSC, VO, SO And DO are equal, which means that these triangles are equal on two sides. From the equality of triangles follows the equality of segments, RA = PB = RS = PD. Point 1 has been proven.
Segments AB And Sun are equal because they are sides of the same square, RA = PB = RS. So triangles AVR And VSR - isosceles and equal on three sides.
In a similar way we find that triangles ABP, VCP, CDP, DAP are isosceles and equal, as required to be proved in paragraph 2.
The area of the lateral surface of a regular pyramid is equal to half the product of the perimeter of the base and the apothem:
![]()
To prove this, let’s choose a regular triangular pyramid.
Given: RAVS- regular triangular pyramid.
AB = BC = AC.
RO- height.
Prove: ![]() . See Fig. 5.
. See Fig. 5.
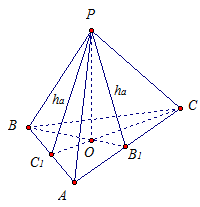
Rice. 5
Proof.
RAVS- regular triangular pyramid. That is AB= AC = BC. Let ABOUT- center of the triangle ABC, Then RO is the height of the pyramid. At the base of the pyramid lies equilateral triangle ABC. notice, that ![]() .
.
Triangles RAV, RVS, RSA- equal isosceles triangles(by property). A triangular pyramid has three side faces: RAV, RVS, RSA. This means that the area of the lateral surface of the pyramid is:
S side = 3S RAW
The theorem has been proven.
The radius of a circle inscribed at the base of a regular quadrangular pyramid is 3 m, the height of the pyramid is 4 m. Find the area of the lateral surface of the pyramid.
Given: regular quadrangular pyramid ABCD,
ABCD- square,
r= 3 m,
RO- height of the pyramid,
RO= 4 m.
Find: S side. See Fig. 6.
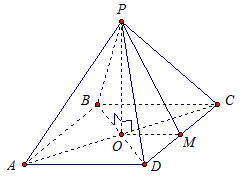
Rice. 6
Solution.
According to the proven theorem, ![]() .
.
Let's first find the side of the base AB. We know that the radius of a circle inscribed at the base of a regular quadrangular pyramid is 3 m.
Then, m.
Find the perimeter of the square ABCD with a side of 6 m:
Consider a triangle BCD. Let M- middle of the side DC. Because ABOUT- middle BD, That ![]() (m).
(m).
Triangle DPC- isosceles. M- middle DC. That is, RM- median, and therefore the height in the triangle DPC. Then RM- apothem of the pyramid.
RO- height of the pyramid. Then, straight RO perpendicular to the plane ABC, and therefore direct OM, lying in it. Let's find the apothem RM from right triangle ROM.
Now we can find lateral surface pyramids:
Answer: 60 m2.
The radius of the circle circumscribed around the base of a regular triangular pyramid is equal to m. The lateral surface area is 18 m 2. Find the length of the apothem.
Given: ABCP- regular triangular pyramid,
AB = BC = SA,
R= m,
S side = 18 m2.
Find: . See Fig. 7.
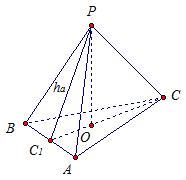
Rice. 7
Solution.
In a right triangle ABC The radius of the circumscribed circle is given. Let's find a side AB this triangle using the theorem of sines.
![]()
Knowing the side of a regular triangle (m), we find its perimeter.
By the theorem on the lateral surface area of a regular pyramid ![]() , Where h a- apothem of the pyramid. Then:
, Where h a- apothem of the pyramid. Then:
![]()
Answer: 4 m.
So, we looked at what a pyramid is, what a regular pyramid is, and we proved the theorem about the lateral surface of a regular pyramid. In the next lesson we will get acquainted with the truncated pyramid.
Bibliography
- Geometry. Grades 10-11: textbook for students educational institutions(basic and profile levels) / I. M. Smirnova, V. A. Smirnov. - 5th ed., rev. and additional - M.: Mnemosyne, 2008. - 288 p.: ill.
- Geometry. 10-11 grade: Textbook for general education educational institutions/ Sharygin I.F. - M.: Bustard, 1999. - 208 p.: ill.
- Geometry. Grade 10: Textbook for general education institutions with in-depth and specialized study mathematics /E. V. Potoskuev, L. I. Zvalich. - 6th ed., stereotype. - M.: Bustard, 008. - 233 p.: ill.
- Internet portal "Yaklass" ()
- Internet portal "Festival pedagogical ideas"First of September" ()
- Internet portal “Slideshare.net” ()
Homework
- Can a regular polygon be the base of an irregular pyramid?
- Prove that disjoint edges of a regular pyramid are perpendicular.
- Find the value dihedral angle at the side of the base of a regular quadrangular pyramid, if the apothem of the pyramid is equal to the side of its base.
- RAVS- regular triangular pyramid. Build linear angle dihedral angle at the base of the pyramid.
Chudaeva E.V., Municipal Educational Institution “Insarskaya Secondary School No. 1”, Insar, Republic of Mordovia
SOLVING GEOMETRIC PROBLEMS
(By Unified State Exam materials)
Task No. 1
Task No. 2
Task No. 3
Task No. 4. Calculate the volume of a regular triangular pyramid whose base side is 6 and whose apothem is equal to 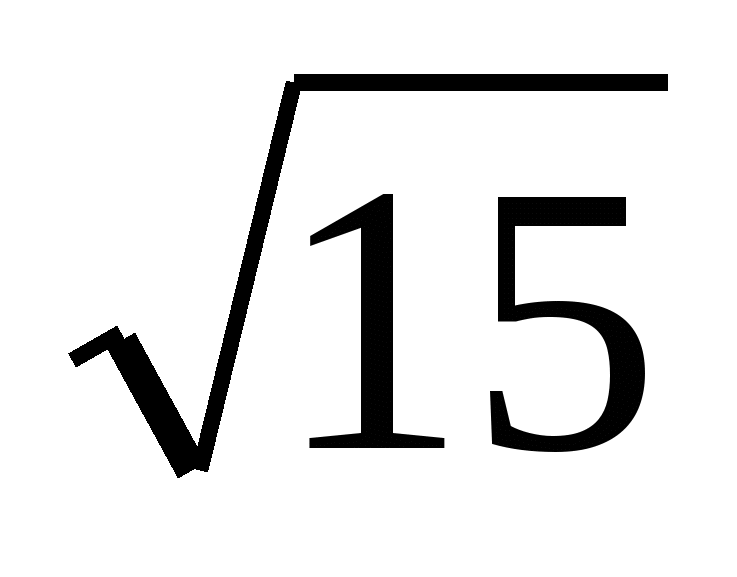 .
.
Problem #5. Calculate the volume of a regular triangular pyramid if the radius of the circle inscribed at the base is 2 and the height of the regular pyramid is 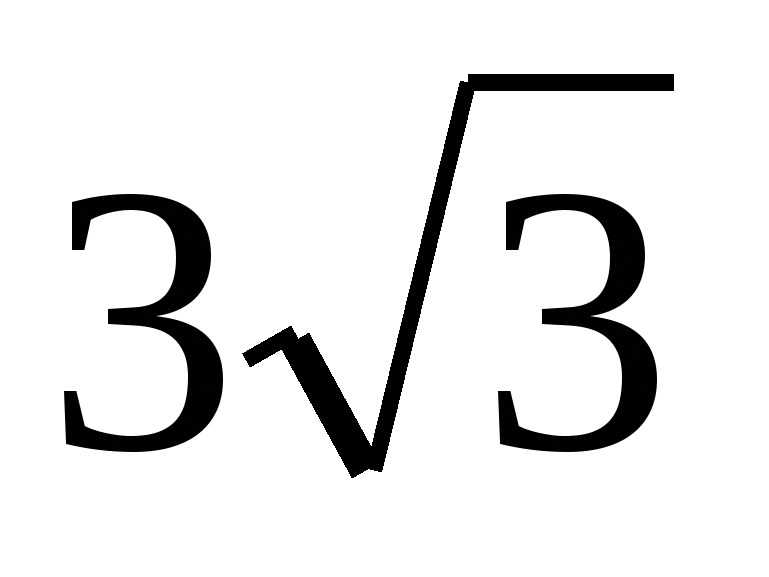 .
.
Problem #6. Calculate the lateral surface area of a regular quadrangular pyramid if its edges are 5 and the radius of the circle circumscribed around the base is 3 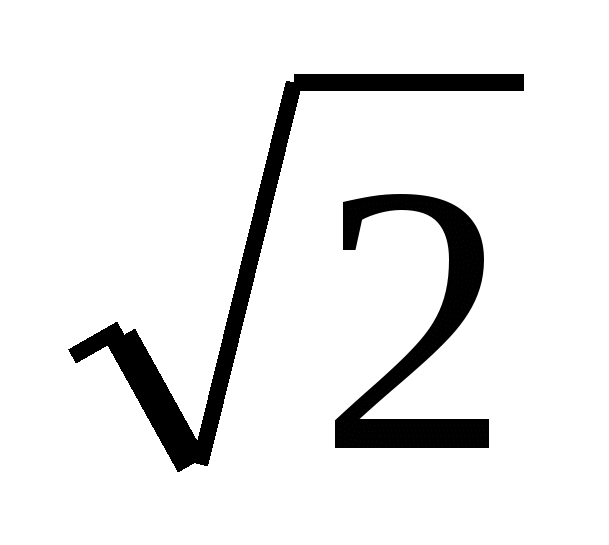 .
.
Problem No. 7
Problem No. 8
Problem No. 9. In the right hexagonal pyramid the side of the base is 2 and the side edge is 2 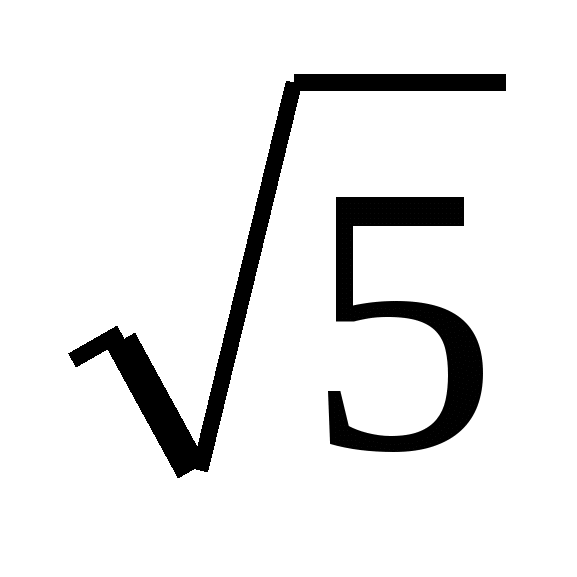 . Find the volume of the pyramid.
. Find the volume of the pyramid.
Problem No. 10R satisfies the equation R 2 + R – 6 = 0. Find the volume of the prism.
Problem No. 11. Near the right one triangular prism the cylinder is described. The distance between the cylinder axis and the side of the prism base is equal to 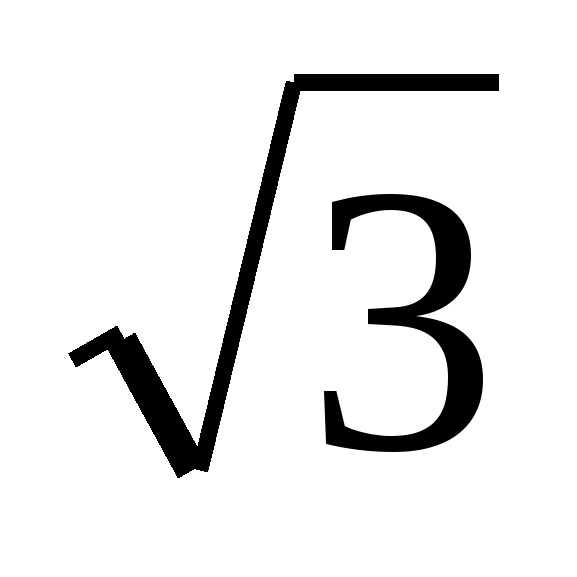 . The height of a cylinder is equal to three of its radii. Find the volume of the prism.
. The height of a cylinder is equal to three of its radii. Find the volume of the prism.
Problem No. 12
Problem No. 13
Problem No. 14. A cylinder is inscribed in a regular quadrangular prism. The volume of the cylinder is 16 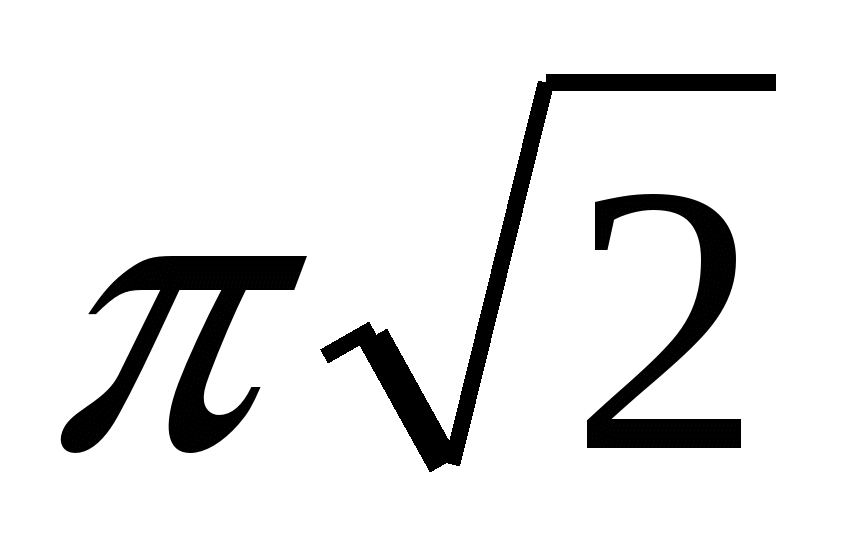 , and the radius of the circle circumscribed around the base of the prism is equal to
, and the radius of the circle circumscribed around the base of the prism is equal to 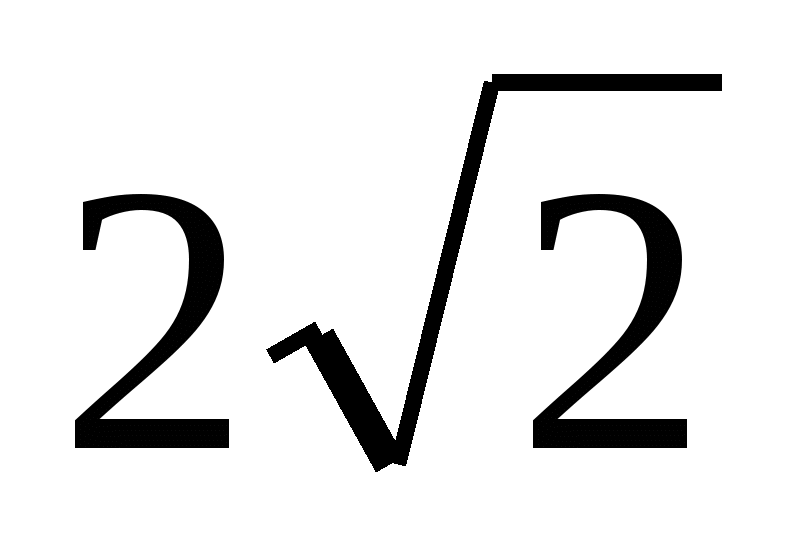 . Find the diagonal of the prism.
. Find the diagonal of the prism.
Problem No. 15. A cylinder is inscribed in a regular hexagonal prism. Find the height of the prism if its area is 54 and the radius of the cylinder is 3.
Problem No. 16. Near the right one hexagonal prism the cylinder is described. The volume of the cylinder is 16 , the height of the cylinder is 4. Find the volume of the prism.
Problem No. 17. A cylinder is described around a regular hexagonal prism. The volume of the cylinder is 10 . Find the volume of a cylinder inscribed in the same prism.
SOLVING GEOMETRIC PROBLEMS
(based on Unified State Exam materials)
Task No. 1 . Calculate the volume of a regular triangular pyramid if the radius of the circle circumscribed around the base is equal to , and the height of the pyramid is equal to 4.
R 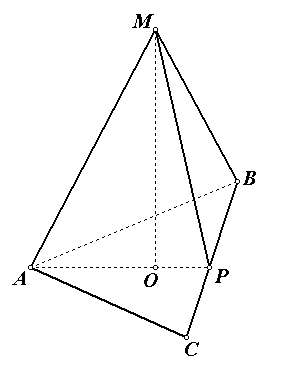 decision.
decision.
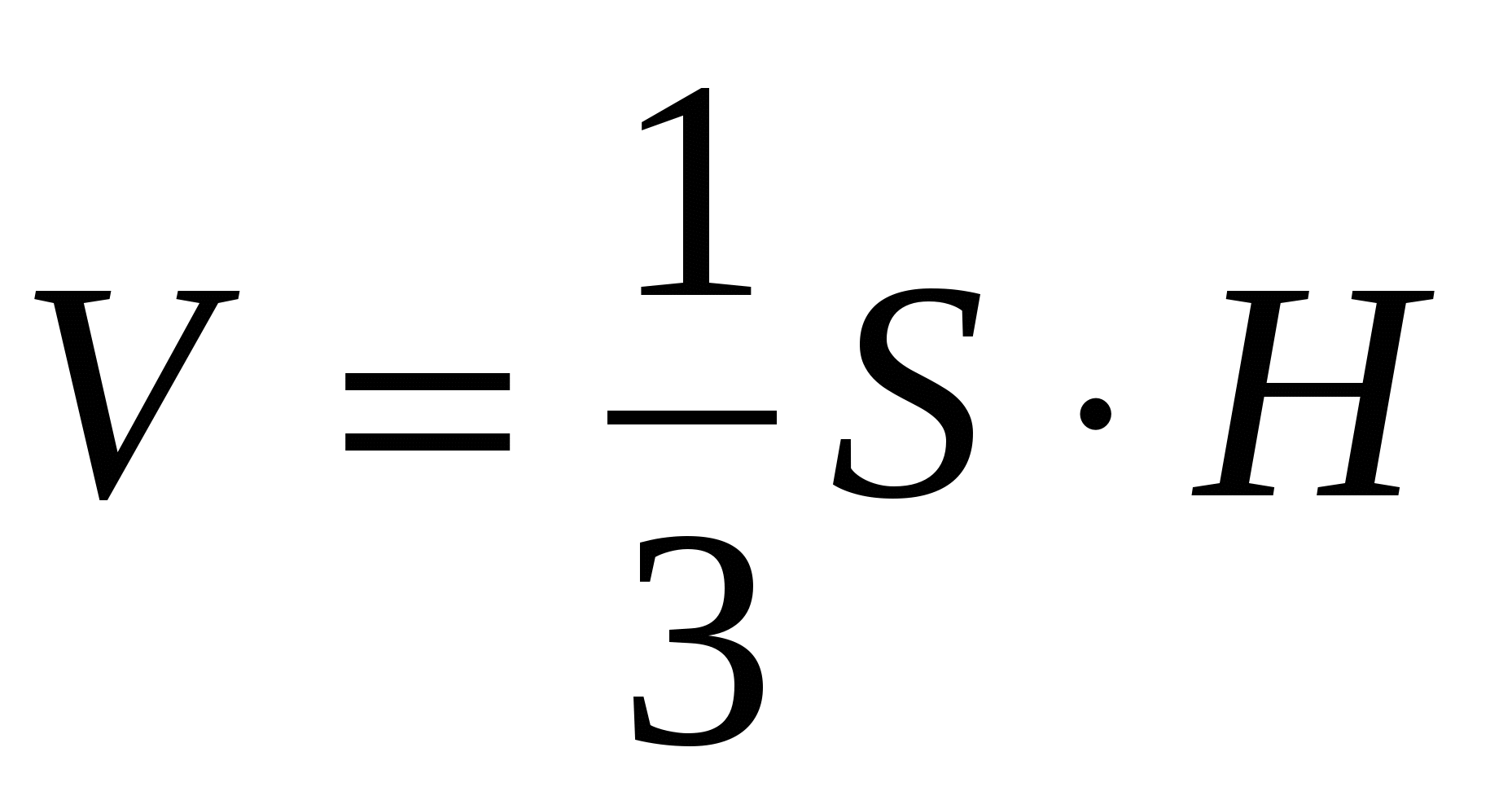 .
.
1) find the side of the base of a regular pyramid using the formula 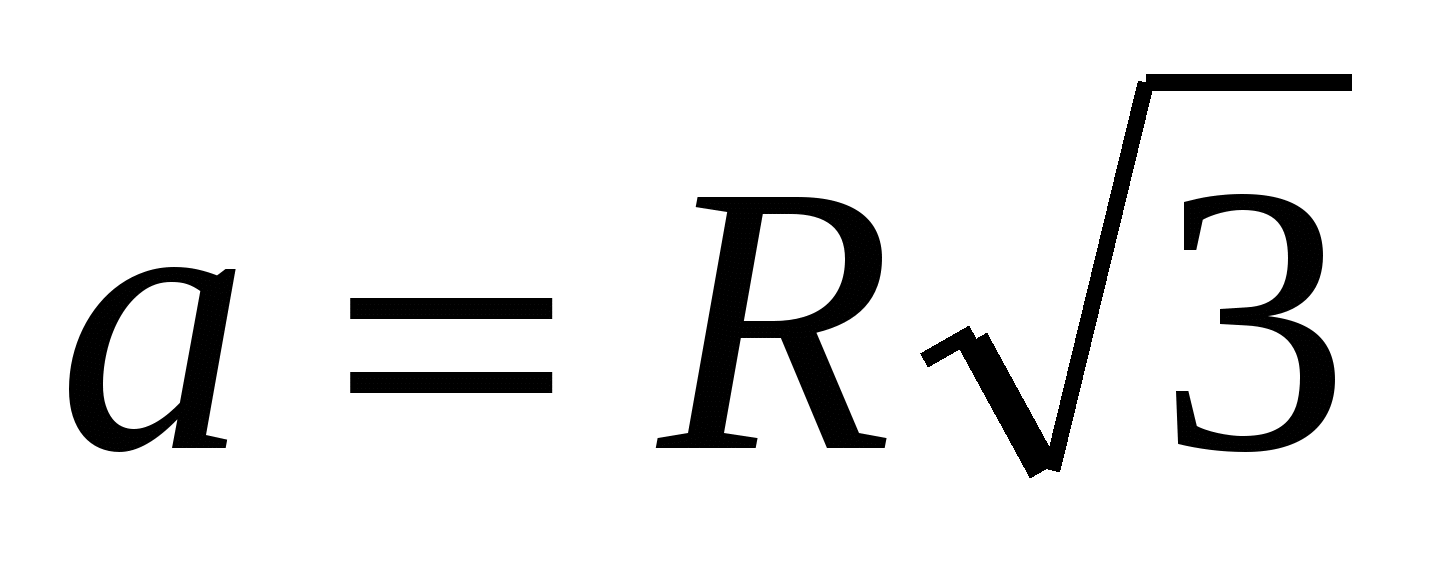 ,
, 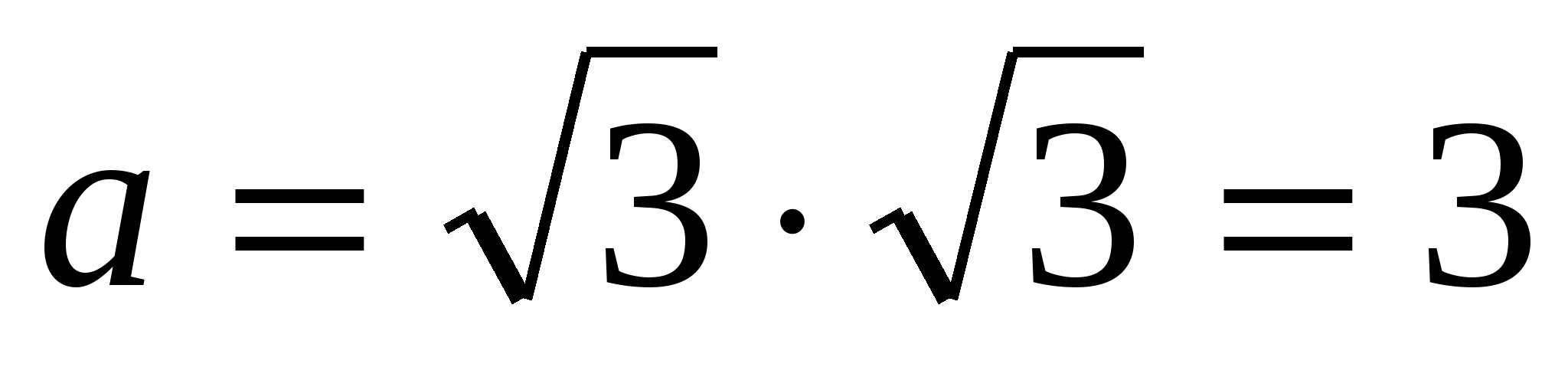 .
