In any language we use abbreviations, shortening words and entire phrases. This allows you to save time and get your point across faster.
English is also no exception.
How to use abbreviations correctly in English? In this article we will look at 2 types of abbreviations.
Using an apostrophe to shorten English words

An apostrophe is superscript as a comma (").
In English we can abbreviate some words. In such cases, we put an apostrophe (") in place of missing letters.
Here are the main accepted abbreviations:
Examples:
He "s studying now.
He is studying now.
We "re ready.
We are ready.
I "m calling him.
I call him.
They don't smoke.
They don't smoke.
I 'll translate.
I will translate.
Using an abbreviation to shorten in English

The abbreviation is conditional abbreviation words or phrases.
They are important to know because they are used every day, both spoken and written.
The following are the most common abbreviations in English.
1. Abbreviations of words that appear in texts, letters or SMS:
Mr(Mister) - Mr.
Mrs(Mistress) - Mrs.
Dr(Doctor) - doctor
St(Saint / Street) - saint or street
N.B.- please note - (Latin nota bene) - note well, note
RSVP- please reply - (French repondez s’il vous plait) - respond to an invitation
e.g.- for example - (Latin exempli gratia) - for example
a.m.(ante meridiem, in the morning) - in the morning
p.m.(post meridiem, in the afternoon) - in the evening
i.e.(id est, that is) - this means
e.g.(exempli gratia, for example) - for example
u(you) - you
etc.(from Latin et cetera) - and so on
2moro(tomorrow) - tomorrow
2day(today) - today
BD or BDAY(birthday) - birthday
2nite(tonight) - in the evening
4ever(forever) - forever
Mrs Smith is our English teacher.
Mrs. Smith is our English teacher.
Could you call me 2day?
Can you call me today?
2. Words that we abbreviate in informal speech:
Lab(laboratory) - laboratory
TV(television) - television
Exam(examination) - exam
Ad(advertisement) - announcement
Case(suitcase) - briefcase
Mum(mother) - mother
Phone(telephone) - telephone
Board(blackboard) - board
Fridge(refrigerator) - refrigerator
Bike(bicycle) - bicycle
Dad(father) - father
Flu(influenza) - flu
He failed the exam.
He failed the exam.
Our refrigerator is broken.
Our refrigerator is broken.
3. Sometimes we shorten entire phrases and use abbreviations:
V.I.P.(very important person) - very important person
P.S.(from Latin “post scriptum”) - after what is written
A.D.(from Latin "Anno Domini") - our era
B.C. / B.C.E.- before Christ - before Christ / before Common Era - before our era
ASAP(as soon as possible) - as soon as possible
2G2BT(too good to be true) - too good to be true
AFAIK(as far as I know) - as far as I know
BTW(by the way) - by the way
RLY(really) - really, really
BRB(be right back) - I'll be back soon
TTYL(talk to you later) - we’ll talk later, “before we get in touch”
IMHO(in my honest opinion) - in my opinion, in my opinion
AKA(also known as) - also known as
TIA(thanks in advance) - thanks in advance
I need it ASAP.
I need this ASAP.
I"ll BRB.
I'll be back soon.
So these are the abbreviations that we use in English.
Reinforcement task
Translate the following sentences into English. Leave your answers in the comments:
1. She forgot her phone.
2. By the way, I was waiting for the call.
3. As far as I know, they left.
4. I won't come tomorrow.
5. Call me as soon as possible.
A contraction is a combination of two or more words into one whole, while letters, such as vowels, are removed from the words. IN writing An apostrophe is written instead of missing letters. Abbreviations in English, as a rule, are used in informal settings (in conversation, in writing). Their goal is to simplify spoken language. They save time in modern society.
English abbreviations- These are abbreviated forms of parts of speech. It is very difficult to imagine a modern foreign language without them. Young people came up with these abbreviations for quick communication and data transfer. Absolutely everyone uses them now. If we compare the Internet correspondence of an English teenager and our schoolboy, then teenagers abroad use abbreviations hundreds of times more. There was even such a case that one girl was so carried away by abbreviations that she wrote an entire essay in the form of special abbreviations and symbols, which could not be immediately read without auxiliary decodings. Therefore, it is necessary to become more familiar with this interesting language.
