A pyramid is called regular if its base is a regular polygon, and the segment connecting the vertex to the center of the base is its height. S. 6.
Slide 6 from the presentation "Pyramid 10th grade". The size of the archive with the presentation is 226 KB.Geometry 10th grade
summary of other presentations“Straight line and plane” - Properties of parallel lines. Axiom of plane. The axiom is straight. Geometry in space. Axiom: there are 4 points that do not lie in the same plane. Axiom of intersection of planes. Corollary of the theorem. Corollary of the axiom. Parallelism of lines and planes in space. Parallelism. 10. Parallelism of a straight line and a plane.
"Pyramids" - Apothems. ?А1А2Р = … = ?Аn-1АnР – r/b. Sfull = Sside. + Sbas. Height is a perpendicular drawn from the top of the pyramid to the plane of the base. Quadrangular pyramid. Area of the pyramid. A pyramid is a polyhedron made up of an n-gon A1A2...An and n triangles. Author: Alina Karsanova, 10B grade student. Sbas. Hexagonal pyramid. Pyramids. Municipal educational institution secondary school No. 5 - “School of Health and Development”, Raduzhny. Correct pyramid. Side All apothems of a regular pyramid are equal to each other.
“Vector in geometry” - A vector is called the sum of vectors and: . Obviously, the vector is the opposite of the vector. Parallelogram rule. Properties of vector addition. The length of a vector (vector) is denoted as follows: . The zero vector is considered to be codirectional with any vector. The sum does not depend on the choice of point A, from which the vector is plotted during addition. The difference between vectors a and b can be found using the formula Where is the vector opposite to the vector.
“Egyptian Pyramids” - Why are the Egyptian Pyramids called a silent treatise on geometry? Hypothesis. Pyramid of Meidum. Draw the correct pyramid RABSM. Draw the height of the RO. Research. Egyptian pyramids are correct. Municipal educational institution secondary school in the village of Stanovoe. 2008 What does proficiency in mathematics mean?
“Polyhedra around us” - How to disagree with the opinion of the bee from the fairy tale “A Thousand and One Nights”: Polyhedra in architecture. The total height of the lighthouse was 117 meters. Title page of J. Cousin’s book “The Book of Perspective.” Geological finds. Alexandrian lighthouse. An octahedron is described around the sphere of Mercury, the planet closest to the Sun. Protozoan. High-rise buildings. Polyhedron.
“Pyramid 10th grade” - Contents. Side rib. R. A. MBOU "Secondary School No. 22 with in-depth study of the English language" in Nizhnekamsk RT. 2. A3. Top of the pyramid. prepared by first category mathematics teacher Idiyatullina A.M. Height. B. Math lesson in 10th grade on the topic “Pyramid”.
SURFACE AREA AND VOLUME OF GEOMETRIC BODIES
§ 114. PYRAMID.
1. Definitions.
A pyramid is a geometric body bounded by a polygon, called the base of the pyramid, and triangles with a common vertex, called the lateral faces.
The common vertex of all lateral faces is called top pyramids.
Height pyramid is called a perpendicular, lowered from the top of the pyramid to its base (Fig. 426).
A pyramid whose base is a regular polygon and whose height passes through the center of the base is called correct. The lateral faces of a regular pyramid are equal isosceles triangles.
The height of the side face of a regular pyramid, lowered from the top to the side of the base, is called apothem pyramids.
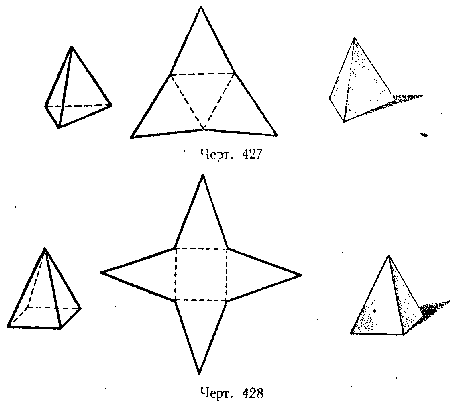
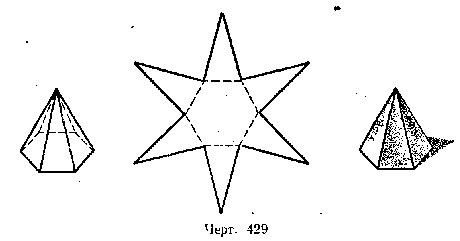
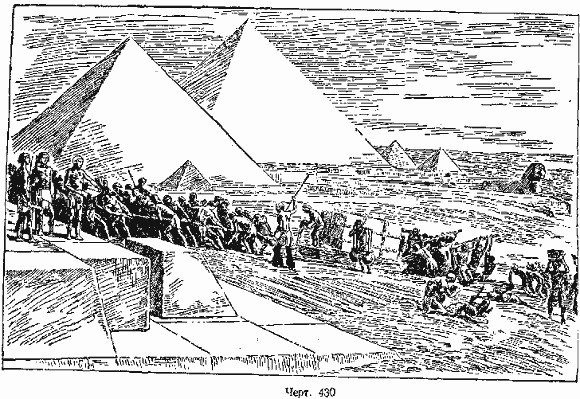
Drawings 427, 428, 429 show images and developments of regular pyramids: triangular, quadrangular and hexagonal. Drawing 430 shows the Egyptian pyramids.