.
2) find the area of the base as the area of a regular triangle 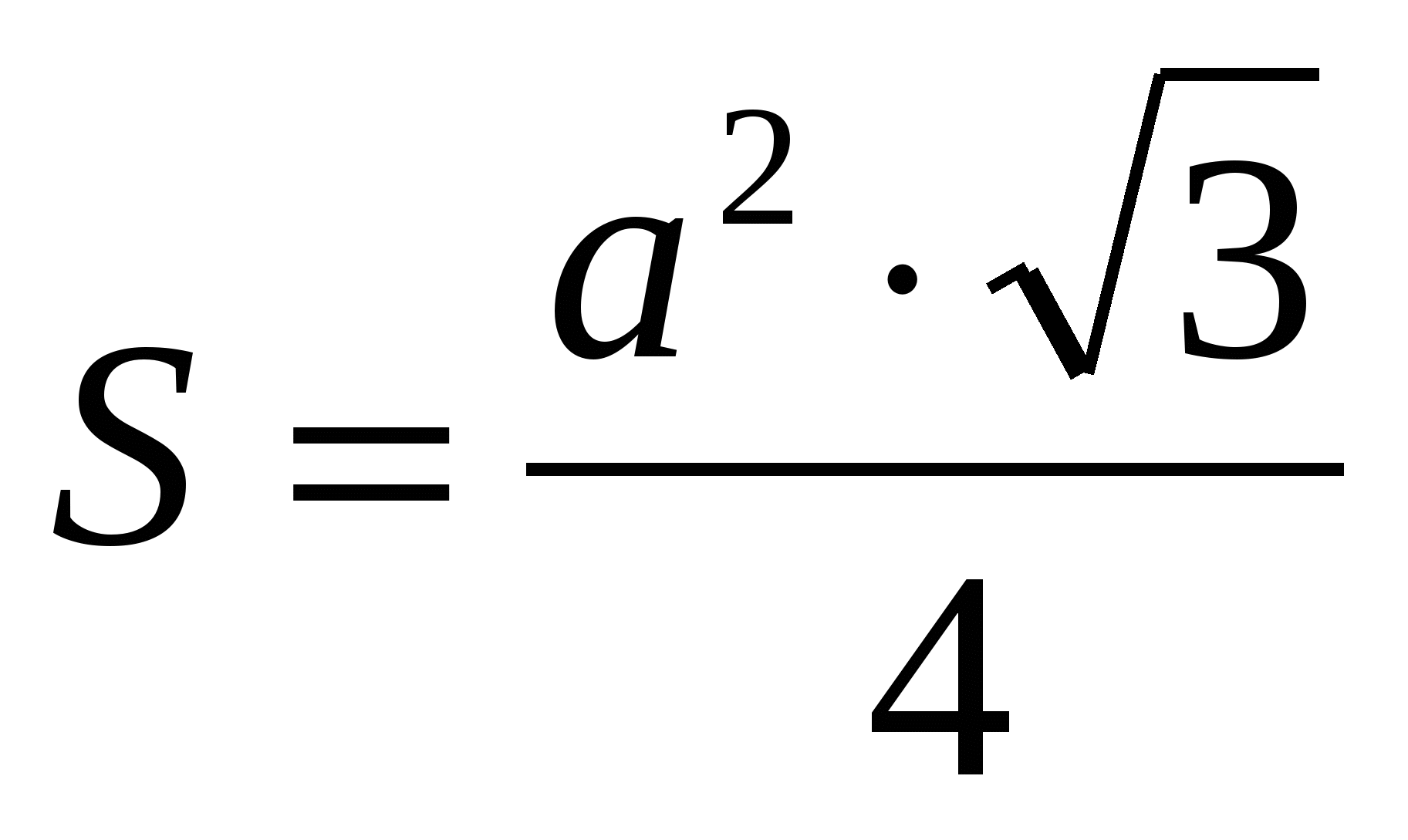 ,
, 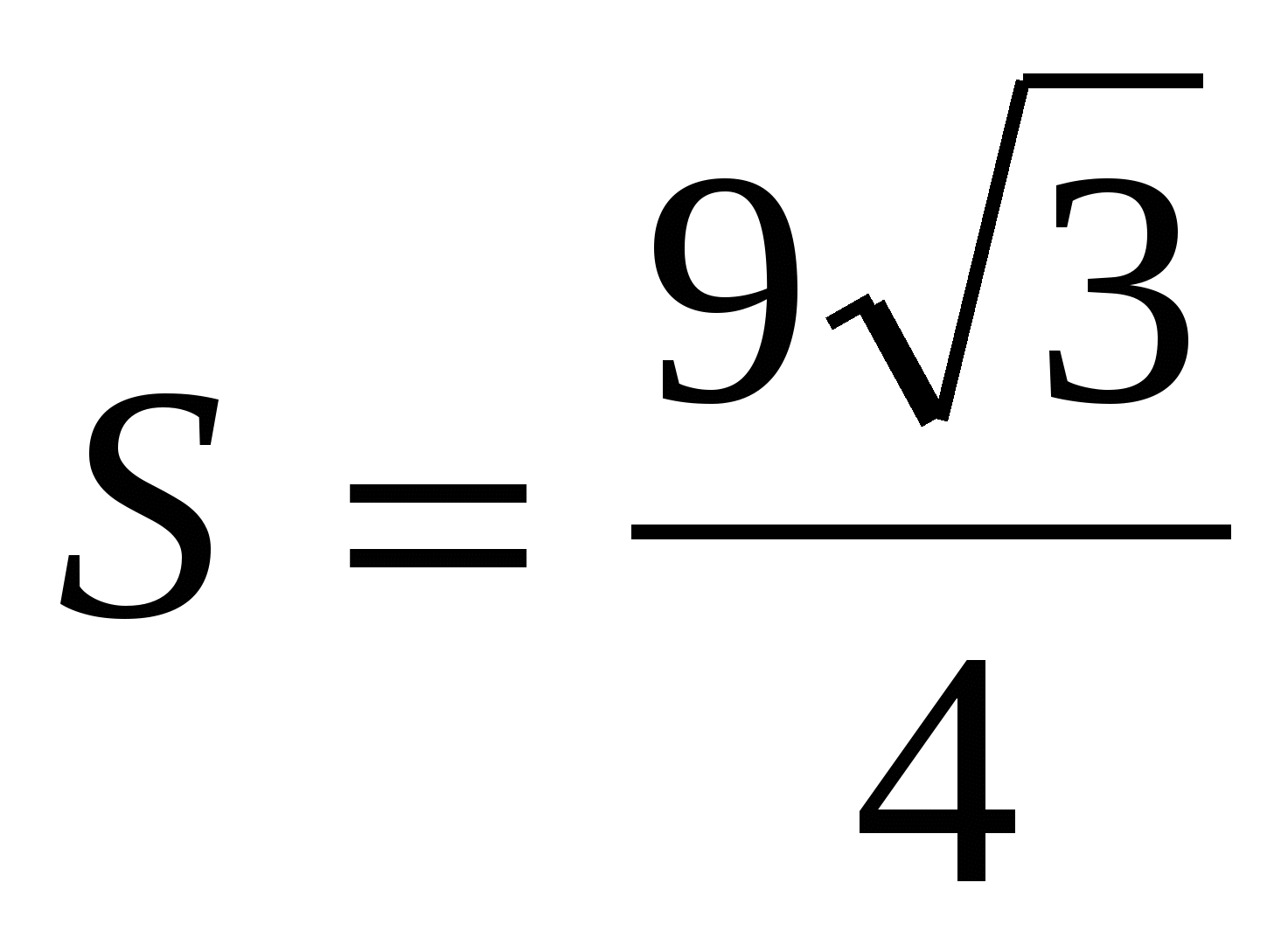 .
.
3) calculate the volume of the pyramid
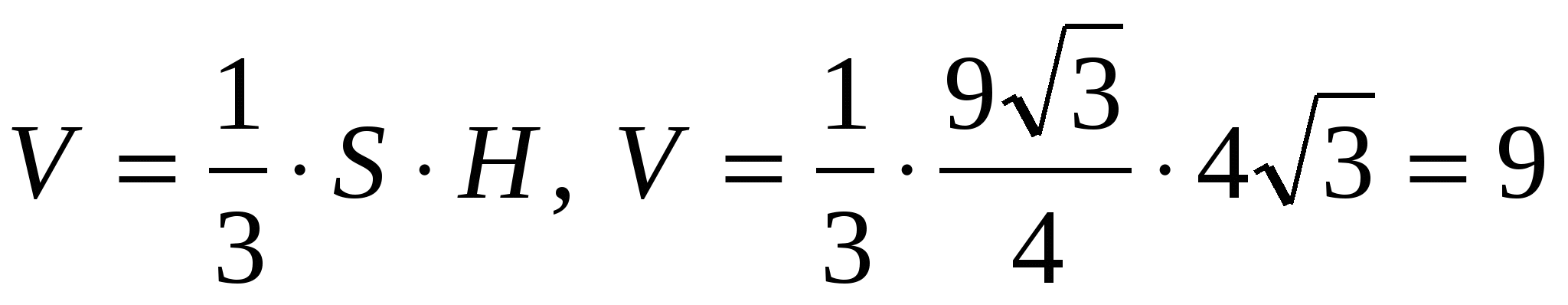 .
.
Answer. 9
Task No. 2 . Calculate the volume of a regular triangular pyramid if the radius of the circle inscribed at the base is equal to , and the lateral edges of the pyramid are equal to 6.
Solution.
1) the radius of the circle inscribed in a regular triangle is 2 times less than the radius of the circle circumscribed about this triangle, i.e. 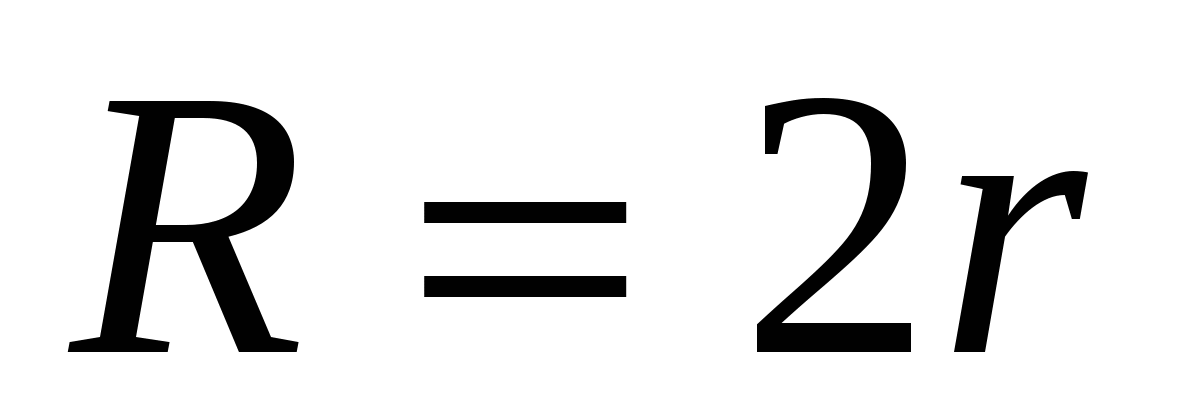 , Then
, Then 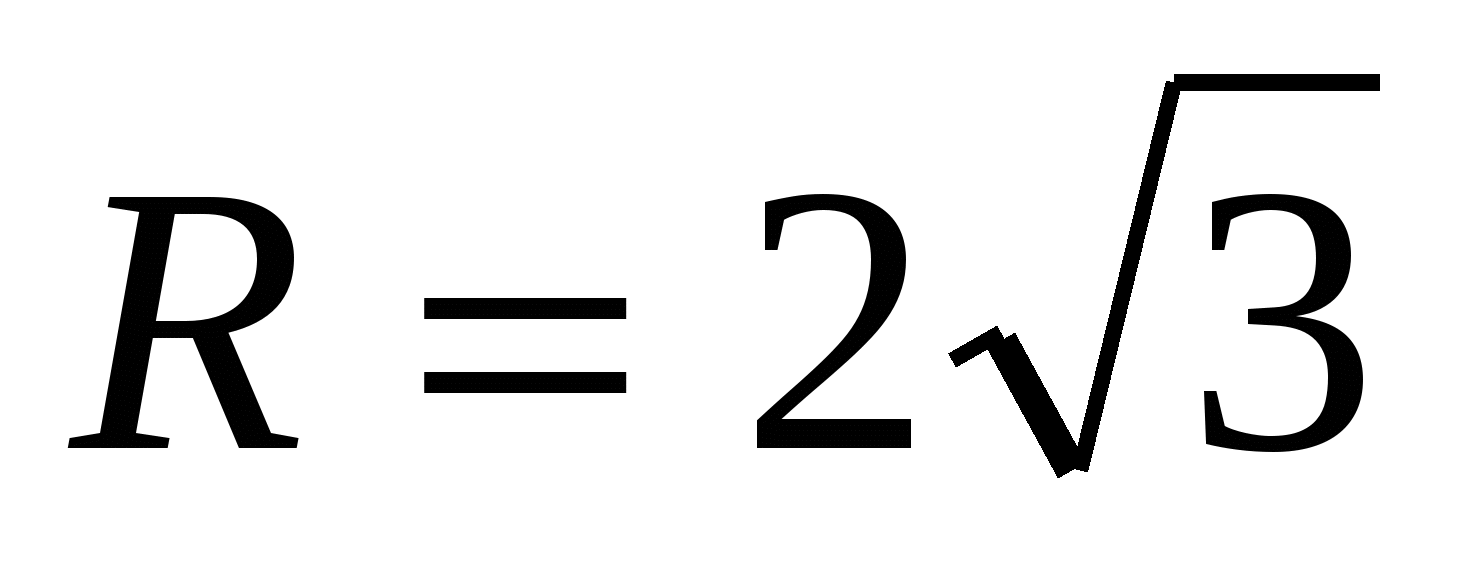 .
.
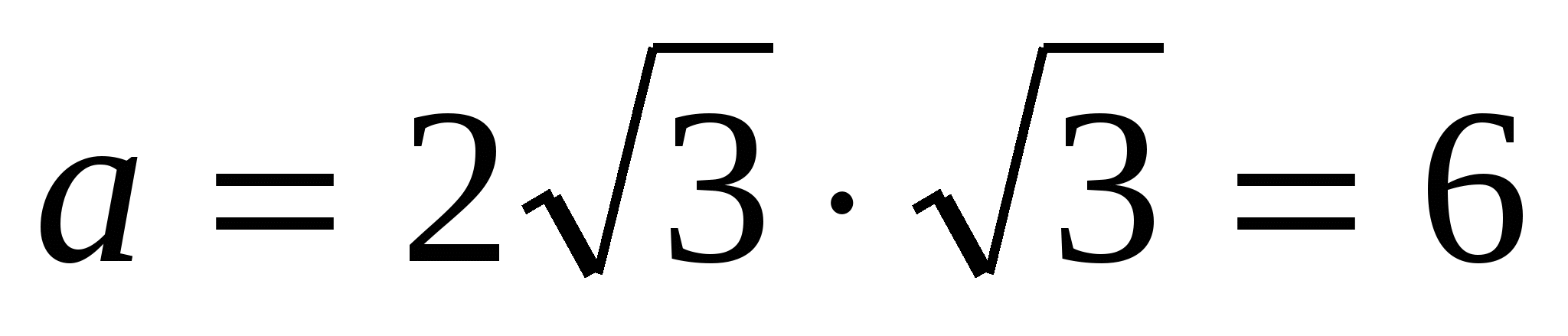 .
.
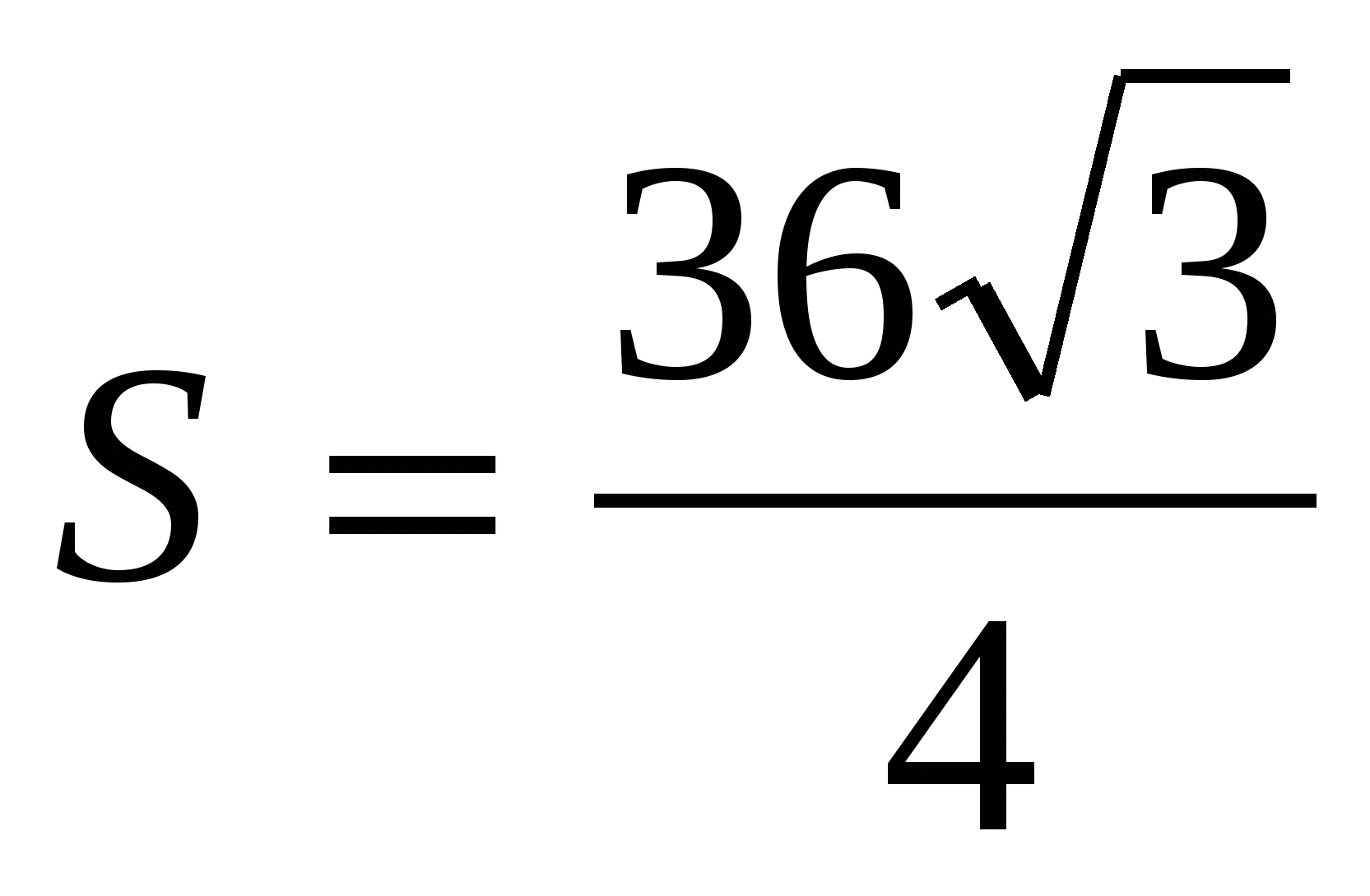 .
.
4) from a right triangle 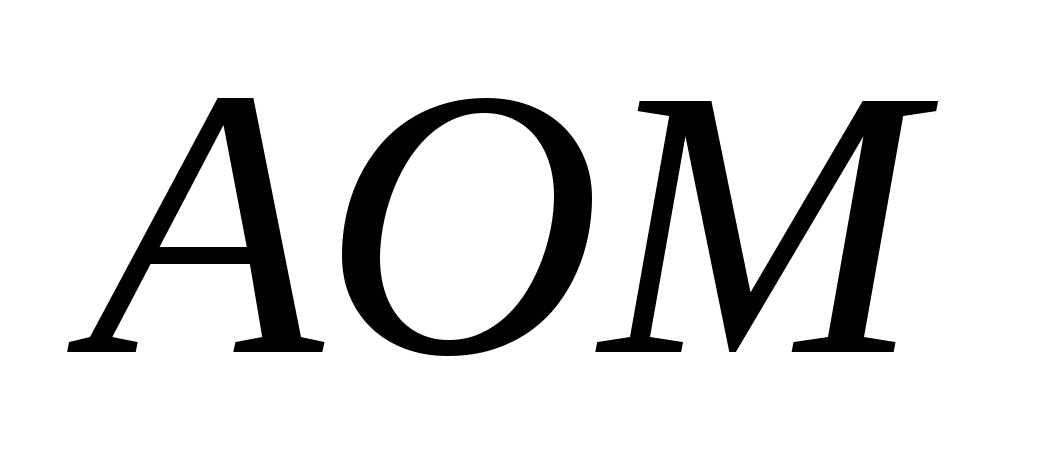 Using the Pythagorean theorem we find the height of the pyramid:
Using the Pythagorean theorem we find the height of the pyramid: 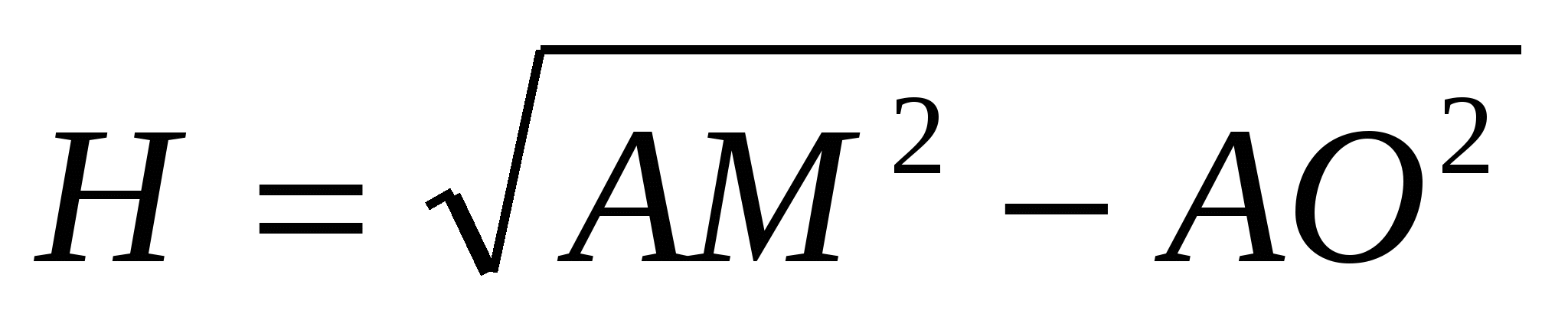 , .
