Trigonometric equations. As part of the mathematics exam, in the first part there is a task related to solving an equation - these are simple equations that can be solved in minutes; many types can be solved orally. Includes: linear, quadratic, rational, irrational, exponential, logarithmic and trigonometric equations.
In this article we will look at trigonometric equations. Their solution differs both in the volume of calculations and in complexity from the other problems in this part. Don’t be alarmed, the word “difficulty” refers to their relative difficulty compared to other tasks.
In addition to finding the roots of the equation themselves, it is necessary to determine the largest negative or smallest positive root. The likelihood that you will get a trigonometric equation on the exam is, of course, small.
There are less than 7% of them in this part of the Unified State Examination. But this does not mean that they should be ignored. In Part C, you also need to solve a trigonometric equation, so a good understanding of the solution technique and understanding of the theory is simply necessary.
Understanding the trigonometry section of mathematics will greatly determine your success in solving many problems. Let me remind you that the answer is a whole number or a finite decimal fraction. After you get the roots of the equation, BE SURE to check. It won’t take much time, and it will save you from making mistakes.
We will also look at other equations in the future, don't miss out! Let us recall the formulas for the roots of trigonometric equations, you need to know them:

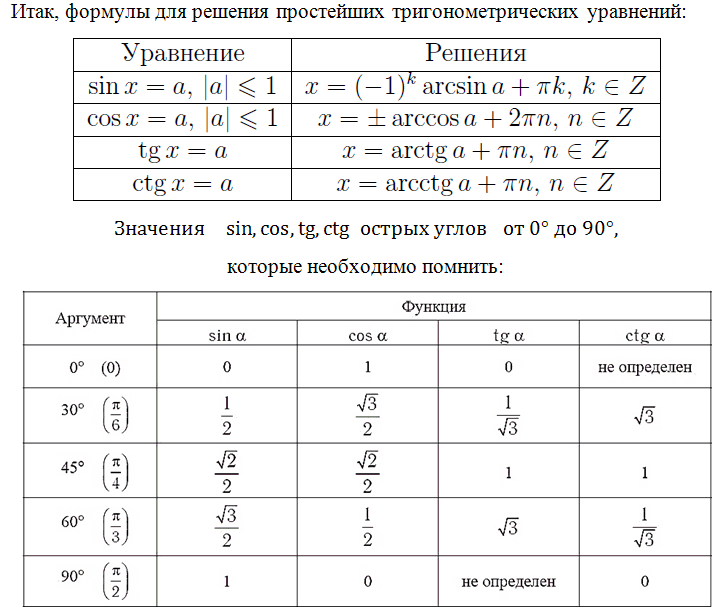
Knowledge of these values is necessary; this is the “ABC”, without which it will be impossible to cope with many tasks. Great, if your memory is good, you easily learned and remembered these values. What to do if you can’t do this, there’s confusion in your head, but you just got confused when taking the exam. It would be a shame to lose a point because you wrote down the wrong value in your calculations.
These values are simple, it is also given in the theory you received in the second letter after subscribing to the newsletter. If you haven't subscribed yet, do so! In the future we will also look at how these values can be determined from a trigonometric circle. It’s not for nothing that it’s called the “Golden Heart of Trigonometry.”
Let me immediately explain, in order to avoid confusion, that in the equations considered below, the definitions of arcsine, arccosine, arctangent using the angle are given X for the corresponding equations: cosx=a, sinx=a, tgx=a, where X can also be an expression. In the examples below, our argument is specified precisely by an expression.
So, let's consider the following tasks:
Find the root of the equation:

Write down the largest negative root in your answer.
The solution to the equation cos x = a is two roots:

Definition: Let the number a in modulus not exceed one. The arc cosine of a number is the angle x lying in the range from 0 to Pi, the cosine of which is equal to a.

Means

Let's express x:

Let's find the largest negative root. How to do it? Let's substitute different values of n into the resulting roots, calculate and choose the largest negative one.
We calculate:
With n = – 2 x 1 = 3 (– 2) – 4.5 = – 10.5 x 2 = 3 (– 2) – 5.5 = – 11.5
With n = – 1 x 1 = 3 (– 1) – 4.5 = – 7.5 x 2 = 3 (– 1) – 5.5 = – 8.5
With n = 0 x 1 = 3∙0 – 4.5 = – 4.5 x 2 = 3∙0 – 5.5 = – 5.5
With n = 1 x 1 = 3∙1 – 4.5 = – 1.5 x 2 = 3∙1 – 5.5 = – 2.5
With n = 2 x 1 = 3∙2 – 4.5 = 1.5 x 2 = 3∙2 – 5.5 = 0.5
We found that the largest negative root is –1.5
Answer: –1.5
Decide for yourself:

Solve the equation:

The solution to the equation sin x = a is two roots:

Either (it combines both of the above):

Definition: Let the number a in modulus not exceed one. The arcsine of a number is an angle x that lies in the range from – 90° to 90°, the sine of which is equal to a.