List of English abbreviations
b - be - to be
n - and - and, a
r - are (form of the verb to be)
c - see - to see
u - you - you, you, you
IC - I see - I see
CU - see you - I see you
BF - boyfriend - friend
GF - girlfriend - friend
BZ - busy - busy
CYT - see you tomorrow - see you tomorrow
etc - et cetera - and so on
RUOK - are you ok? - are you all right?
HRU - how are you? - How are you?
MU - miss you - I miss you
NP - no problem - no problem
ASAP - as soon as possible - as soon as possible
TNX, THX, TX - thank you - thank you
YW - you are welcome - please contact
PLS, PLZ - please - please
BTW - by the way - by the way
BFF - best friend forever - best friend forever
HAND - have a nice day - have a nice day
IDK - I don't now - I don't know
MSG - message
CLD - could - be able, be able to
GD - good - good
VGD - very good - very good
RLY - really - really
TTYL - talk to you later - let's talk later
LOL - laughing out loud - laughing out loud
IMHO - in my humble opinion - in my humble opinion
ROFL - rolling on the floor laughing - rolling on the floor laughing
BRB - be right back - I'll be back soon
GTG - got to go - I'm leaving (I have to go)
XOXO - hugs and kisses - hugs and kisses
2u - to you - you
2u2 - to you too - you too
2day - today - today
2moro - tomorrow - tomorrow
2night - tonight - in the evening
b4 - before - before
4ever - forever - forever
gr8 - greate - great
f8 - fate - fate
l8 - late - late
l8r - later - later
10q - thank you - thank you
Where are English abbreviations used?
They are mainly used when writing messages on social networks, on forums, in chat rooms, and special language exchange resources. At first, only programmers communicated in this way, now the whole world. This the whole system letters and signs that need to be learned for simple communication. They are somewhat reminiscent of hieroglyphs, when one sign means a whole sentence. Auxiliary and modal verbs are abbreviated and negative particle not.
Types of abbreviations
There are 4 types of abbreviations in English:
- graphic (found in written sources - books, letters, dictionaries);
The oldest group of such abbreviations are words of Latin origin. Such words are written abbreviated, but in oral speech are read in full. - lexical - abbreviations. In turn, they are divided into the following subgroups:
a) initials - capital letters of countries, companies;
b) syllabic - abbreviations based on the initial syllables of complex words;
c) partially abbreviated - abbreviations that include 2 words: one is abbreviated, the second is used in full. - mergers;
- digital.
Countersense or abbreviation of words exists in every living language. This often causes a problem for those who have just started learning, for example, English. Often it is in songs that one can trace the counter-sense, when one tries to grasp the meaning, but due to the abbreviation of the words, nothing is clear. Therefore, you need to learn to understand the abbreviations that native speakers of this language know and use in everyday speech.
English abbreviations- these are abbreviated forms of some parts of speech ( don't, I"m, etc.), which are widely used in colloquial and informal speech and writing.
Abbreviations in English
The table below shows abbreviations in English and examples of their use.
| Unabbreviated form | Short form | Example |
| I am | I"m | I"m (= I am) already here. I'm already here. |
| I have | I"ve | I"ve (= I have) seen that movie several times. I've watched this movie several times. |
| I will | I"ll | I"ll (= I will) deal with this. I will take care of it. |
| I had / I would | I"d | I"d (= I had) done it by the time you came. I had done it by the time you arrived. I promised you I"d (= I would) do it. |
| You are | You"re | You"re (= you are) one of the best students in this class. You are one of best students in this class. |
| You have | You"ve | You"ve (= you have) been such a good friend to me. You have been such a good friend to me. |
| You will | You"ll | You"ll (= you will) see him soon enough. You'll meet him pretty soon. |
| You had/you would | You'd | You passed the test because you"d (= you had) prepared for it. You passed test because I prepared for it in advance. You"d (= you would) like it, I"m sure. |
| He is / he has | He's | He"s (= he is) a very talented actor. He is a very talented actor. He "s (= he has) never lied to us. |
| He won't | He"ll | He"ll (= he will) show up, he is just running a little late. He will come, he is only a little late. |
| He had/he would | He"d | He"d (= he had) helped me a lot to finish the work by your arrival. He helped me finish my work before you arrived. He"d (= he would) be very glad to contribute. |
| She is / she has | She's | She"s (= she is) standing by the window. She is standing by the window. She"s (= she has) got a lot of money. |
| She will | She"ll | She"ll (= she will) come over to our house tonight. She will come to us this evening. |