, .
5) calculate the volume of the pyramid
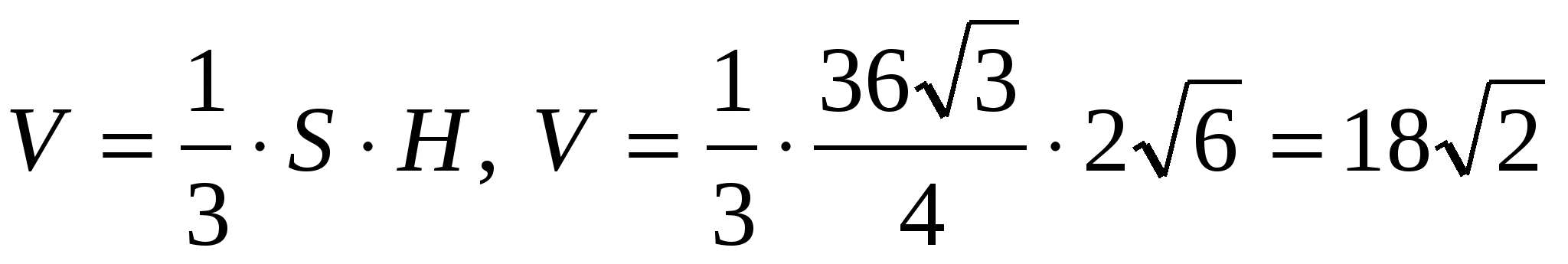 .
.
Answer. 18.
Task No. 3 . Calculate the lateral surface area of a regular triangular pyramid if the radius of the circle circumscribed near the base is equal to , and the height of the pyramid is equal to 1.
R 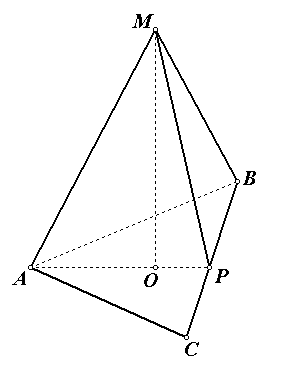 decision.
decision.
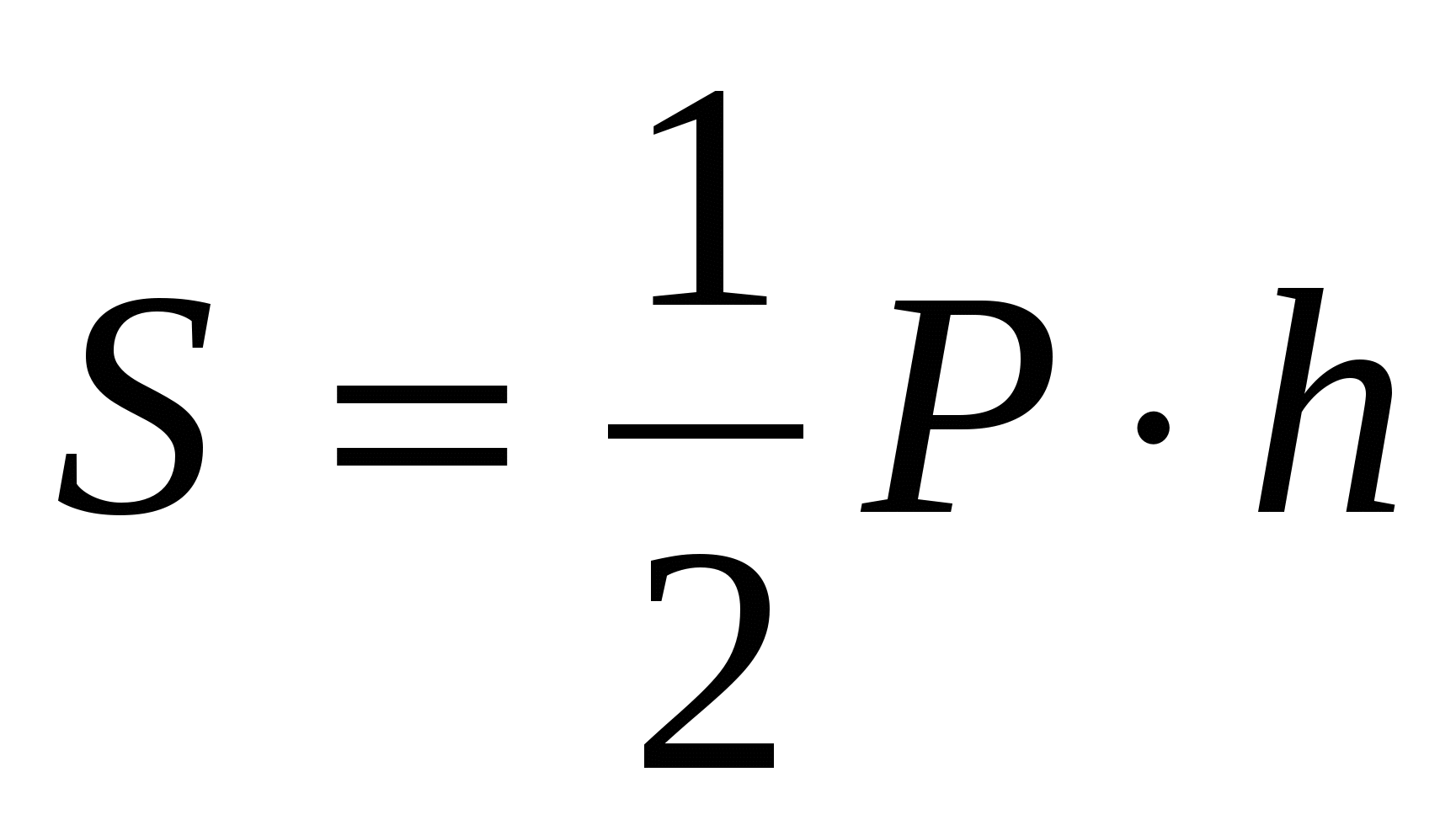
1) find the side of the base of a regular pyramid using the formula , .
2) find the perimeter of the base P = 3· A,
P = 9.
3) the radius of the circle inscribed in a regular triangle is 2 times less than the radius of the circle circumscribed about this triangle, i.e. , Then 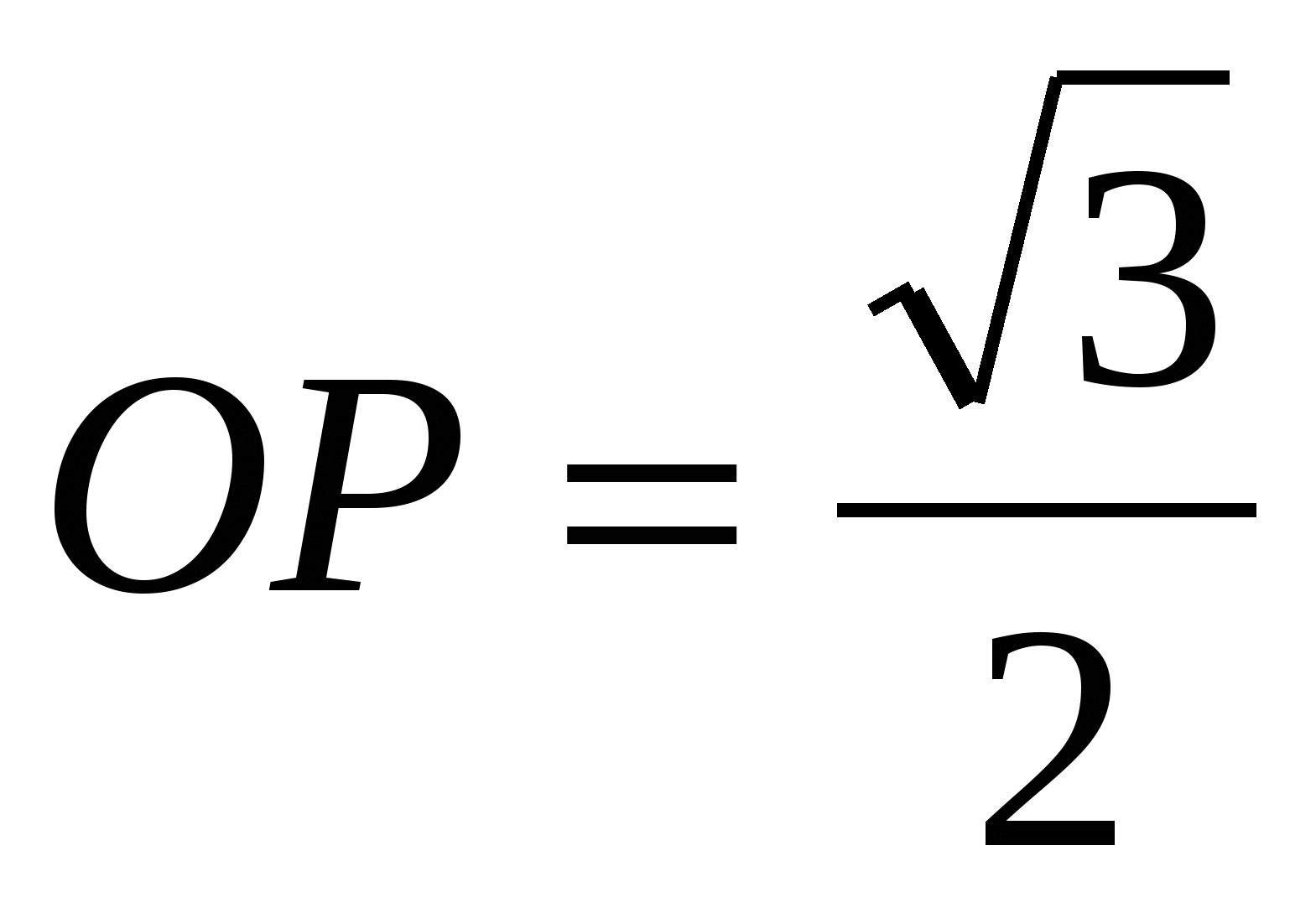 .
.
4) from a right triangleMPA
MR
: ![]() ,
,
MR
= 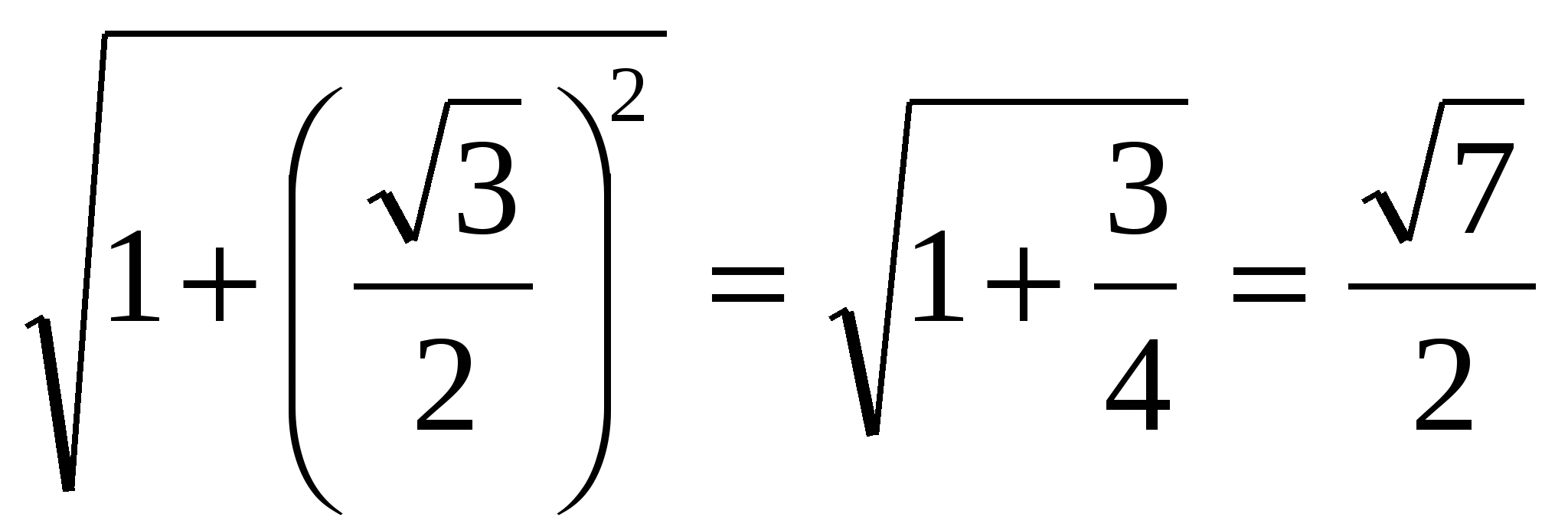
5) calculate the area of the lateral surface of a regular pyramid:
,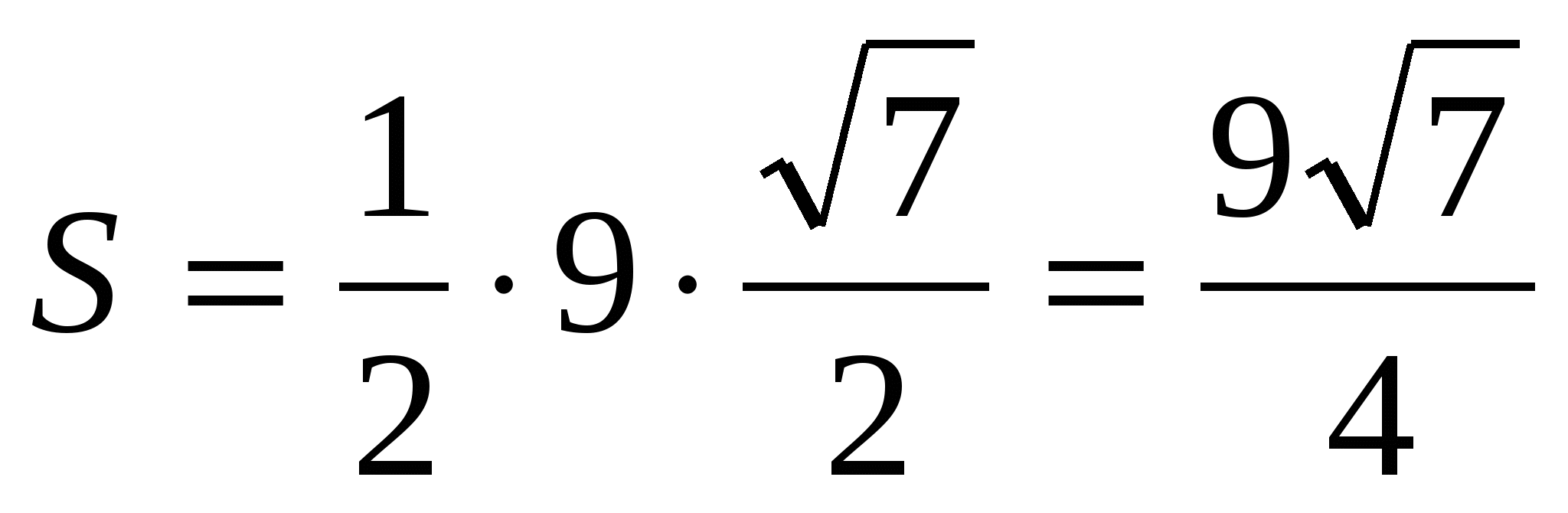 .
.
Answer. 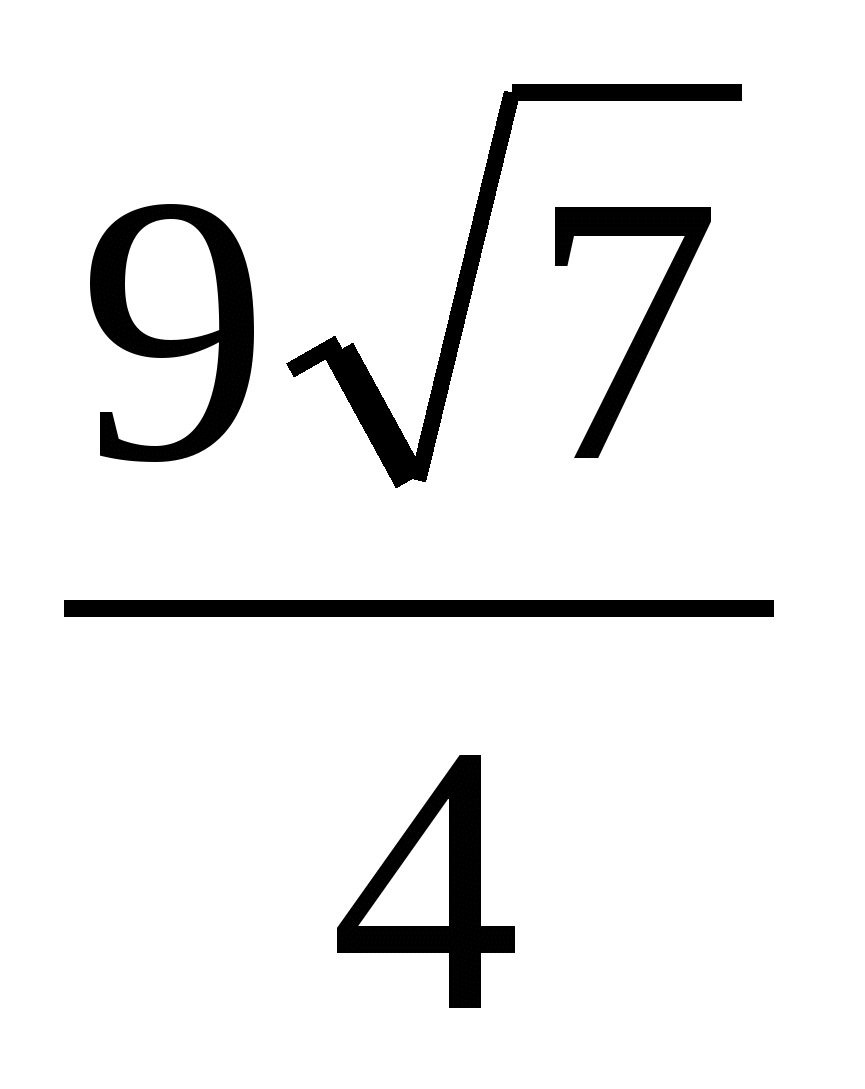 .
.
Task No. 4 . Calculate the volume of a regular triangular pyramid whose base side is 6 and whose apothem is 6.
Solution. ,
1) find the radius of the circles described near the base and inscribed in the base: , 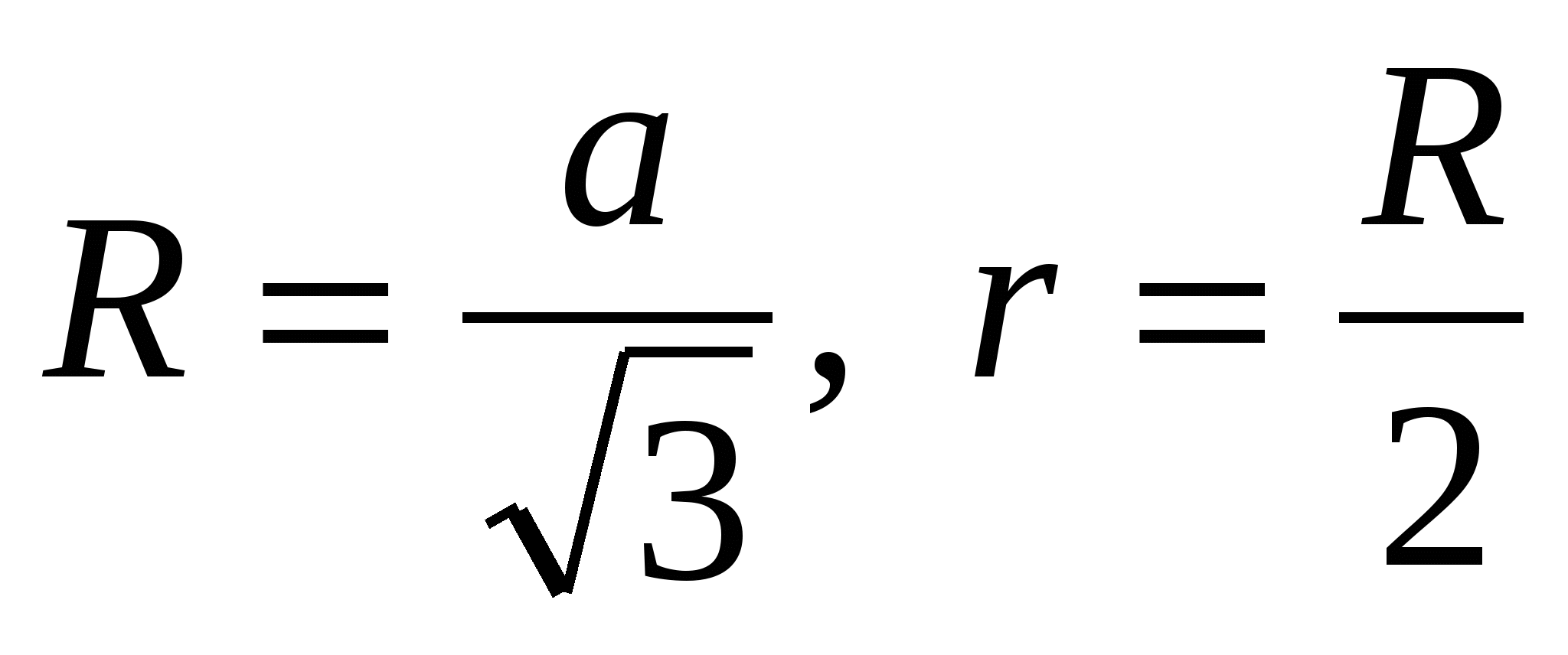 that is
that is 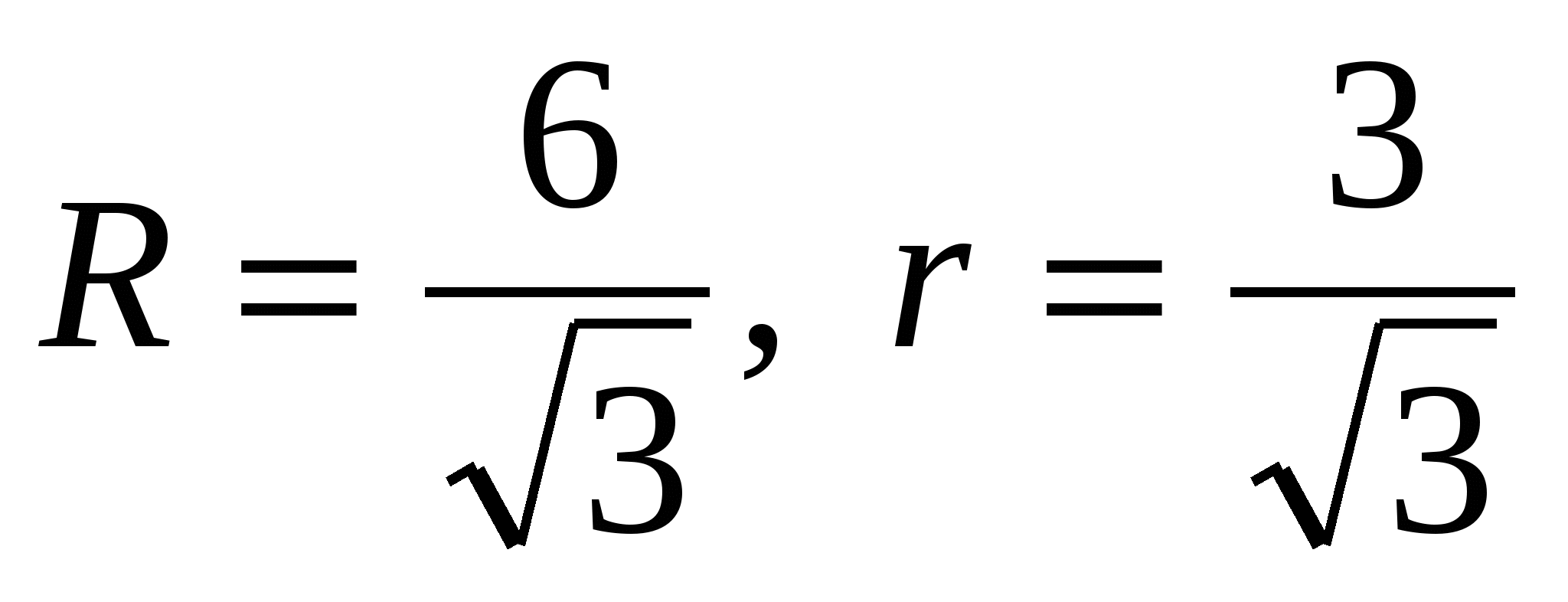 .