Means

Express x (multiply both sides of the equation by 4 and divide by Pi):

Let's find the smallest positive root. Here it is immediately clear that when substituting negative values of n we get negative roots. Therefore, we will substitute n = 0,1,2...
When n = 0 x = (– 1) 0 + 4∙0 + 3 = 4
When n = 1 x = (– 1) 1 + 4∙1 + 3 = 6
When n = 2 x = (– 1) 2 + 4∙2 + 3 = 12
Let's check with n = –1 x = (–1) –1 + 4∙(–1) + 3 = –2
So the smallest positive root is 4.
Answer: 4
Decide for yourself:

Solve the equation:

Write the smallest positive root in your answer.
Quite often in problems of increased complexity we encounter trigonometric equations containing modulus. Most of them require a heuristic approach to solution, which is completely unfamiliar to most schoolchildren.
The problems proposed below are intended to introduce you to the most typical techniques for solving trigonometric equations containing a modulus.
Problem 1. Find the difference (in degrees) of the smallest positive and largest negative roots of the equation 1 + 2sin x |cos x| = 0.
Solution.
Let's expand the module:
1) If cos x ≥ 0, then the original equation will take the form 1 + 2sin x · cos x = 0.
Using the double angle sine formula, we get:
1 + sin 2x = 0; sin 2x = -1;
2x = -π/2 + 2πn, n € Z;
x = -π/4 + πn, n € Z. Since cos x ≥ 0, then x = -π/4 + 2πk, k € Z.
2) If cos x< 0, то заданное уравнение имеет вид 1 – 2sin x · cos x = 0. По формуле синуса двойного угла, имеем:
1 – sin 2x = 0; sin 2x = 1;
2x = π/2 + 2πn, n € Z;
x = π/4 + πn, n € Z. Since cos x< 0, то x = 5π/4 + 2πk, k € Z.
3) The largest negative root of the equation: -π/4; smallest positive root of the equation: 5π/4.
The required difference: 5π/4 – (-π/4) = 6π/4 = 3π/2 = 3 180°/2 = 270°.
Answer: 270°.
Problem 2. Find (in degrees) the smallest positive root of the equation |tg x| + 1/cos x = tan x.
Solution.
Let's expand the module:
1) If tan x ≥ 0, then
tan x + 1/cos x = tan x;
The resulting equation has no roots.
2) If tg x< 0, тогда
Tg x + 1/cos x = tg x;
1/cos x – 2tg x = 0;
1/cos x – 2sin x / cos x = 0;
(1 – 2sin x) / cos x = 0;
1 – 2sin x = 0 and cos x ≠ 0.
Using Figure 1 and the condition tg x< 0 находим, что x = 5π/6 + 2πn, где n € Z.
3) The smallest positive root of the equation is 5π/6. Let's convert this value to degrees:
5π/6 = 5 180°/6 = 5 30° = 150°.
Answer: 150°.
Problem 3. Find the number of different roots of the equation sin |2x| = cos 2x on the interval [-π/2; π/2].
Solution.
Let's write the equation in the form sin|2x| – cos 2x = 0 and consider the function y = sin |2x| – cos 2x. Since the function is even, we will find its zeros for x ≥ 0.
sin 2x – cos 2x = 0; Let's divide both sides of the equation by cos 2x ≠ 0, we get:
tg 2x – 1 = 0;
2x = π/4 + πn, n € Z;
x = π/8 + πn/2, n € Z.
Using the parity of the function, we find that the roots of the original equation are numbers of the form
± (π/8 + πn/2), where n € Z.
Interval [-π/2; π/2] belong to the numbers: -π/8; π/8.
So, two roots of the equation belong to the given interval.
Answer: 2.
This equation could also be solved by opening the module.
Problem 4. Find the number of roots of the equation sin x – (|2cos x – 1|)/(2cos x – 1) · sin 2 x = sin 2 x on the interval [-π; 2π].
Solution.
1) Consider the case when 2cos x – 1 > 0, i.e. cos x > 1/2, then the equation takes the form:
sin x – sin 2 x = sin 2 x;
sin x – 2sin 2 x = 0;
sin x(1 – 2sin x) = 0;
sin x = 0 or 1 – 2sin x = 0;
sin x = 0 or sin x = 1/2.
Using Figure 2 and the condition cos x > 1/2, we find the roots of the equation:
x = π/6 + 2πn or x = 2πn, n € Z.
2) Consider the case when 2cos x – 1< 0, т.е. cos x < 1/2, тогда исходное уравнение принимает вид:
sin x + sin 2 x = sin 2 x;
x = 2πn, n € Z.
Using Figure 2 and the cos x condition< 1/2, находим, что x = π + 2πn, где n € Z.
Combining the two cases, we get:
x = π/6 + 2πn or x = πn.
3) Interval [-π; 2π] belong to the roots: π/6; -π; 0; π; 2π.
Thus, the given interval contains five roots of the equation.
Answer: 5.
Problem 5. Find the number of roots of the equation (x – 0.7) 2 |sin x| + sin x = 0 on the interval [-π; 2π].
Solution.
1) If sin x ≥ 0, then the original equation takes the form (x – 0.7) 2 sin x + sin x = 0. After taking the common factor sin x out of brackets, we get:
sin x((x – 0.7) 2 + 1) = 0; since (x – 0.7) 2 + 1 > 0 for all real x, then sinx = 0, i.e. x = πn, n € Z.
2) If sin x< 0, то -(x – 0,7) 2 sin x + sin x = 0;
sin x((x – 0.7) 2 – 1) = 0;