Exercises.
Make developments of the regular pyramids shown in drawings 427, 428, 429, and make pyramid models from them.
2. Surface area of the pyramid.
To determine the area of the lateral surface of the pyramid, you need to find the sum of the areas of all its lateral faces.
If you add the area of its base to the area of the lateral surface of a pyramid, you get the total surface area of the pyramid.
For brevity they say: the lateral surface of the pyramid and the complete surface of the pyramid, omitting the word “area”.
Exercises.
1. At the base of a regular pyramid is a triangle with a side of 12 cm. The apothem of the pyramid is 20 cm.
Calculate:
a) base area,
b) lateral surface,
c) the complete surface of this pyramid.
2. The lateral faces of a regular triangular pyramid are equilateral triangles. The side of the base is equal A see Calculate the lateral and total surface of this pyramid (Fig. 431).
3. Solve this problem again by arranging the faces of the pyramid in the form of a parallelogram (Fig. 432).
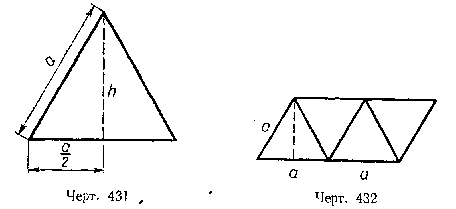
3. Volume of the pyramid.
In high school, it is proven that the volume of a pyramid is 1/3 of the volume of a prism, which has the same base as the pyramid and the same height (Fig. 433).
Therefore, the volume of the pyramid is calculated by the formula:
where V is the volume of the pyramid, S is the area of the base, H is the height of the pyramid.
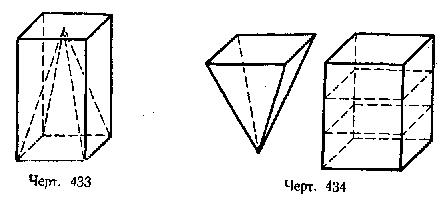
To illustrate this formula, it is recommended to make a straight quadrangular prism and a quadrangular pyramid from cardboard, having equal bases and equal heights. If this pyramid is filled, for example, with sand and then poured this sand into the prism made, then the sand will fill only 1/3 of the prism’s capacity. To fill a prism with sand, you need to pour sand into it three times from the filled pyramid (Fig. 434).
Exercises.
Using the above formula, solve a number of problems using the data in the table below.
Definition 1. A pyramid is called regular if its base is a regular polygon, and the vertex of such a pyramid is projected into the center of its base.
Definition 2. A pyramid is called regular if its base is a regular polygon and its height passes through the center of the base.
Regular truncated pyramid
If you draw a section parallel to the base of the pyramid, then the body enclosed between these planes and the side surface is called a truncated pyramid. A truncated pyramid is called regular if the pyramid from which it was derived is regular.
Properties of a regular pyramid
- side ribs are equal
- apothems are equal
- side faces are equal
- all lateral faces are equal isosceles triangles
- in any regular pyramid you can both fit and describe a sphere around it
- if the centers of the inscribed and circumscribed spheres coincide, then the sum of the plane angles at the top of the pyramid is equal to π, and each of them, respectively, where n is the number of sides of the base polygon
- The area of the lateral surface of a regular pyramid is equal to half the product of the perimeter of the base and the apothem
Correct pyramid
Note. This is part of a lesson with geometry problems (section stereometry, problems about the pyramid). If you need to solve a geometry problem that is not here, write about it in the forum. In tasks, instead of the "square root" symbol, the sqrt() function is used, in which sqrt is the square root symbol, and the radical expression is indicated in brackets.For simple radical expressions, the sign "√" can be used.
Task
The apothem of a regular triangular pyramid is 4 cm, and the dihedral angle at the base is 60 degrees. Find the volume of the pyramid.
Solution.
Since the pyramid is regular, consider the following:
- The height of the pyramid is projected onto the center of the base
- According to the problem, the center of the base of a regular pyramid is an equilateral triangle
- The center of an equilateral triangle is both the center of an inscribed and circumscribed circle.
- The height of the pyramid forms a right angle with the plane of the base
The volume of the pyramid can be found using the formula:
V = 1/3 Sh
Since the apothem of a regular pyramid forms a right triangle together with the height of the pyramid, we use the theorem of sines to find the height. In addition, let's take into account:
- The first leg of the right triangle under consideration is the altitude, the second leg is the radius of the inscribed circle (in a regular triangle, the center is simultaneously the center of the inscribed and circumscribed circle), the hypotenuse is the apothem of the pyramid
- The third angle of a right triangle is equal to 30 degrees (the sum of the angles of a triangle is 180 degrees, the angle of 60 degrees is given by condition, the second angle is a straight line according to the properties of the pyramid, the third is 180-90-60 = 30)
- sine of 30 degrees is equal to 1/2
- sine of 60 degrees is equal to the root of three in half
- the sine of 90 degrees is 1
According to the sine theorem:
4 / sin(90) = h / sin(60) = r / sin(30)
4 = h / (√3 / 2) = 2r
where