.
2) find the area of the base as the area of a regular triangle, 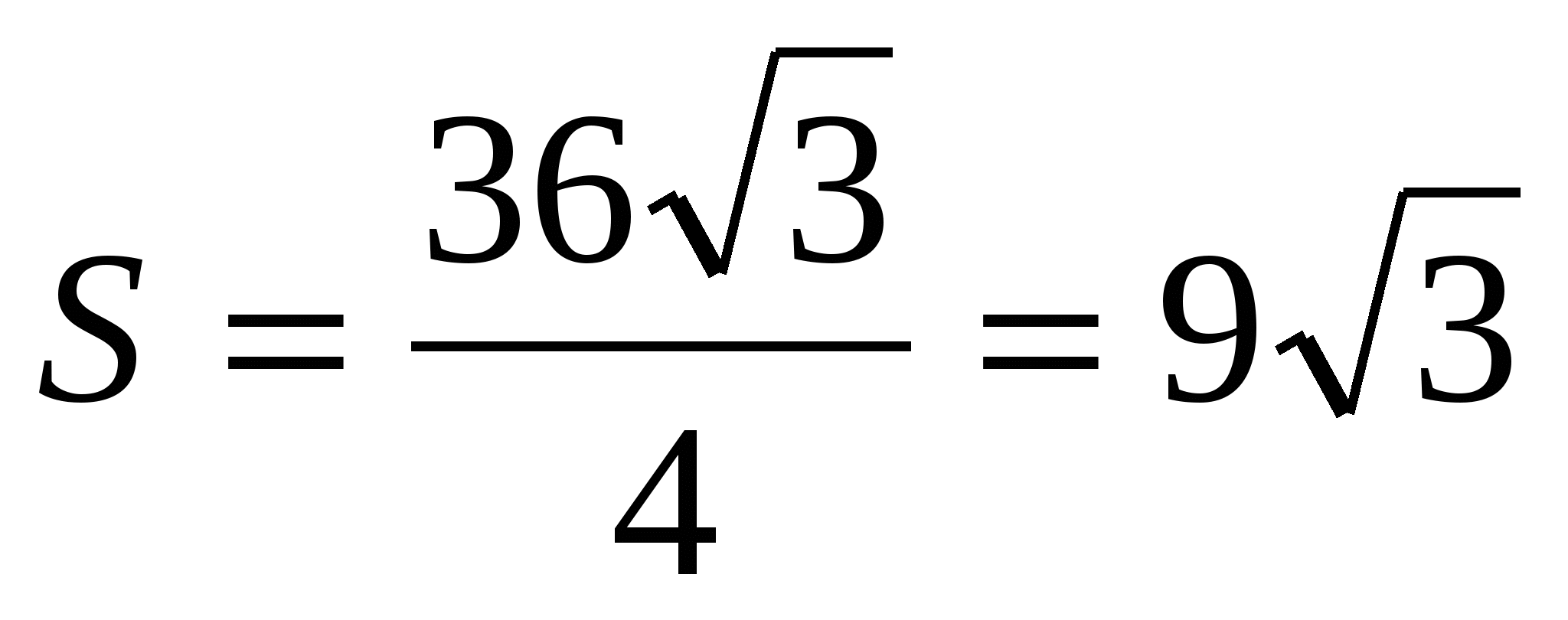 .
.
MPA
Using the Pythagorean theorem we find the height:  , MO =
, MO = 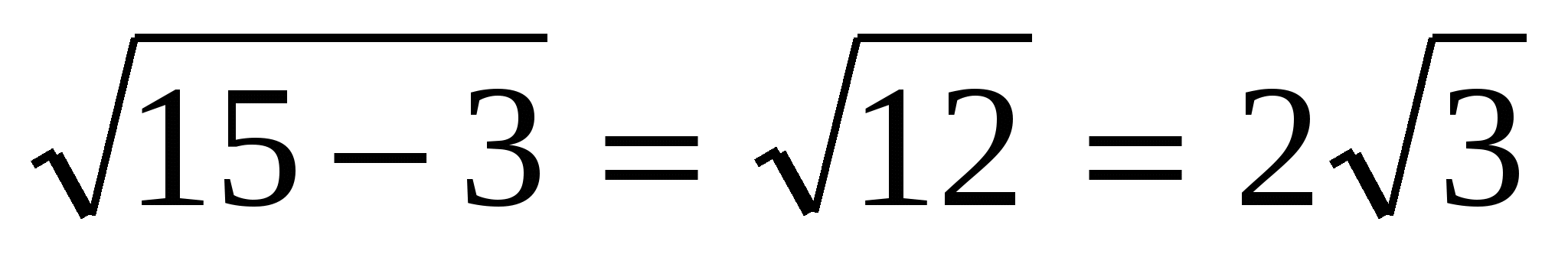 .
.
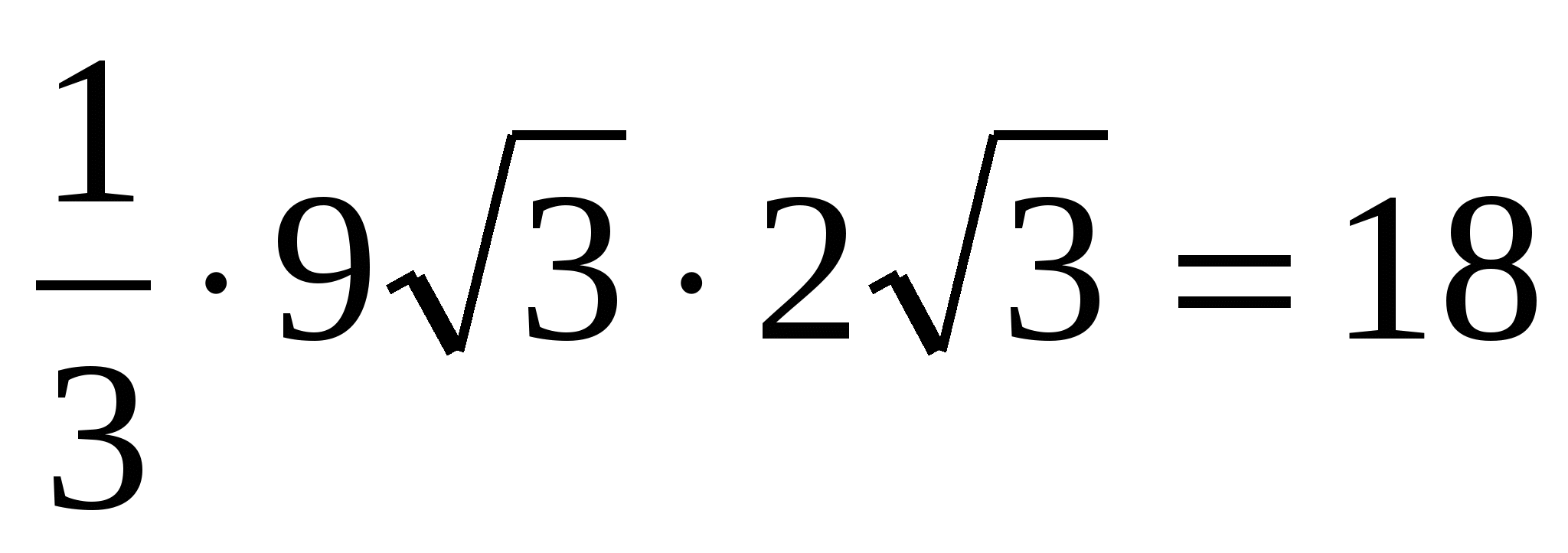 .
.
Answer. 18.
Problem #5 . Calculate the volume of a regular triangular pyramid if the radius of the circle inscribed at the base is 2 and the height of the regular pyramid is .
Solution.
1) the radius of the circle inscribed in a regular triangle is 2 times less than the radius of the circle circumscribed about this triangle, i.e. , Then 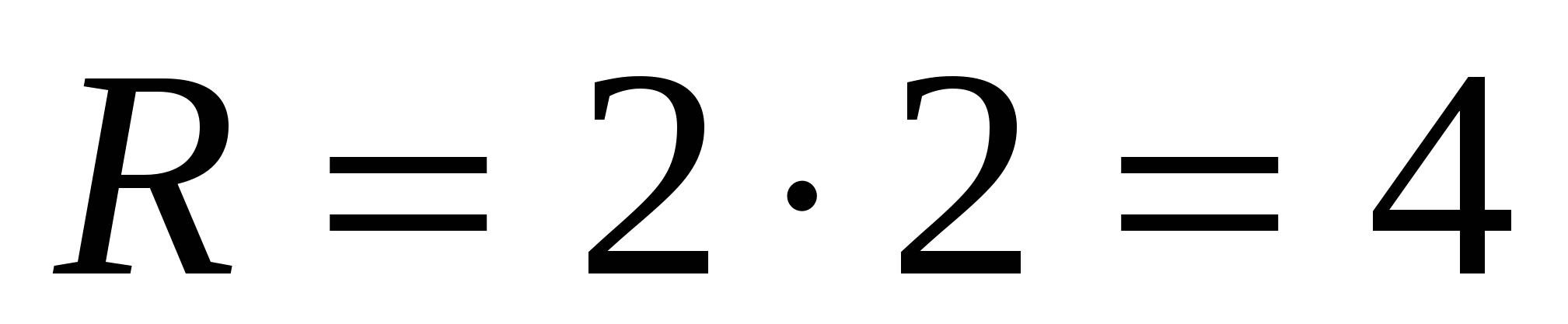 .
.
2) find the side of the base of a regular pyramid using the formula, 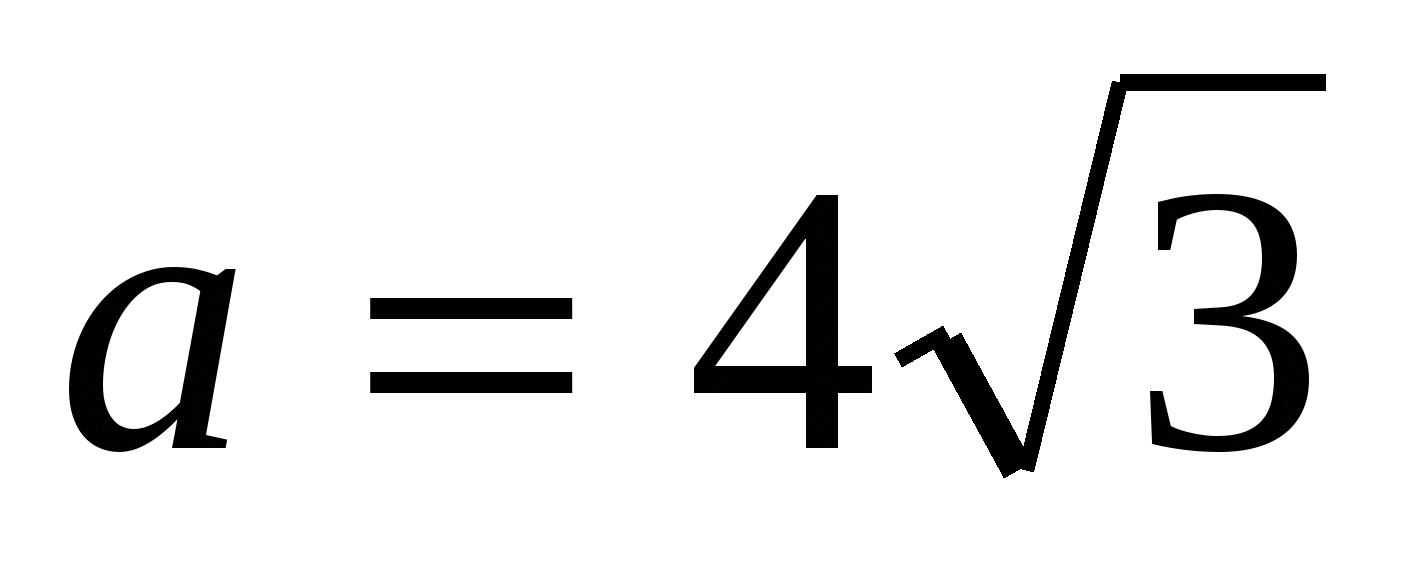 .
.
3) find the area of the base as the area of a regular triangle, 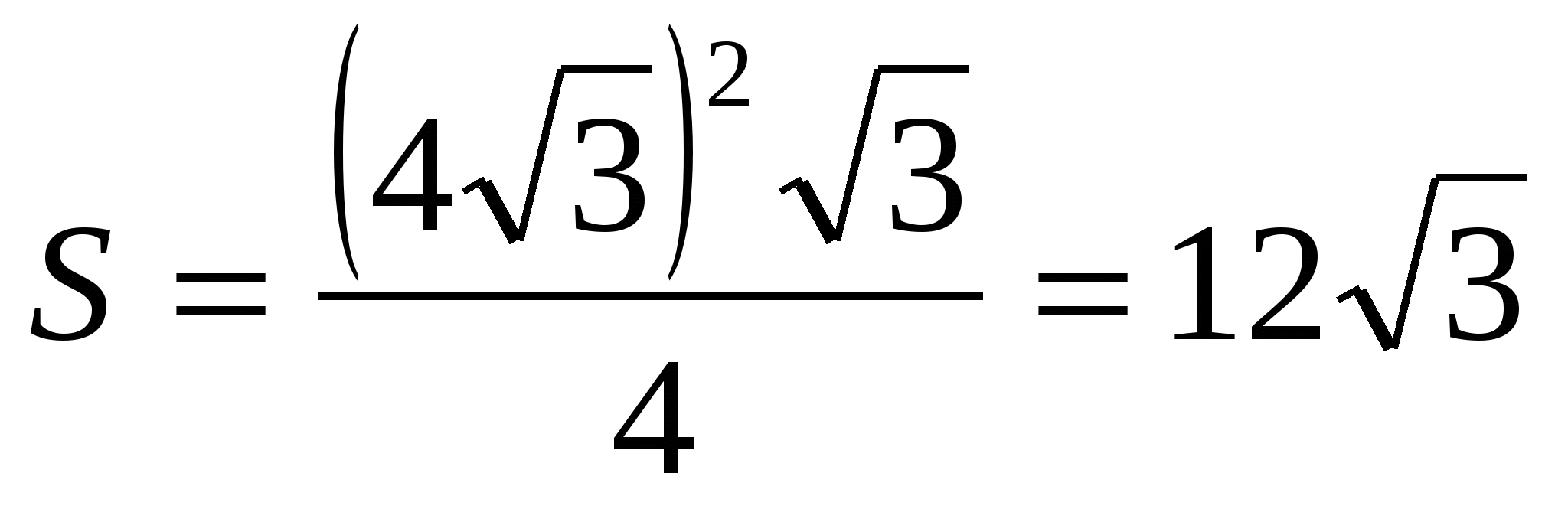 .
.
4) calculate the volume of a regular pyramid: = 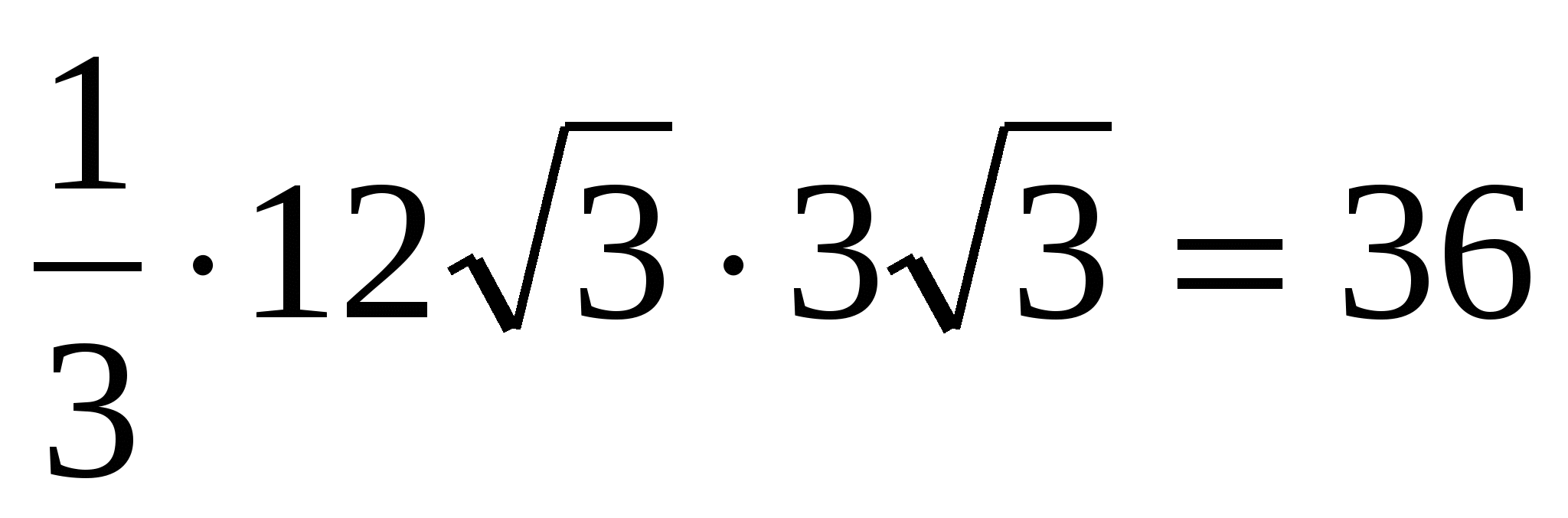 .
.
Answer. 36.
Problem #6 . Calculate the lateral surface area of a regular quadrangular pyramid if its edges are 5 and the radius of the circle circumscribed around the base is 3.
R  decision
.
decision
.
1) find the side of the base using the formula 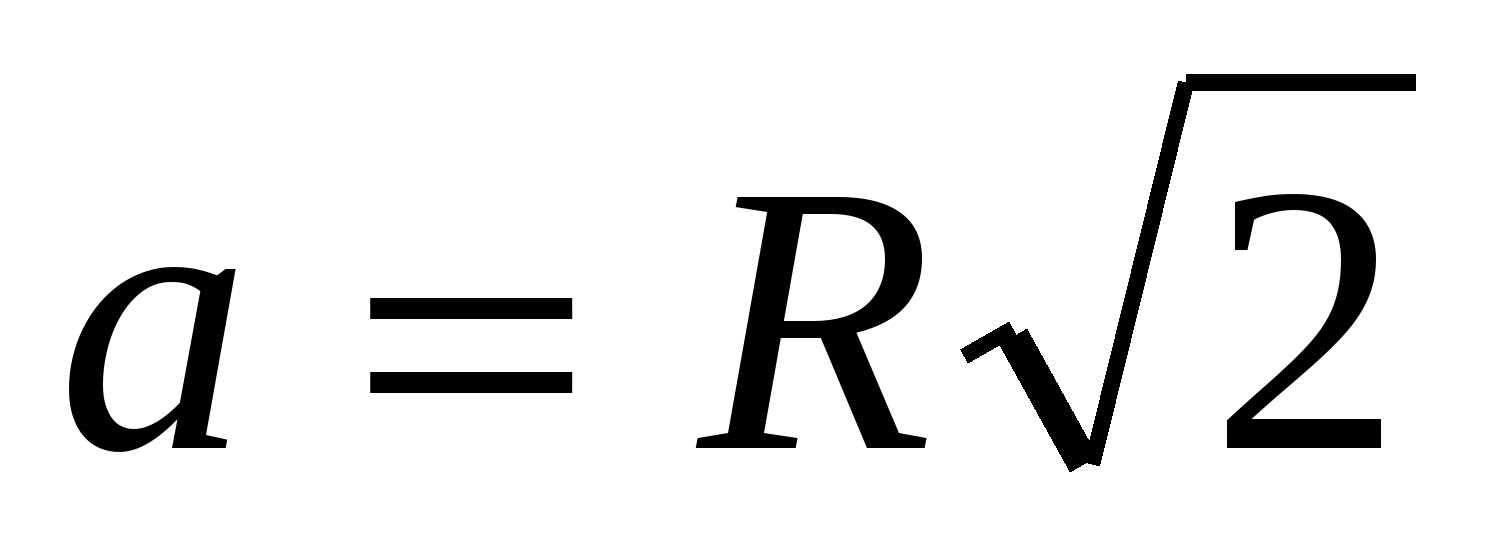 , i.e.