sinx = 0 or (x – 0.7) 2 + 1 = 0. Since sin x< 0, то (x – 0,7) 2 = 1. Извлекаем квадратный корень из левой и правой частей последнего уравнения, получим:
x – 0.7 = 1 or x – 0.7 = -1, which means x = 1.7 or x = -0.3.
Taking into account the condition sinx< 0 получим, что sin (-0,3) ≈ sin (-17,1°) < 0 и sin (1,7) ≈ sin (96,9°) >0, which means only the number -0.3 is the root of the original equation.
3) Interval [-π; 2π] belong to the numbers: -π; 0; π; 2π; -0.3.
Thus, the equation has five roots on a given interval.
Answer: 5.
You can prepare for lessons or exams using various educational resources that are available on the Internet. Currently anyone  a person simply needs to use new information technologies, because their correct, and most importantly appropriate, use will help increase motivation in studying the subject, increase interest and help better assimilate the necessary material. But do not forget that the computer does not teach you to think; the information received must be processed, understood and remembered. Therefore, you can turn to our online tutors for help, who will help you figure out how to solve the problems that interest you.
a person simply needs to use new information technologies, because their correct, and most importantly appropriate, use will help increase motivation in studying the subject, increase interest and help better assimilate the necessary material. But do not forget that the computer does not teach you to think; the information received must be processed, understood and remembered. Therefore, you can turn to our online tutors for help, who will help you figure out how to solve the problems that interest you.
Still have questions? Don't know how to solve trigonometric equations?
To get help from a tutor -.
The first lesson is free!
blog.site, when copying material in full or in part, a link to the original source is required.
Maintaining your privacy is important to us. For this reason, we have developed a Privacy Policy that describes how we use and store your information. Please review our privacy practices and let us know if you have any questions.
Collection and use of personal information
Personal information refers to data that can be used to identify or contact a specific person.
You may be asked to provide your personal information at any time when you contact us.
Below are some examples of the types of personal information we may collect and how we may use such information.
What personal information do we collect:
- When you submit an application on the site, we may collect various information, including your name, phone number, email address, etc.
How we use your personal information:
- The personal information we collect allows us to contact you with unique offers, promotions and other events and upcoming events.
- From time to time, we may use your personal information to send important notices and communications.
- We may also use personal information for internal purposes, such as conducting audits, data analysis and various research in order to improve the services we provide and provide you with recommendations regarding our services.
- If you participate in a prize draw, contest or similar promotion, we may use the information you provide to administer such programs.
Disclosure of information to third parties
We do not disclose the information received from you to third parties.
Exceptions:
- If necessary - in accordance with the law, judicial procedure, in legal proceedings, and/or on the basis of public requests or requests from government authorities in the territory of the Russian Federation - to disclose your personal information. We may also disclose information about you if we determine that such disclosure is necessary or appropriate for security, law enforcement, or other public importance purposes.
- In the event of a reorganization, merger, or sale, we may transfer the personal information we collect to the applicable successor third party.
Protection of personal information
We take precautions - including administrative, technical and physical - to protect your personal information from loss, theft, and misuse, as well as unauthorized access, disclosure, alteration and destruction.
Respecting your privacy at the company level
To ensure that your personal information is secure, we communicate privacy and security standards to our employees and strictly enforce privacy practices.