, i.e. 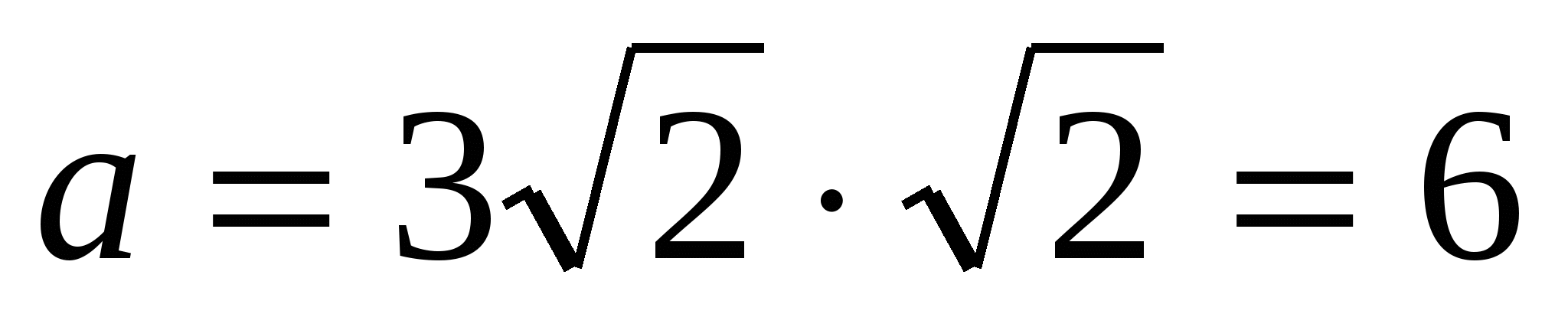 .
.
2) find the perimeter of the base: R = 4A,
P = 24.
3) from a right triangleM
DR
Using the Pythagorean theorem we find the apothemMR
: 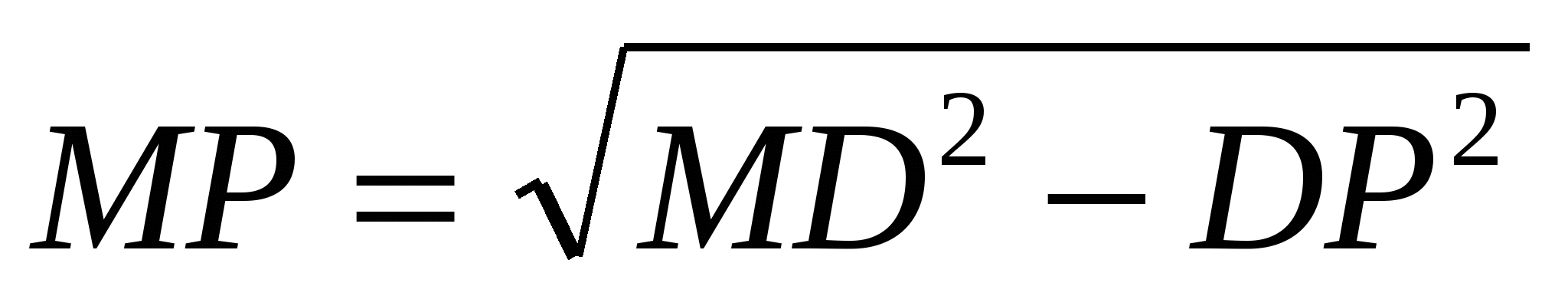 ,
D.P. =
,
D.P. =
Then: MR
= 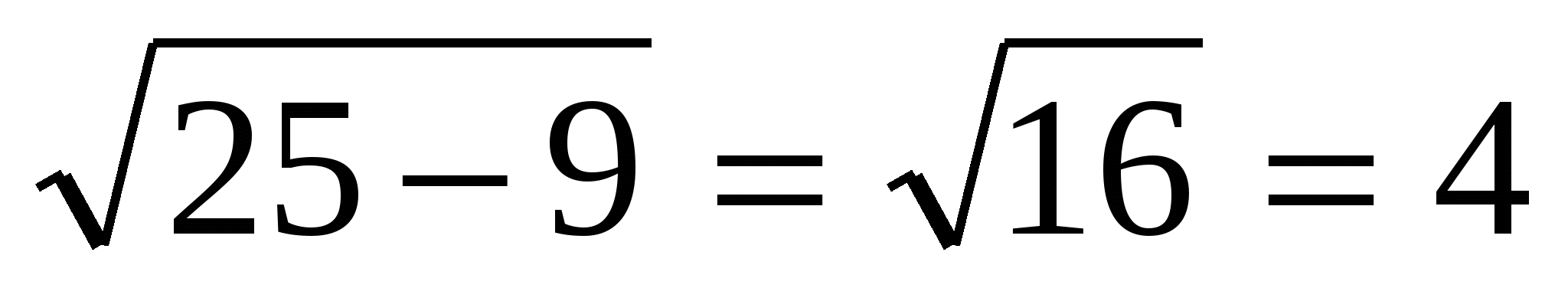 .
.
4) calculate the area of the lateral surface of the pyramid: = 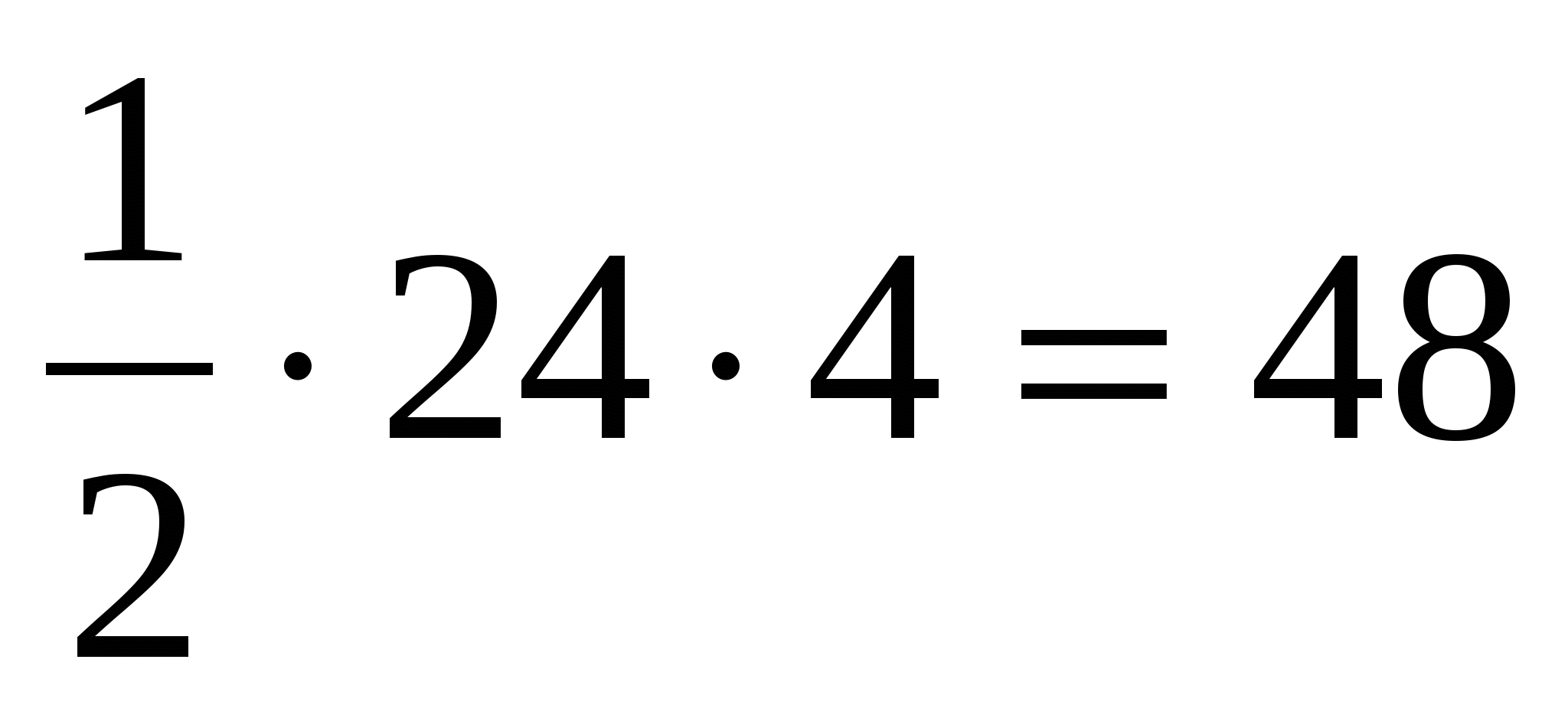 .
.
Answer. 48.
Problem No. 7 . In the right quadrangular pyramid The lateral surface area is 16 and the base area is 4. Find the height of the pyramid.
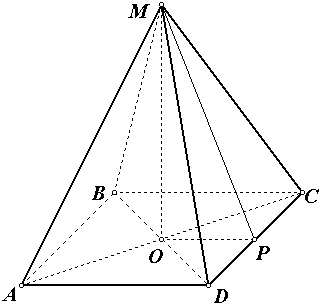
Solution.
1) find the side of the base: since the base of the pyramid is a square with an area equal to 4, then the side of the square is 2, and its perimeter is 8.
2) by condition = 16 i.e.
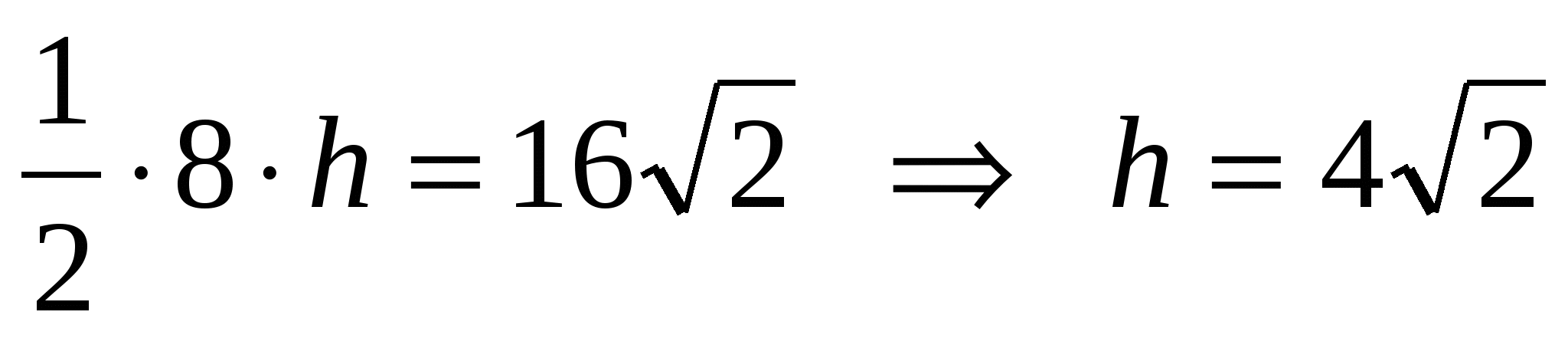 .
.
3) from a right triangleMPA
Using the Pythagorean theorem we find the height: , taking into account that OP = 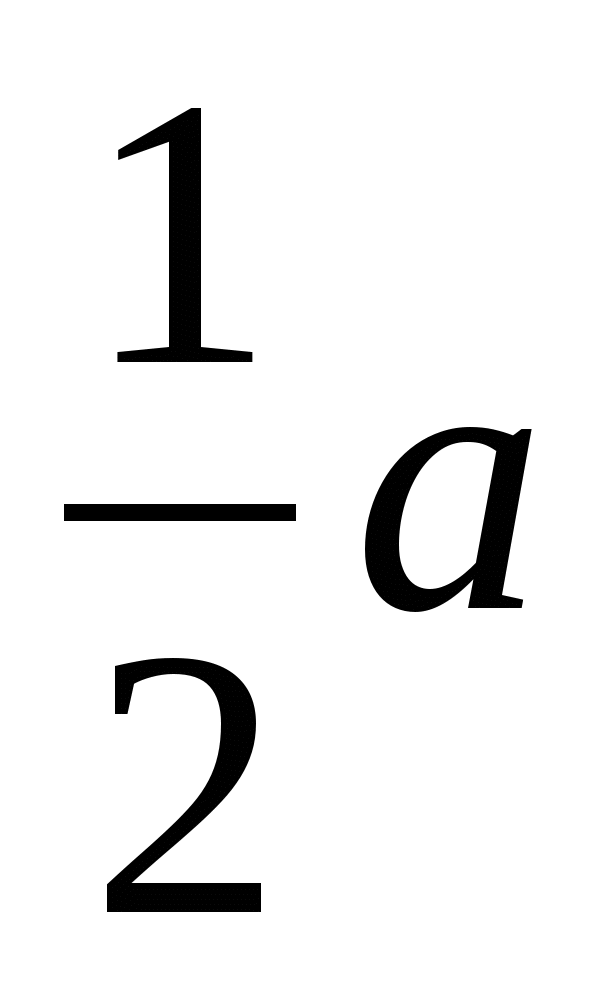 = 1, we get: MO =
= 1, we get: MO = 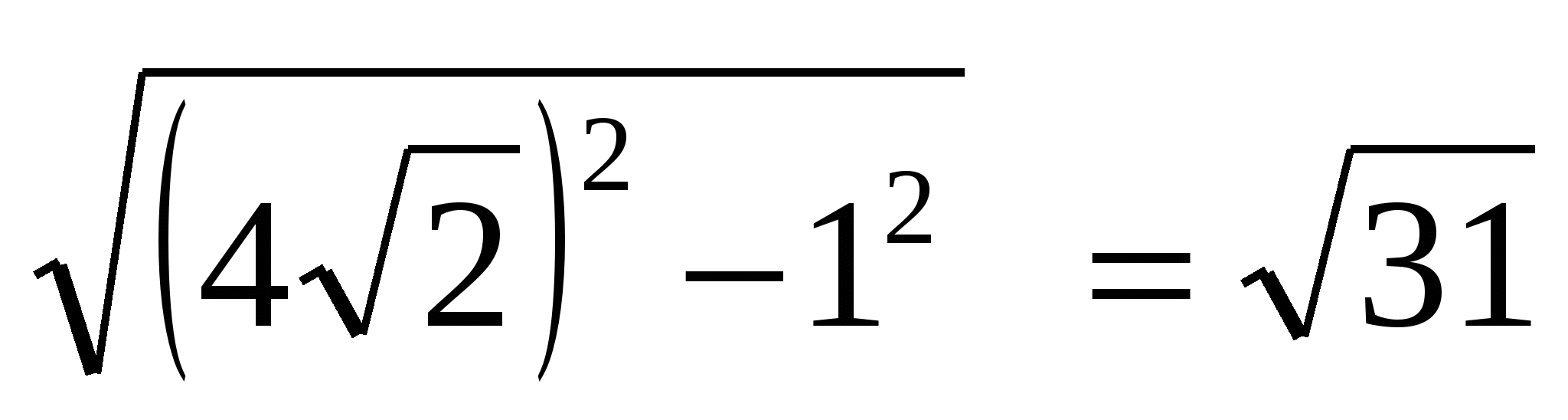 .
.
Answer. 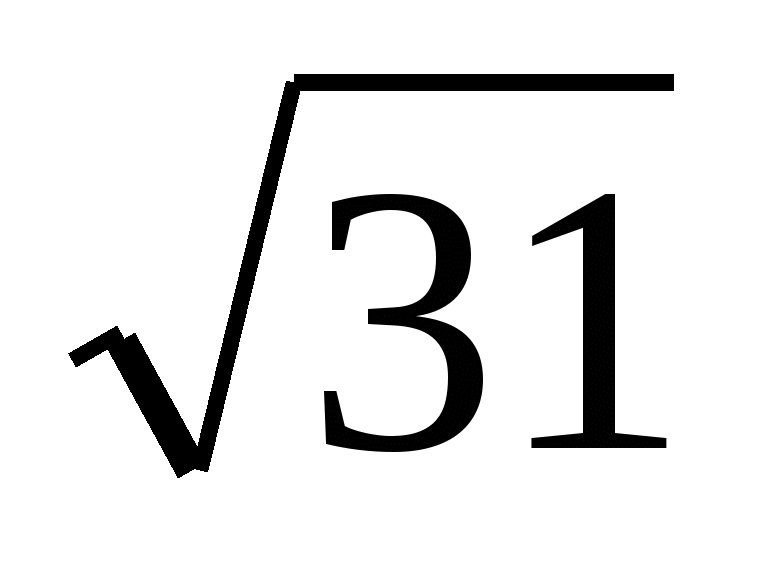 .
.

Problem No. 8. Calculate the volume of a regular hexagonal pyramid if the side of the base is 4 and the side edges of the pyramid are 5.
Solution.
1) the side of the base of a regular hexagon is equal to the radius of the circle circumscribed around it, i.e. 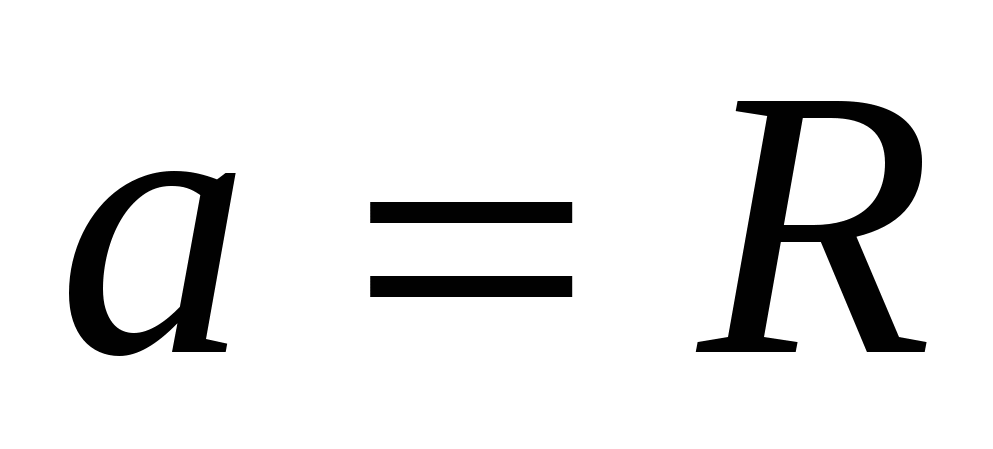 ,
, 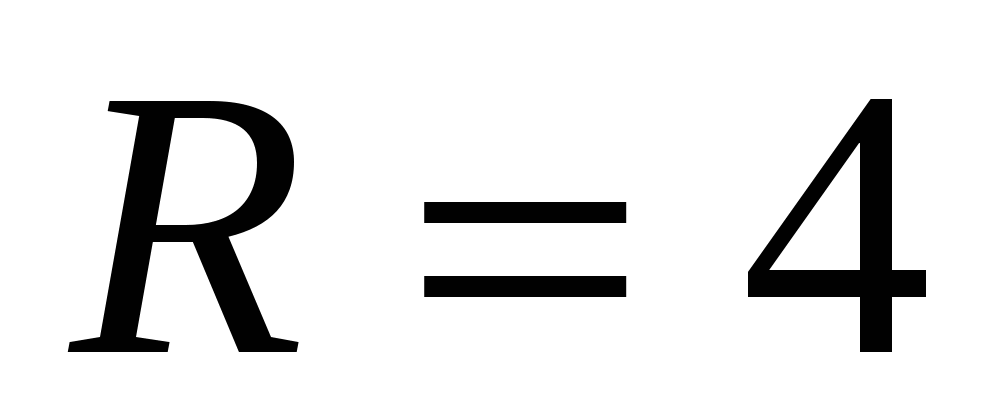
2) find the area of a regular hexagon using the formula 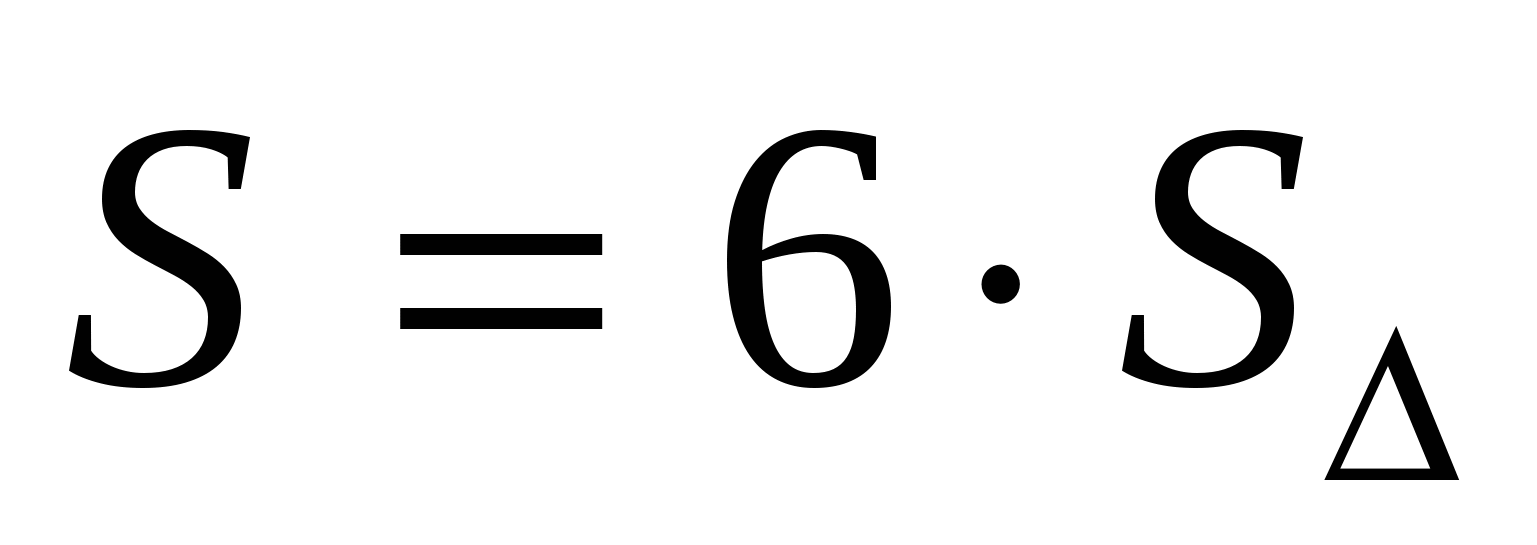 or
or 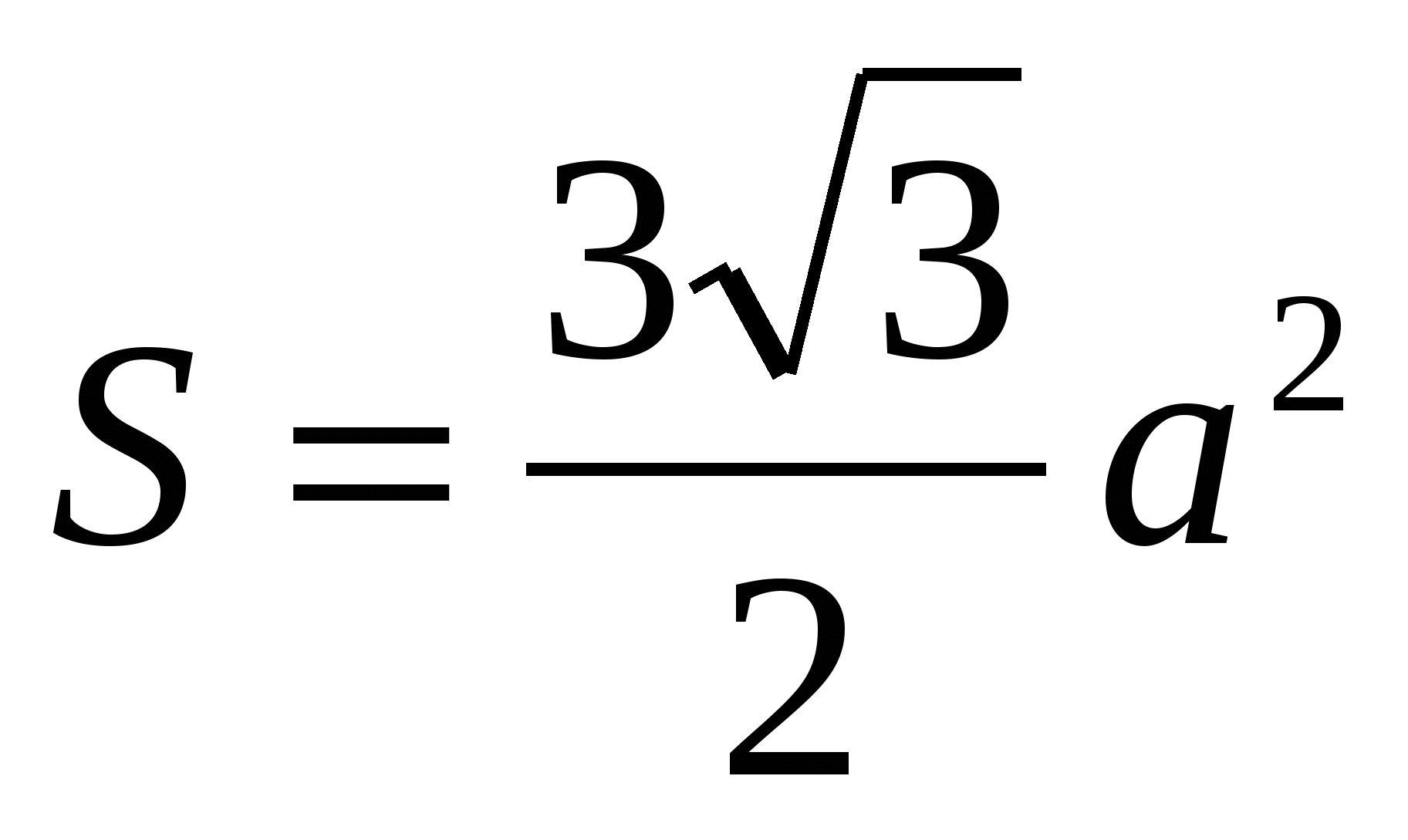 = 24.
= 24.
3) from a right triangleMOU let's find the height MO : .
4) calculate the volume of the pyramid: = 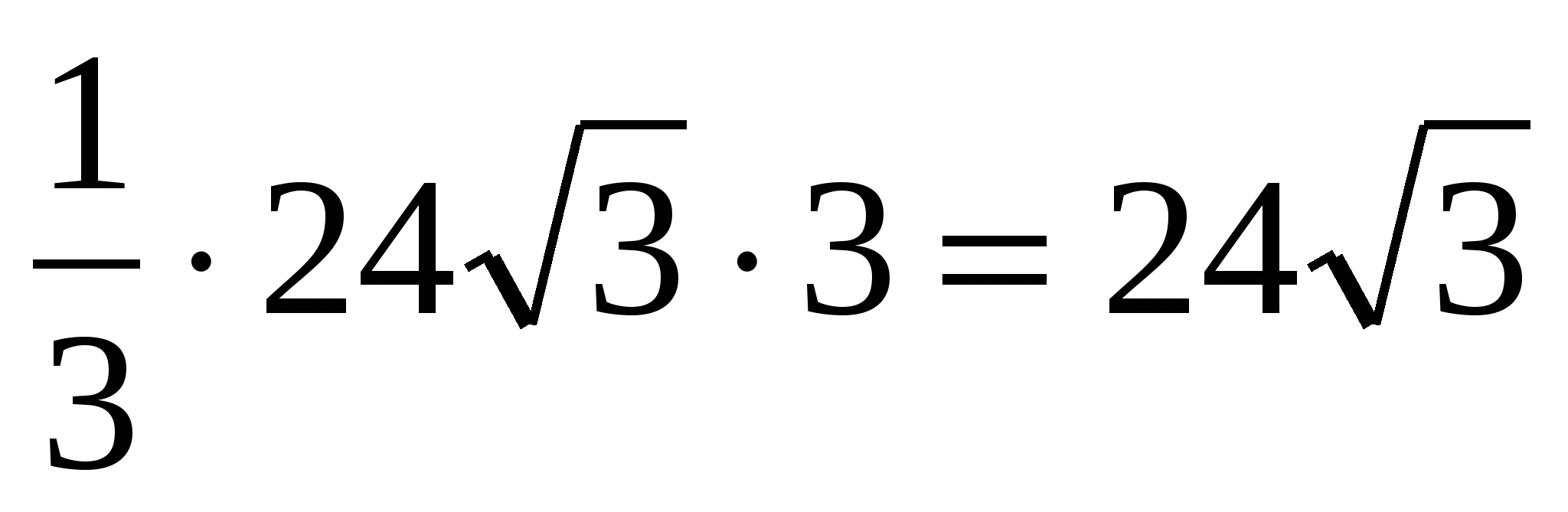 .
.
Answer. 24.
Problem No. 9 . In a regular hexagonal pyramid, the base side is 2 and the side edge is 2. Find the volume of the pyramid.
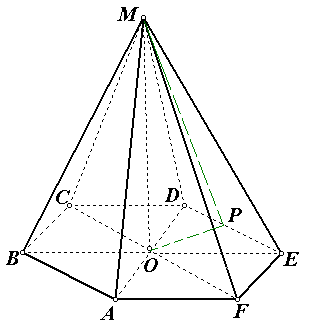
Solution.
1) find the area of a regular hexagon using the formula or = 12.
2) from a right triangleMOU let's find the height MO, considering that in regular hexagon : .
3) calculate the volume of the pyramid: = 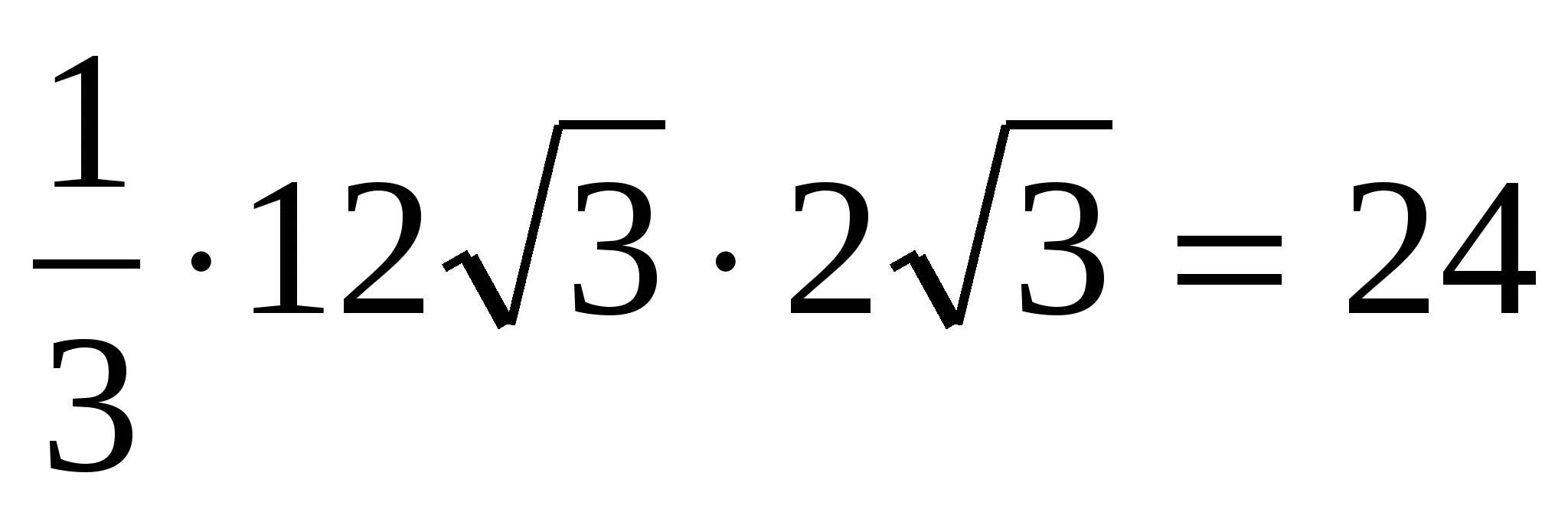 .
.
Answer: 24.
Problem No. 10 . A cylinder is described around a regular triangular prism. The height of the cylinder is 5, and the radius of its base isRsatisfies the equationR 2 + R – 6 = 0. Find the volume of the prism.
R 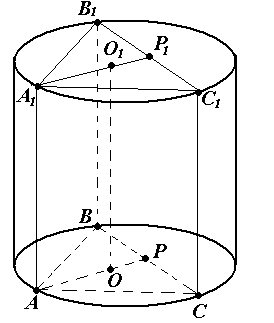 decision.
V = S
·
H
decision.
V = S
·
H
1) since the prism is inscribed in the cylinder, the height of the prism is equal to the height of the cylinder, and the base of the prism is inscribed in the base of the cylinder, N = 5.
2) by condition R satisfies the equation R 2 + R – 6 = 0, solving which we find
R 1 = - 3, R 2 = 2, since the radius is a positive value, then -3 does not satisfy the conditions of the problem.
3) find the side of the inscribed regular triangle using the formula 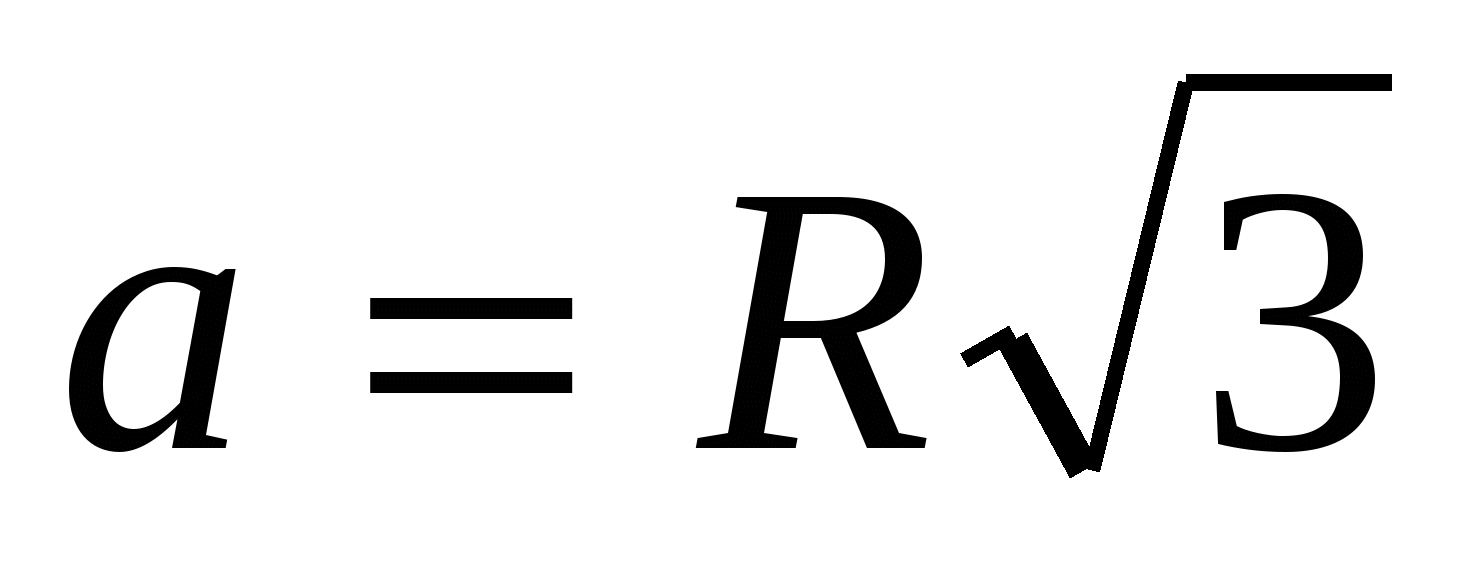 ,
, 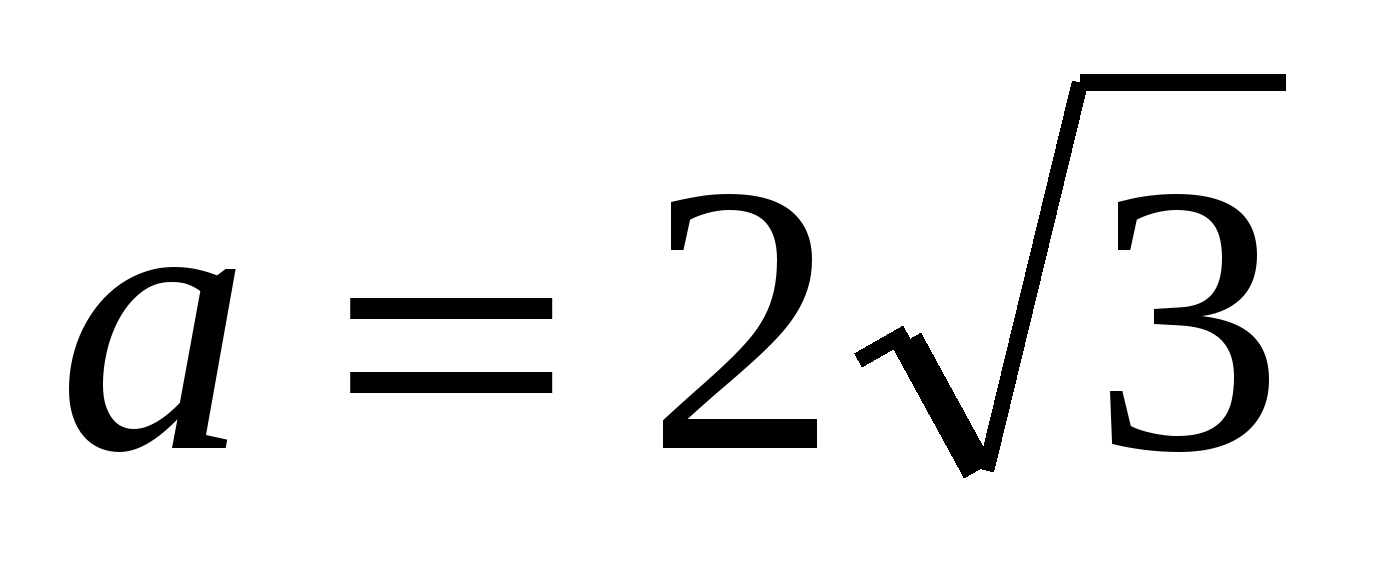 .
.
4) find the area of the base correct prism, as the area of a regular triangle: 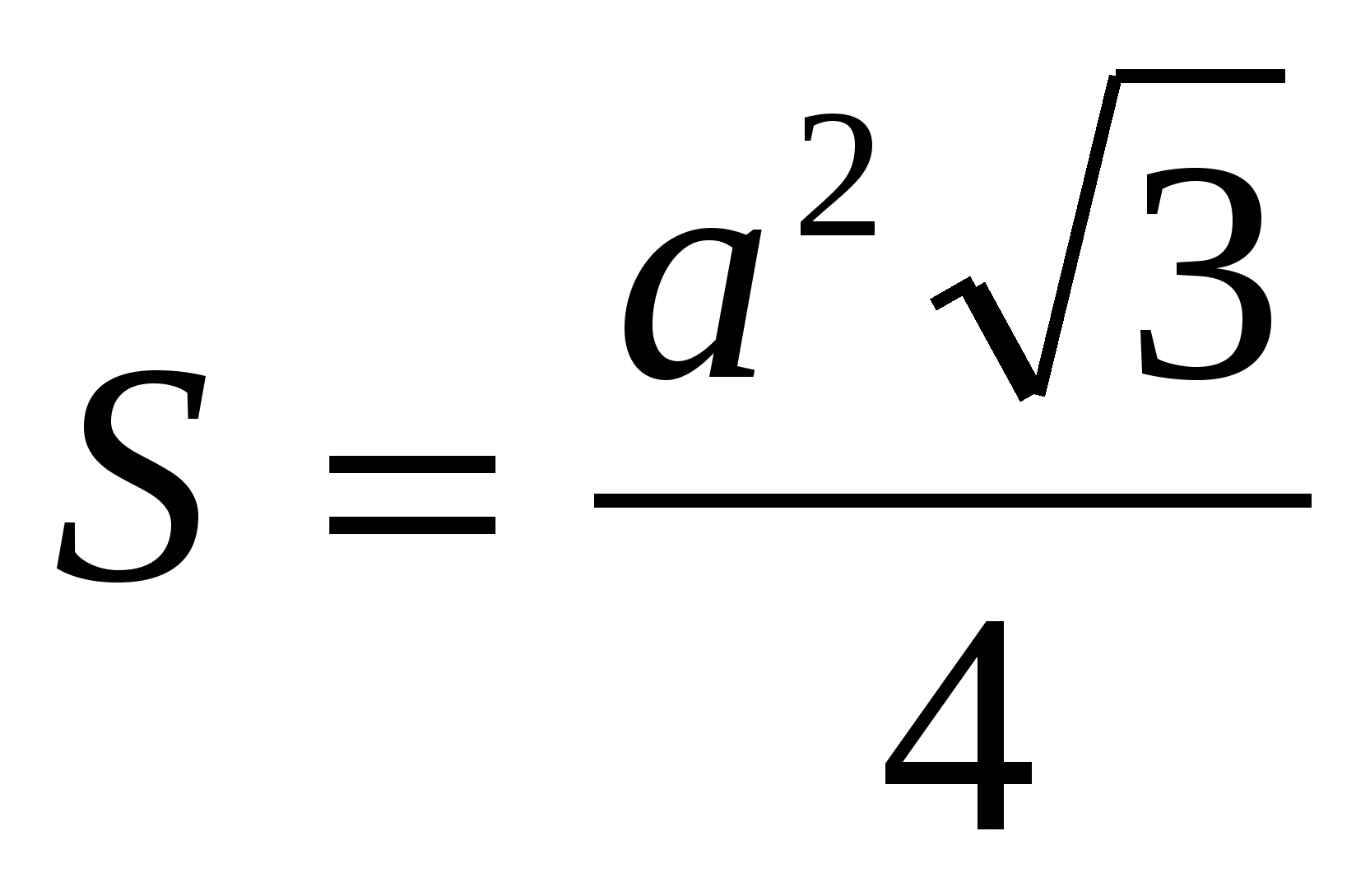 =
= 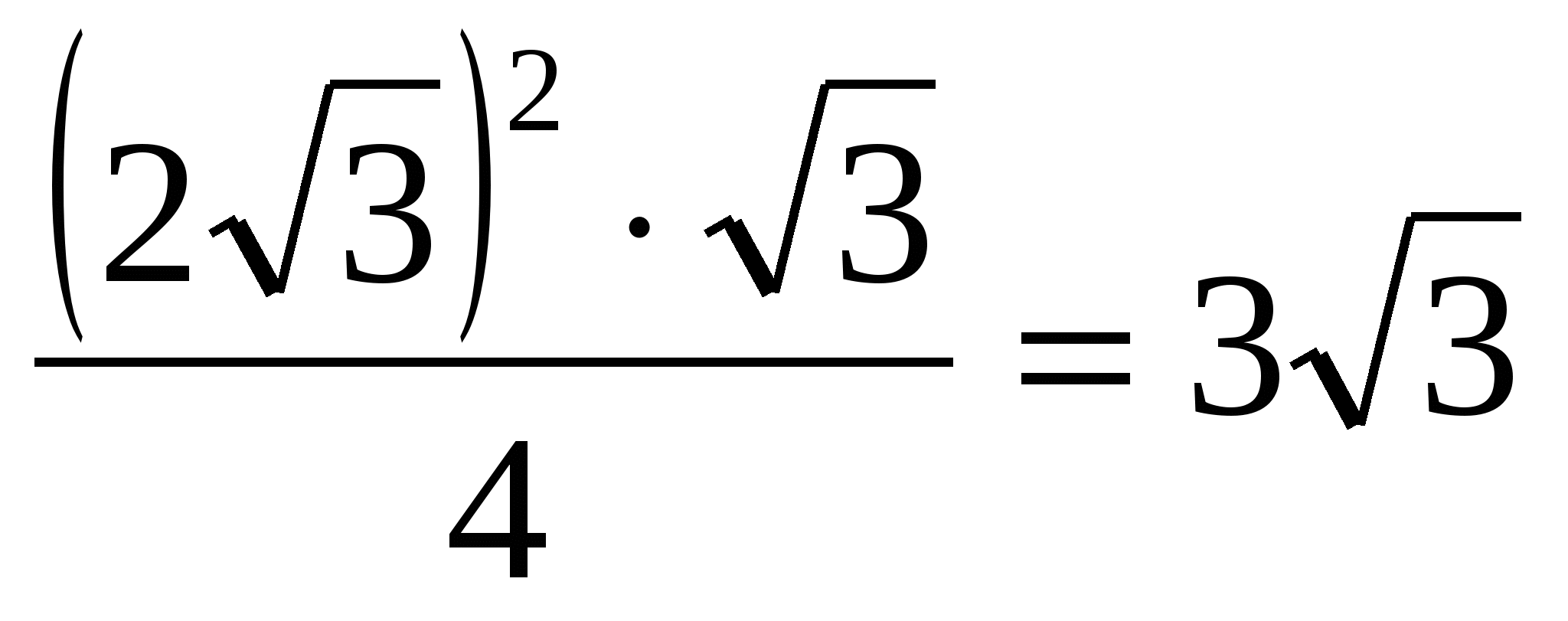
5) calculate the volume of the prism:V =
S
·
H =
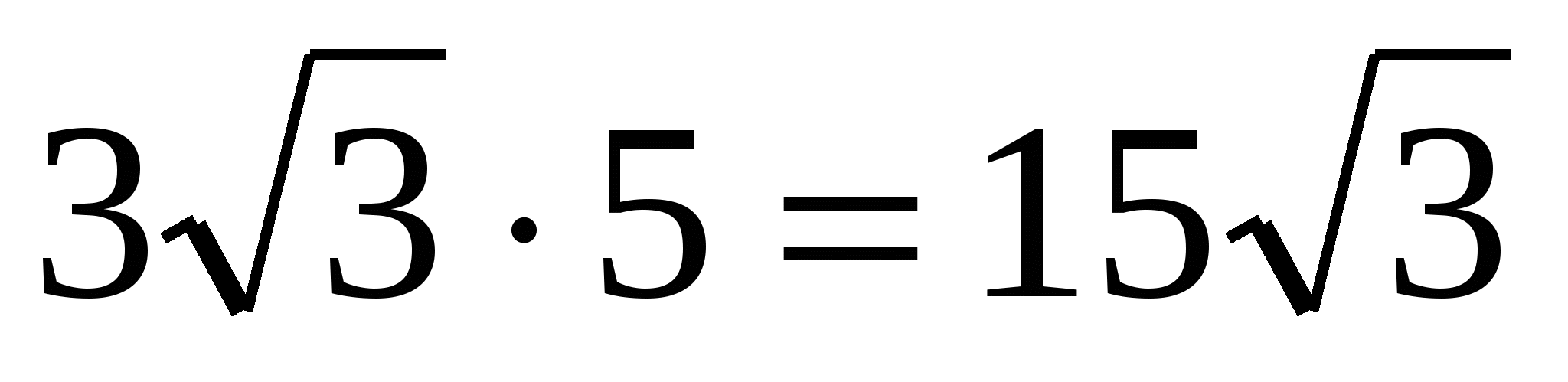 .
.
Answer. 15.
Problem No. 11 . A cylinder is described around a regular triangular prism. The distance between the axis of the cylinder and the side of the base of the prism is equal to . The height of a cylinder is equal to three of its radii. Find the volume of the prism.
Solution. V = S · H
1) Since the prism is inscribed in the cylinder, the height of the prism is equal to the height of the cylinder, and the base of the prism is inscribed in the base of the cylinder, according to the condition N = 3 R..
2) The distance between the axis of the cylinder and the side of the base of the prism is equal to the radius of the inscribed triangleABC
circles, i.e. 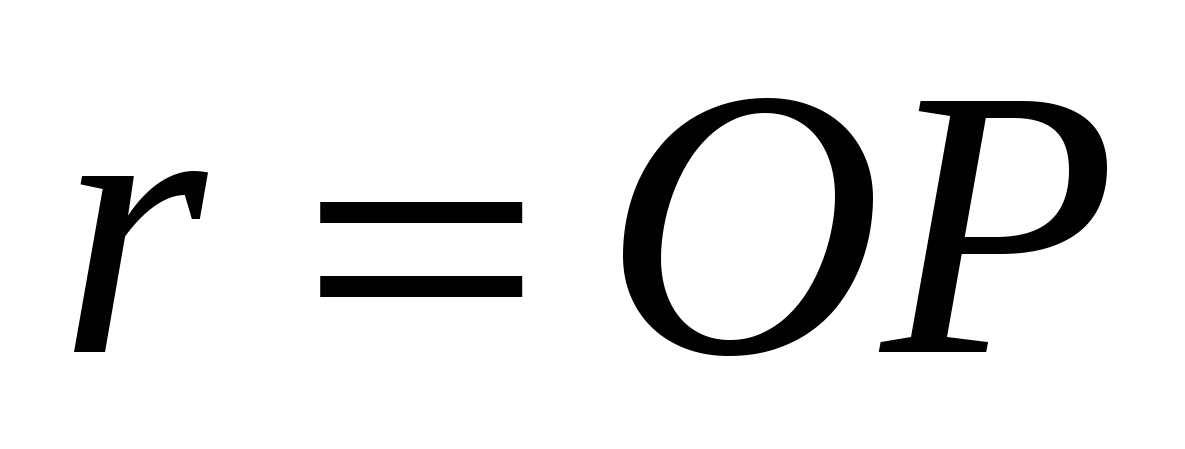 , and by condition is equal to .
, and by condition is equal to .
3) the radius of the circle inscribed in a regular triangle is 2 times less than the radius of the circle circumscribed about this triangle, i.e. , Then .
4) find the side of the inscribed regular triangle using the formula, 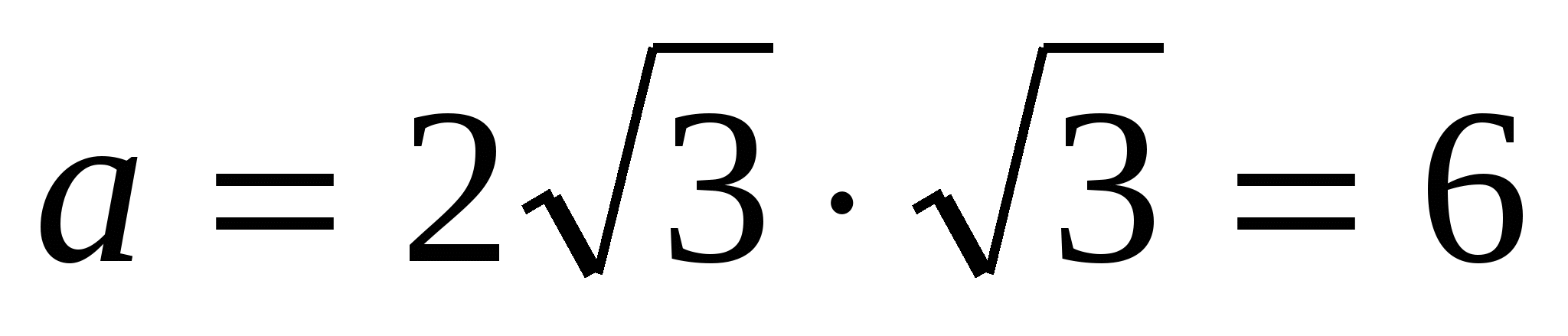 .
.
5) find the area of the base of a regular prism, as the area of a regular triangle: = 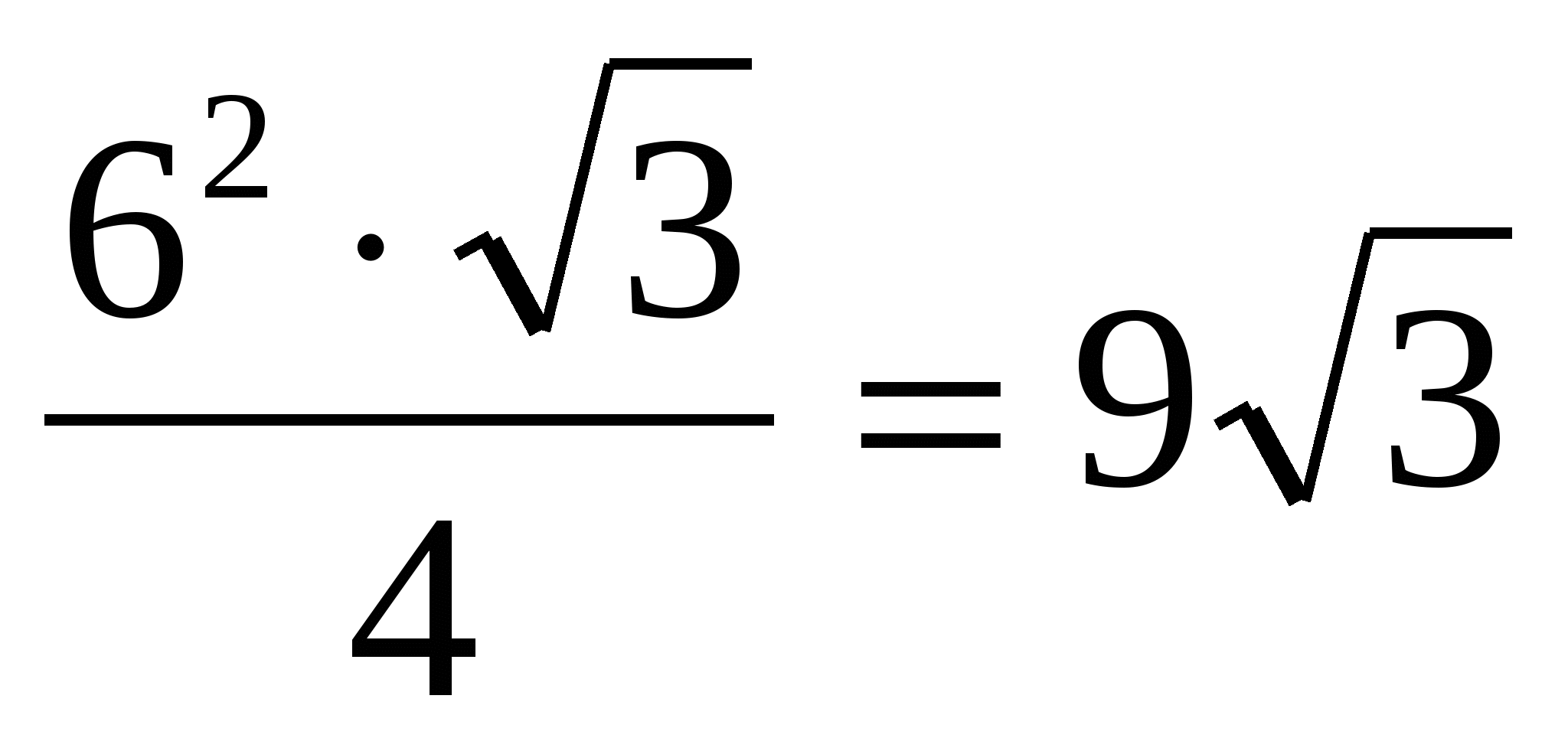
6) calculate the volume of the prism:V =
S
·
H =
S·
3
·
R =
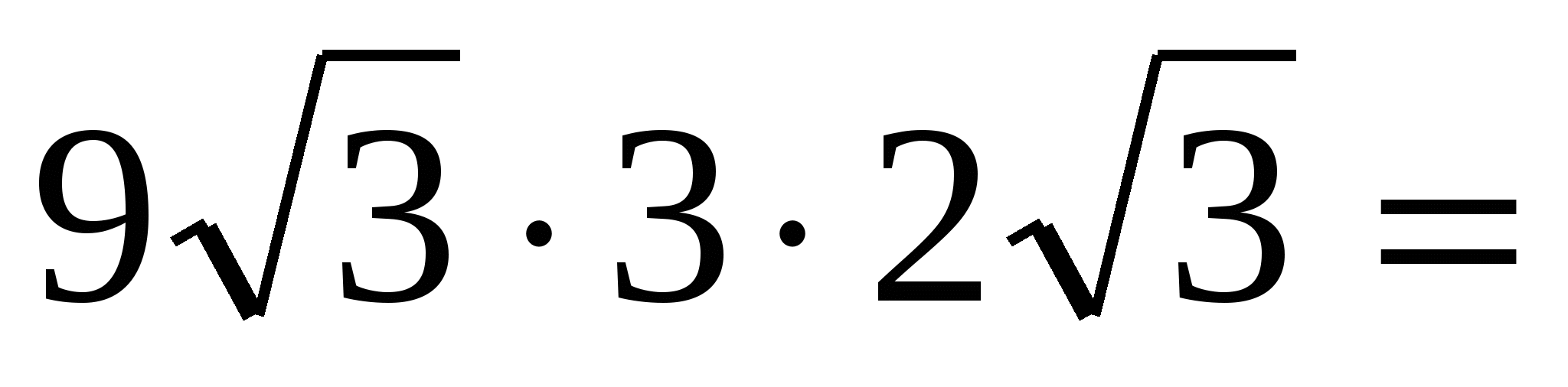 162.
162.
Answer. 162.
Problem No. 12. A cylinder is described around a regular triangular prism. The lateral surface area of the cylinder is 16 . Find the volume of the prism if the side of its base is 5.
Solution. V = S · H
2) Find the area of the base of a regular prism as the area of a regular triangle: = 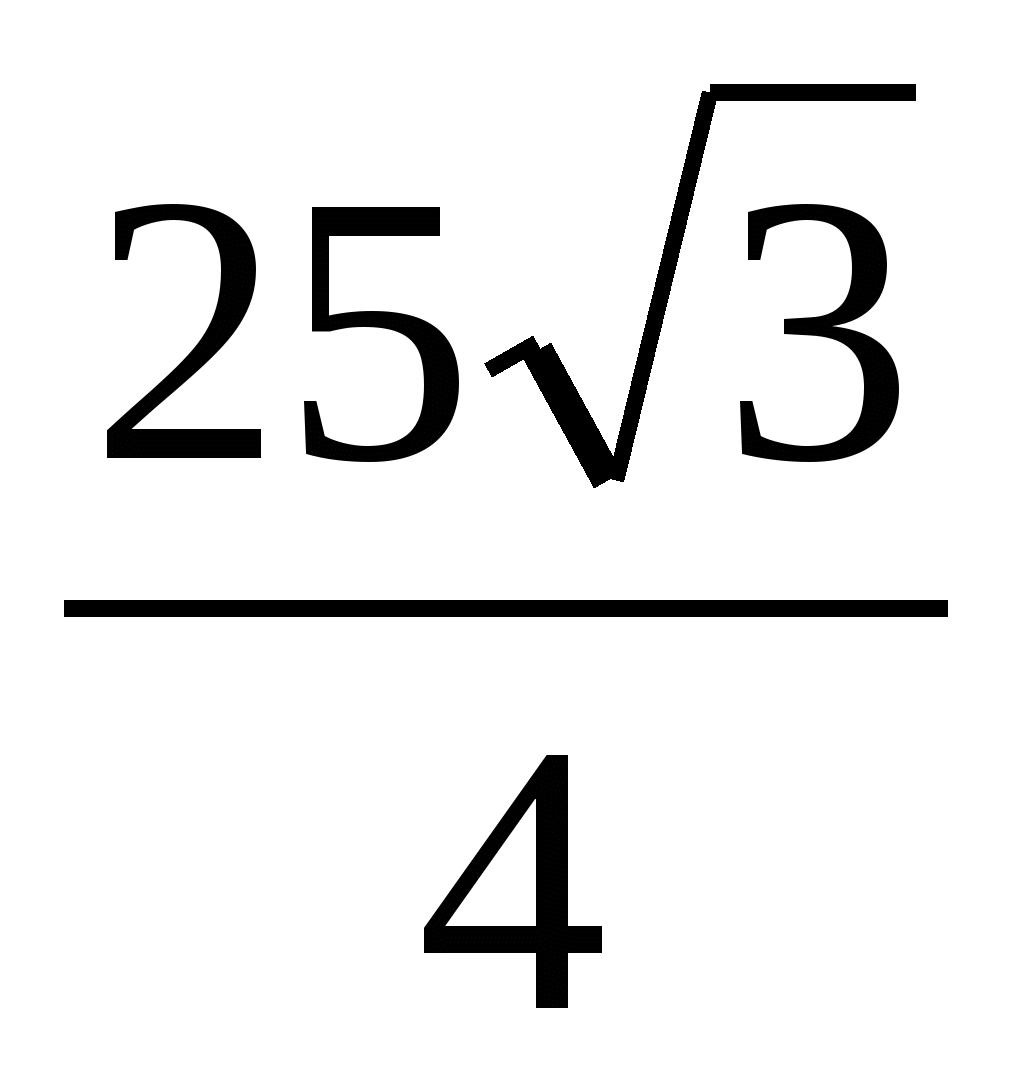 .
.
3) The side of an inscribed regular triangle is found by the formula, then 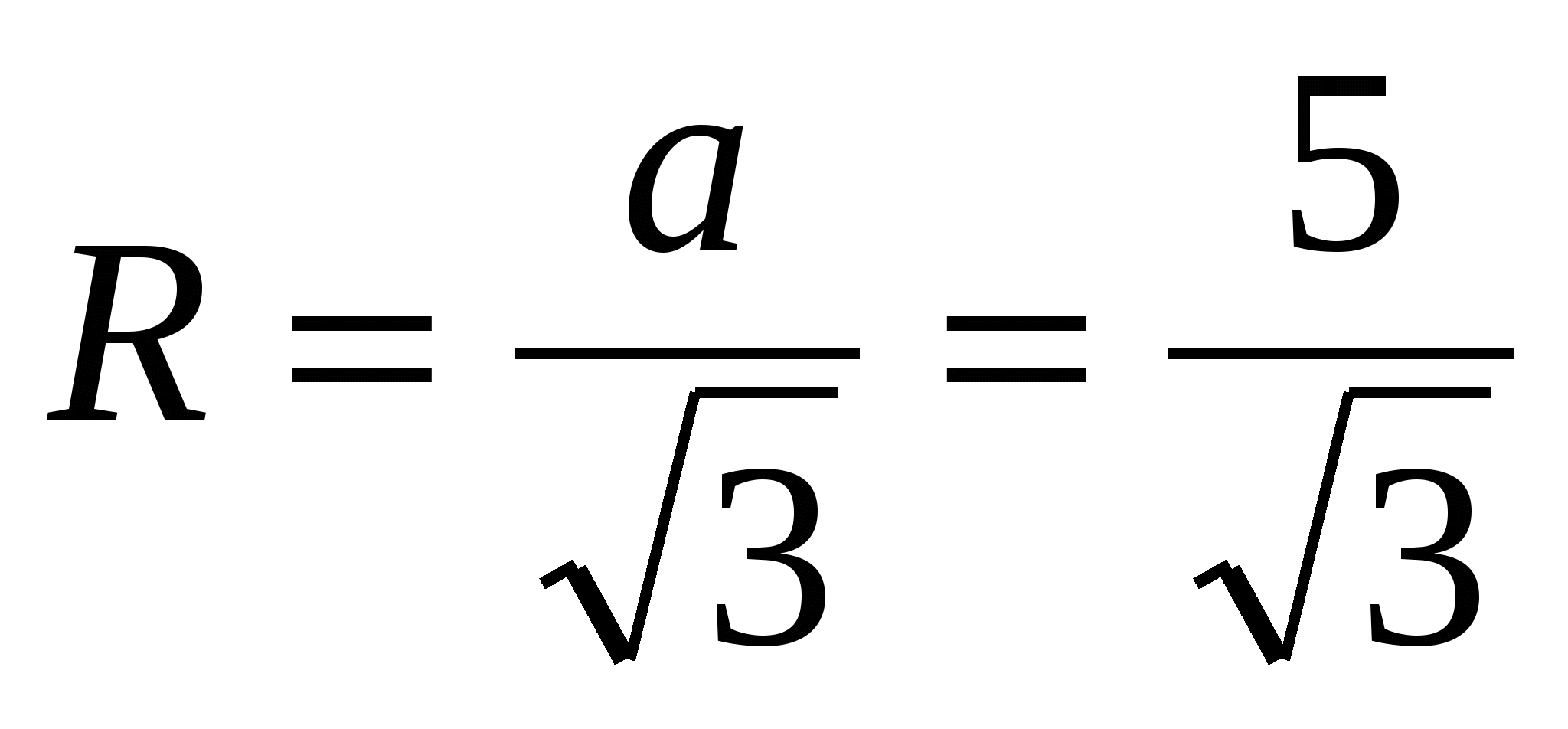 .
.
4) According to the condition, the area of the lateral surface of the cylinder is 16·
those. 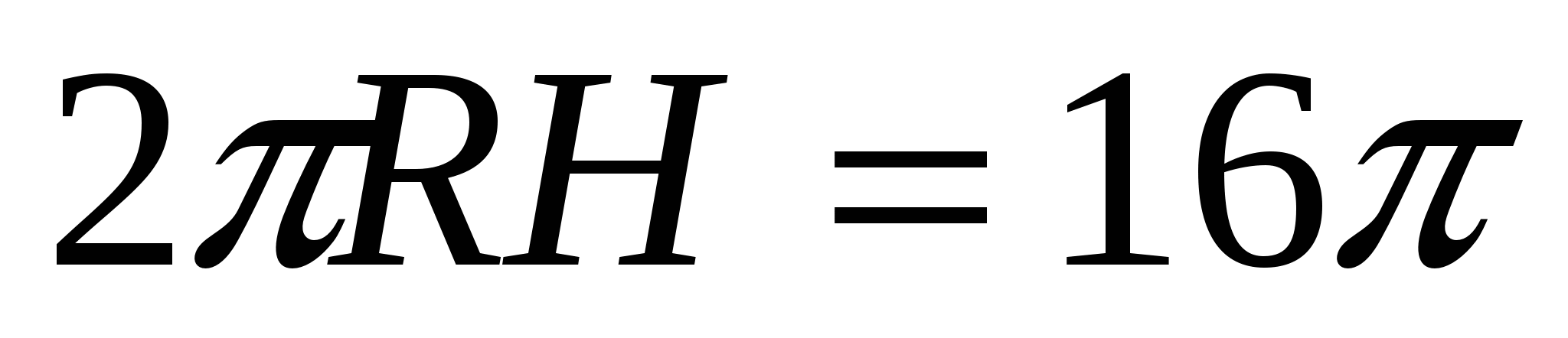 , whereN
=
, whereN
= 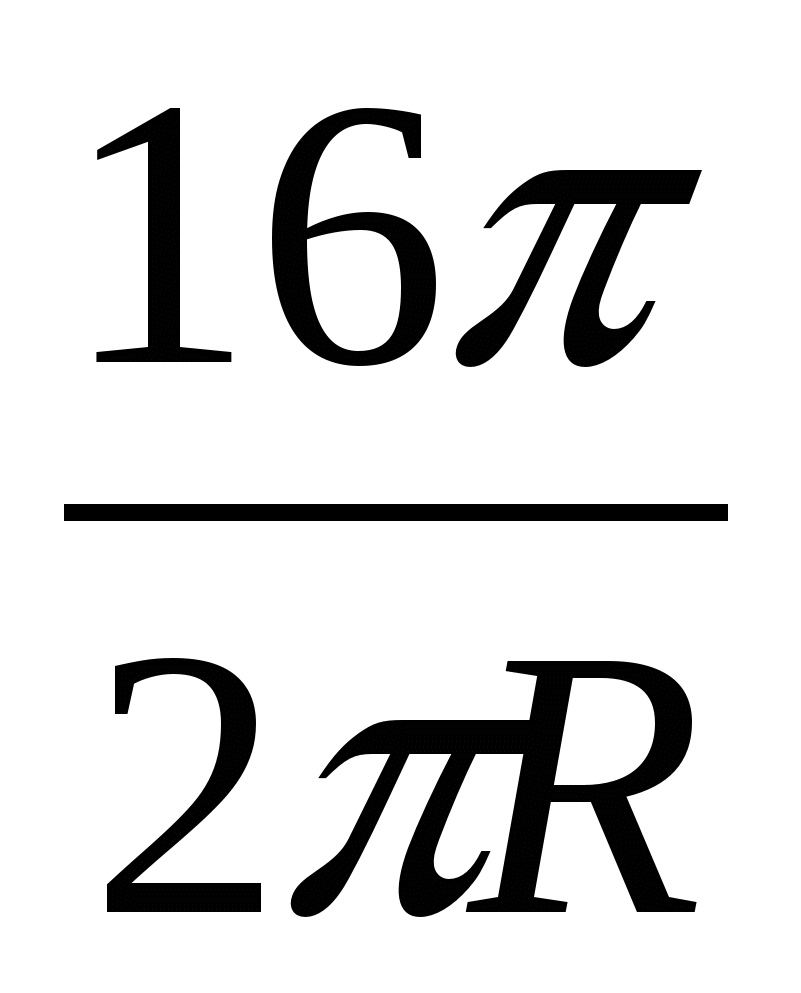 =
= 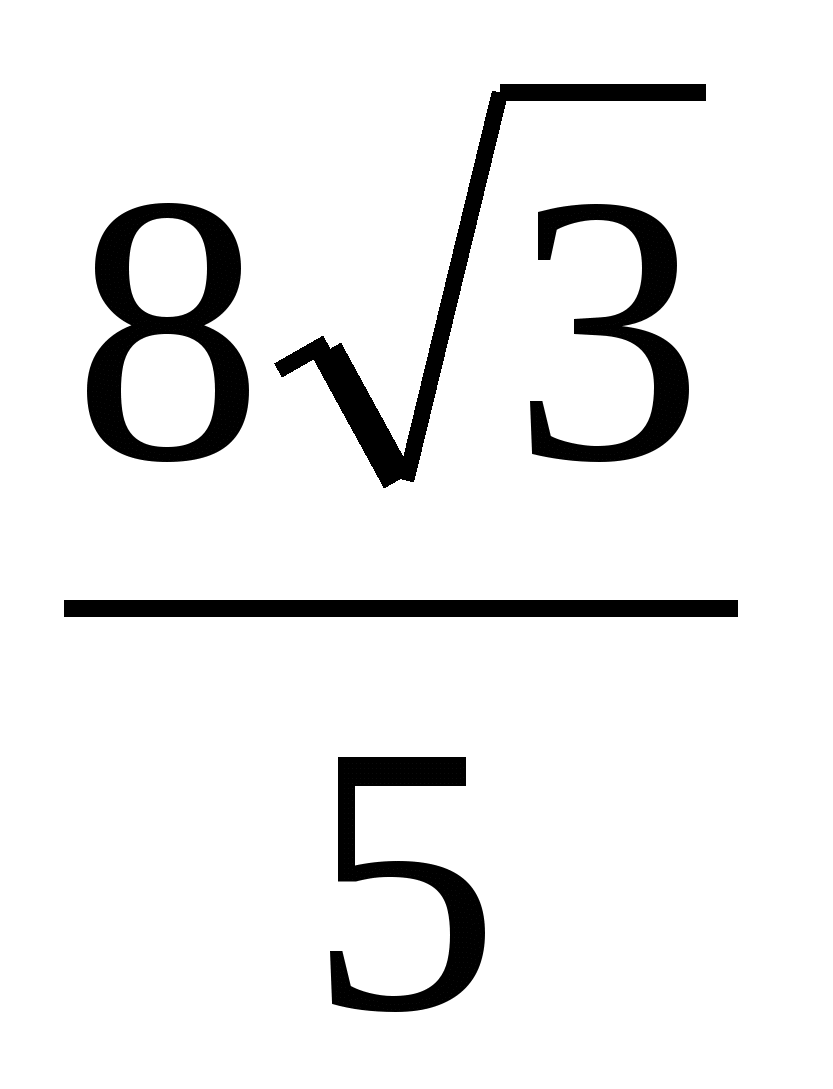 .
.
5) Calculate the volume of the prism:V = S · H = · = 30.
Answer. thirty.
Problem No. 13. Near the right one quadrangular prism A cylinder is described whose lateral surface area is 20. Find the lateral surface area of the prism.
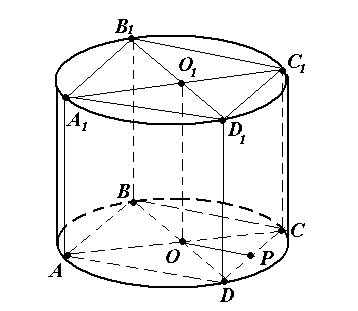 Solution.
Solution. 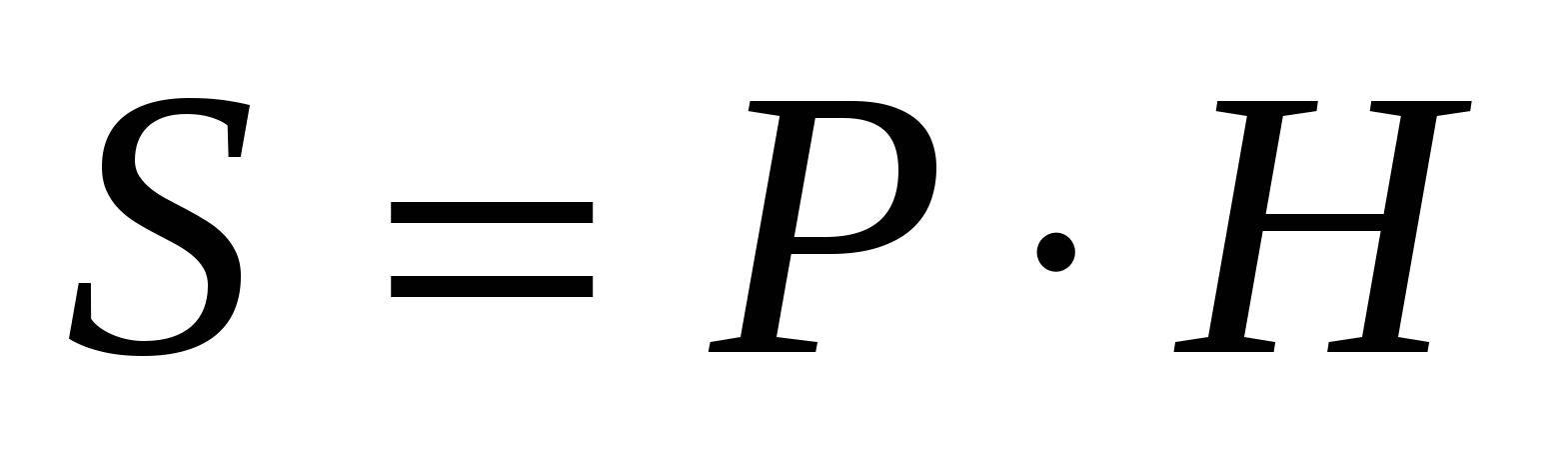
1) Since the prism is inscribed in the cylinder, the height of the prism is equal to the height of the cylinder, and the base of the prism is inscribed in the base of the cylinder.
2) According to the condition, the area of the lateral surface of the cylinder is 20
, i.e. 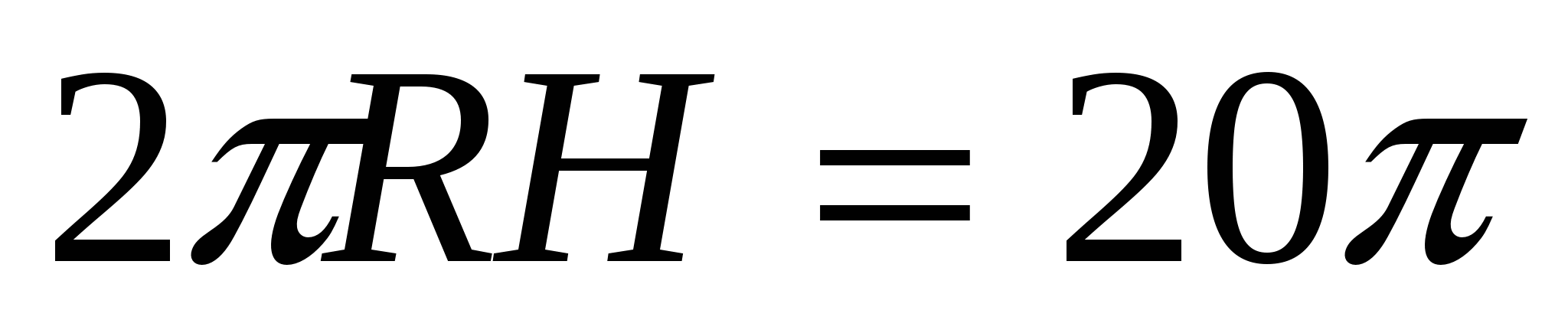 ,
, 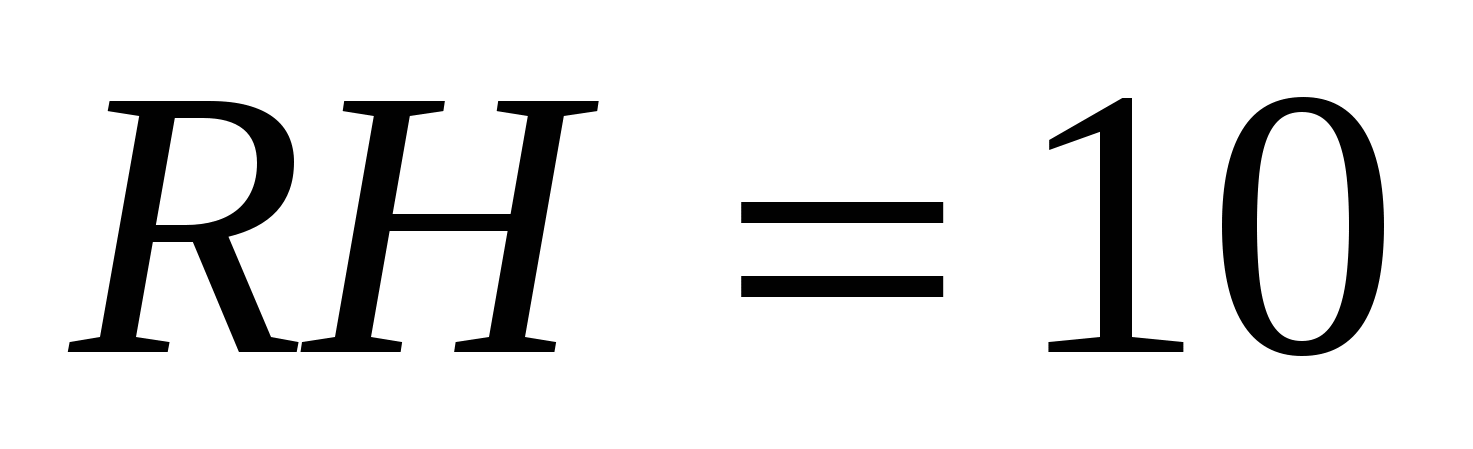 .
.
3) since the prism is regular, then at its base lies a square with a side 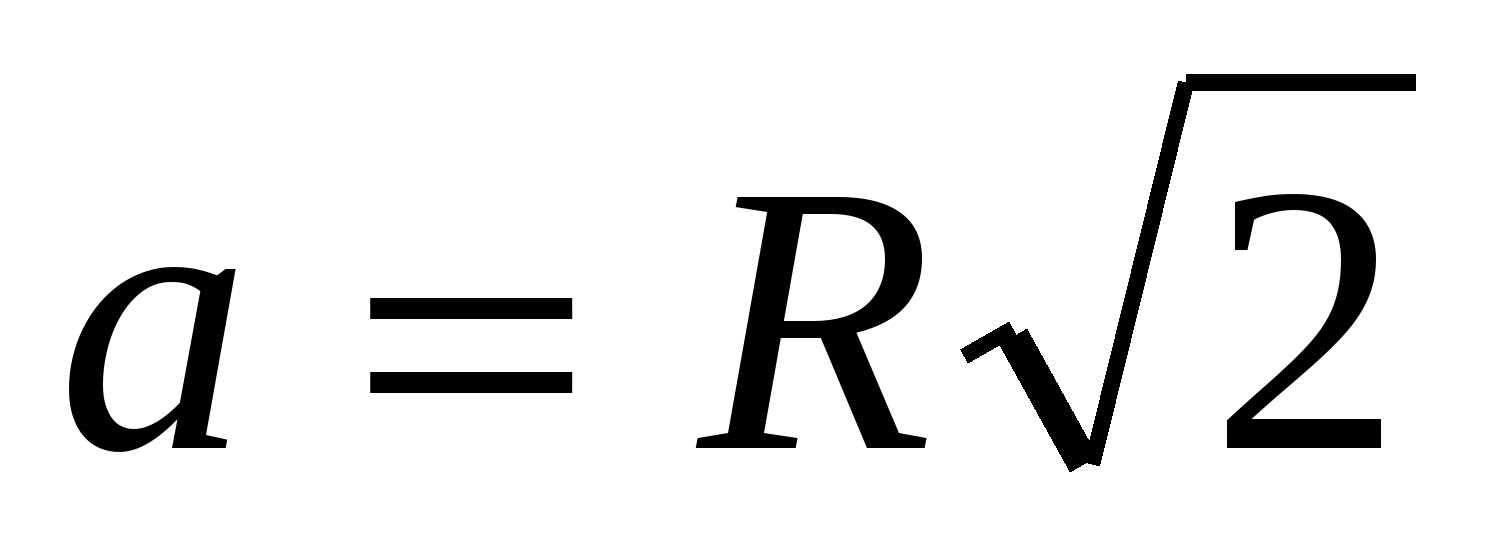 , then the perimeter of the base is equal to
, then the perimeter of the base is equal to 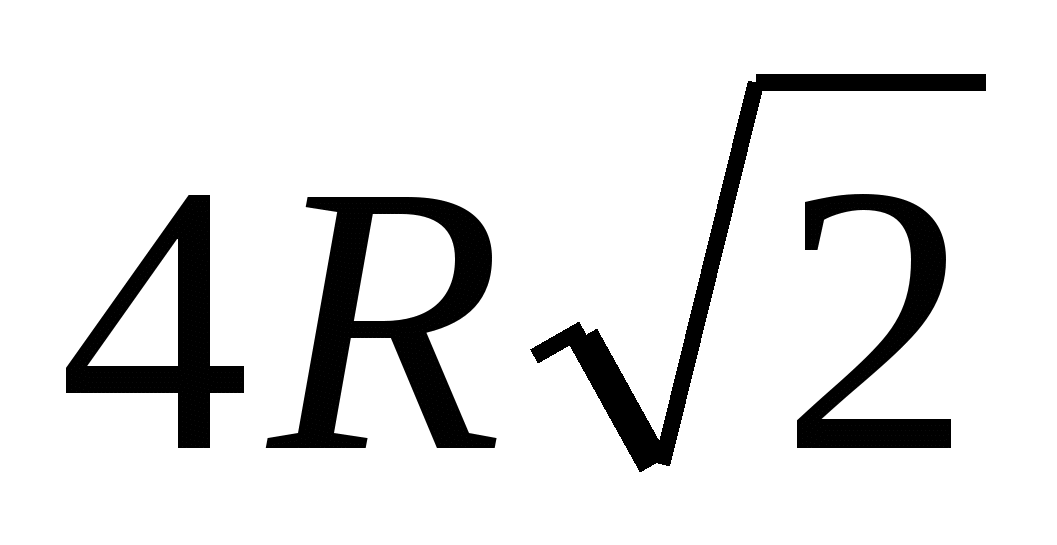 .
.
4) calculate the area of the lateral surface of the prism = ., i.e. – 36 a
· 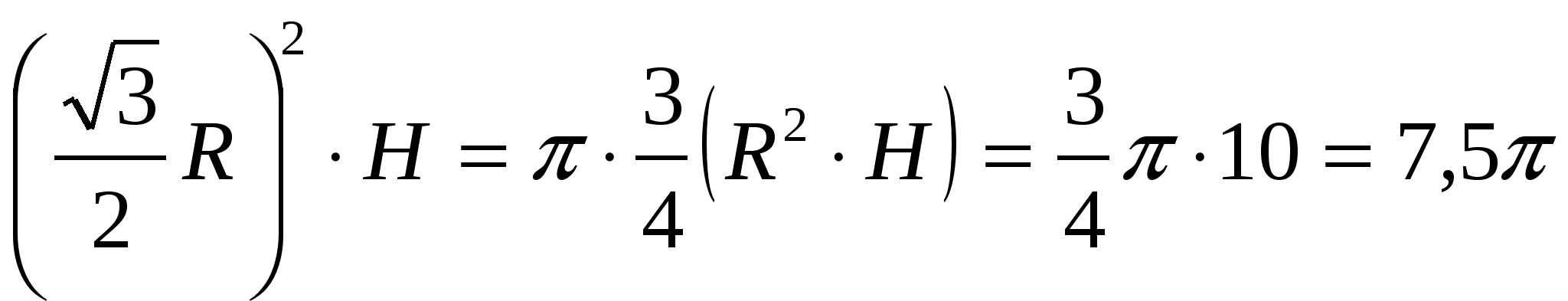 .
.
Answer. 7.5 .
Chudaeva E.V., Municipal Educational Institution “Insarskaya Secondary School No. 1”, Insar, Republic of Mordovia
SOLVING GEOMETRIC PROBLEMS
(based on Unified State Exam materials)
Task No. 1
Task No. 2
Task No. 3
Task No. 4
Problem #5
Problem #6
Problem No. 7
Problem No. 8
Problem No. 9
Problem No. 10R satisfies the equation R 2 + R – 6 = 0. Find the volume of the prism.
Problem No. 11
Problem No. 12
Problem No. 13
Problem No. 14. A cylinder is inscribed in a regular quadrangular prism. The volume of the cylinder is 16, and the radius of the circle circumscribed around the base of the prism is . Find the diagonal of the prism.
Problem No. 15. A cylinder is inscribed in a regular hexagonal prism. Find the height of the prism if its area is 54 and the radius of the cylinder is 3.
Problem No. 16. A cylinder is described around a regular hexagonal prism. The volume of the cylinder is 16 , the height of the cylinder is 4. Find the volume of the prism.
Problem No. 17. A cylinder is described around a regular hexagonal prism. The volume of the cylinder is 10 . Find the volume of a cylinder inscribed in the same prism.
SOLVING GEOMETRIC PROBLEMS
(based on Unified State Exam materials)
Task No. 1 . Calculate the volume of a regular triangular pyramid if the radius of the circle circumscribed around the base is equal to , and the height of the pyramid is equal to 4.
Solution.
3) calculate the volume of the pyramid
Answer. 9
Task No. 2 . Calculate the volume of a regular triangular pyramid if the radius of the circle inscribed at the base is equal to , and the lateral edges of the pyramid are equal to 6.
Solution.
4) from a right triangle using the Pythagorean theorem we find the height of the pyramid: , .
5) calculate the volume of the pyramid
Answer. 18.
Task No. 3 . Calculate the lateral surface area of a regular triangular pyramid if the radius of the circle circumscribed near the base is equal to , and the height of the pyramid is equal to 1.
Solution.
1) find the side of the base of a regular pyramid using the formula , .
2) find the perimeter of the base P = 3· A,
P = 9.
4) from a right triangleMPA MR : ,
MR =
5) calculate the area of the lateral surface of a regular pyramid:
Answer. .
Task No. 4 . Calculate the volume of a regular triangular pyramid whose base side is 6 and whose apothem is 6.
Solution. ,
1) find the radius of the circles described near the base and inscribed in the base: , that is .
2) find the area of the base as the area of a regular triangle, .
MPA Using the Pythagorean theorem we find the height: , MO = .
Answer. 18.
Problem #5 . Calculate the volume of a regular triangular pyramid if the radius of the circle inscribed at the base is 2 and the height of the regular pyramid is .
Solution.
1) the radius of the circle inscribed in a regular triangle is 2 times less than the radius of the circle circumscribed about this triangle, i.e. , Then .
2) find the side of the base of a regular pyramid using the formula , .
3) find the area of the base as the area of a regular triangle, .
4) calculate the volume of a regular pyramid: = .
Answer. 36.
Problem #6 . Calculate the lateral surface area of a regular quadrangular pyramid if its edges are 5 and the radius of the circle circumscribed around the base is 3.
Solution .
1) find the side of the base using the formula, i.e. .
2) find the perimeter of the base: R = 4A,
P = 24.
3) from a right triangleM DR Using the Pythagorean theorem we find the apothemMR : , D.P. =
Then: MR = .
4) calculate the area of the lateral surface of the pyramid: = .
Answer. 48.
Problem No. 7 . In a regular quadrangular pyramid, the lateral surface area is 16 and the base area is 4. Find the height of the pyramid.
Solution.
1) find the side of the base: since the base of the pyramid is a square with an area equal to 4, then the side of the square is 2, and its perimeter is 8.
2) by condition = 16 i.e.
3) from a right triangleMPA Using the Pythagorean theorem we find the height: , taking into account that OR = = 1, we obtain: MO = .
Answer. .
Problem No. 8. Calculate the volume of a regular hexagonal pyramid if the side of the base is 4 and the side edges of the pyramid are 5.
Solution.
1) the side of the base of a regular hexagon is equal to the radius of the circle circumscribed around it, i.e. ,
2) find the area of a regular hexagon using the formula or = 24.
3) from a right triangleMOU let's find the height MO : .
4) calculate the volume of the pyramid: =.
Answer. 24.
Problem No. 9 . In a regular hexagonal pyramid, the base side is 2 and the side edge is 2. Find the volume of the pyramid.
Solution.
1) find the area of a regular hexagon using the formula or = 12.
2) from a right triangleMOU let's find the height MO, given that in a regular hexagon: .
3) calculate the volume of the pyramid: =.
Answer: 24.
Problem No. 10 . A cylinder is described around a regular triangular prism. The height of the cylinder is 5, and the radius of its base isRsatisfies the equationR 2 + R – 6 = 0. Find the volume of the prism.
Solution. V = S · H
1) since the prism is inscribed in the cylinder, the height of the prism is equal to the height of the cylinder, and the base of the prism is inscribed in the base of the cylinder, N = 5.
2) by condition R satisfies the equation R 2 + R – 6 = 0, solving which we find
R 1 = - 3, R 2 = 2, since the radius is a positive value, then -3 does not satisfy the conditions of the problem.
3) find the side of the inscribed regular triangle using the formula , .
4) find the area of the base of a regular prism, as the area of a regular triangle: =
5) calculate the volume of the prism:V =
S
·
H =
.
Answer. 15.
Problem No. 11 . A cylinder is described around a regular triangular prism. The distance between the axis of the cylinder and the side of the base of the prism is equal to . The height of a cylinder is equal to three of its radii. Find the volume of the prism.
Solution. V = S · H
1) Since the prism is inscribed in the cylinder, the height of the prism is equal to the height of the cylinder, and the base of the prism is inscribed in the base of the cylinder, according to the condition N = 3 R..
2) The distance between the axis of the cylinder and the side of the base of the prism is equal to the radius of the inscribed triangleABC circles, i.e. , and by condition is equal to .
3) the radius of the circle inscribed in a regular triangle is 2 times less than the radius of the circle circumscribed about this triangle, i.e. , Then .
4) find the side of the inscribed regular triangle using the formula , .
5) find the area of the base of a regular prism, as the area of a regular triangle: =
6) calculate the volume of the prism:V = S · H = S· 3 · R = 162.
Answer. 162.
Problem No. 12. A cylinder is described around a regular triangular prism. The lateral surface area of the cylinder is 16 . Find the volume of the prism if the side of its base is 5.
Solution. V = S · H
2) Find the area of the base of a regular prism, as the area of a regular triangle: =.
3) The side of an inscribed regular triangle is found by the formula, then .
4) According to the condition, the area of the lateral surface of the cylinder is 16· i.e. where from N = = .
5) Calculate the volume of the prism:V = S · H = · = 30.
Answer. thirty.
Problem No. 13. A cylinder is described around a regular quadrangular prism, the lateral surface area of which is 20. Find the lateral surface area of the prism.
Solution.
1) Since the prism is inscribed in the cylinder, the height of the prism is equal to the height of the cylinder, and the base of the prism is inscribed in the base of the cylinder.
2) According to the condition, the area of the lateral surface of the cylinder is 20 , i.e. , .
3) since the prism is regular, then at its base lies a square with side , then the perimeter of the base is equal to .
4) calculate the area of the lateral surface of the prism = ., and the radius of the cylinder is 3. , the height of the cylinder is 4. Find the volume of the prism. .
5) write down the formula for calculating the volume of a cylinder inscribed in a prism:V = S · H, those.:
V = = ·.
Answer. 7.5 .