| She had/she would | She"d | She"d (= she had) called me before she came. She called before she came. She said that she"d (= she would) give me a call during the lunch-break. |
| It is / it has | It's | It"s (= it is) hot today. Today it's hot. It"s (= it has) never been so hot. |
| We are | We"re | We"re (= we are) coming, we"re almost there. We're on our way, we're almost there. |
| We have | We"ve | We"ve (= we have) tried to get a hold of you, but failed. We tried to contact you, but were unable to. |
| We will | We'll | We"ll (= we will) watch over the kids. We'll look after the children. |
| We had/we would | We"d | We"d (= we had) traveled from Germany to Spain. We traveled from Germany to Spain. We"d (= we would) be much obliged if you helped us. |
| They are | They"re | We"re (= we are) going to talk about it next time. We'll talk about this next time. |
| They have | They"ve | I hear that they"ve (= they have) been told everything. I heard that they were told everything. |
| They will | They"ll | I hope they"ll (= they will) be on time. I hope they won't be late. |
| They had / they would | They"d | They"d (= they had) done their work long before I started doing mine. They did their job long before I started mine. I talked to them and they promised they"d (= they would) do everything in their power. |
| There is / there has | There's | There"s (=there is) little time left. There is little time left. There"s (= there has) been a very nice Chinese restaurant down the street before, but now it"s gone. |
| There will | There"ll | They say there"ll (= there will) be a new school in our district. They say a new school will appear in our area. |
| There had / there would | There"d | There"d (= there had) been many people here before. There used to be a lot of people here. I knew there"d (= the would) be a way. |
| Are not | Aren't | They aren't (= are not) here yet. They're not here yet. |
| Cannot | Can't | I can"t (= cannot) do it because I am very busy. I can't do this because I'm very busy. |
| Could not | Couldn't | Why couldn"t (= could not) you come in time? Why couldn't you come on time? |
| Dare not | Daren"t | I daren"t (= dare not) say it. I don't dare say it. |
| Didn't | Didn't | Helen says she didn't (= did not) know anything about it. Helen said she knew nothing about it. |
| Doesn't | Doesn't | He doesn't (= does not) like this book. He doesn't like this book. |
| Don't | Don't | Whatever you do, just don"t (= do not) touch my antique statuettes. Do what you want, just don’t touch the antique figurines. |
| Had not | Hadn't | We hadn't (= had not) seen such a beautiful place before we went there. We had never seen such a beautiful place before we came there. |
| Has not | Hasn't | Sam hasn't (= has not) read that magazine yet, give it to him. Sam hasn't read this magazine yet, give it to him. |
| Have not | Haven't | I haven"t (= have not) finished working yet, give me some more time. I haven't finished working yet, wait a little longer. |
| Is not | Isn't | I don"t know why he isn"t (= is not) there. I don't know why it's not there. |
| Might not | Mightn't | You should call him first, he mightn"t (= might not) be home yet. Better call him first, maybe he's not home yet. |
| Must not | Mustn't | You mustn"t (= must not) work so hard, have a little rest. You can't work so hard, take some rest. |
| Need not | Needn't | The teacher has said that we needn"t (= need not) do this exercise. Teacher said we don't need to do this exercise. |
| Ought not | Oughtn't | Tell him that he oughtn"t (= ought not) to speak with his parents like that. Tell him he shouldn't talk to his parents like that. |
| Shall not | Shan"t | Don"t come tomorrow, I shan"t (= shall not) be able to help you. Don't come tomorrow, I won't be able to help you. |
| Should not | Shouldn't | We shouldn"t (= should not) hurry, the work should be done very carefully. There is no need to rush, the work must be done very carefully. |
| Was not | Wasn't | I wasn"t (= was not) ready to go when you called me. I wasn't ready to go when you called. |
| Were not | Weren't | They weren't (= were not) going to come. They weren't going to come. |
| Will not | Won't | We won't (= will not) let you down. We won't let you down. |
| Wouldn't | Wouldn't | If I were you I wouldn't (= would not) underestimate him. If I were you, I wouldn't underestimate him. |
Notes:
1. There is a non-standard form in spoken English ain"t, which may be an abbreviation of the forms am not, are not, is not, have not or has not(however, this form has a strong informal connotation):
He ain"t going to come. = He is not going to come.
He will not come.
Don"t talk to me like that – you ain"t my master. = You are not my master.
Don't talk to me like that, you are not my master.
I ain"t got anything to read. = I have not got anything to read.
I have nothing to read.
2. Abbreviations daren"t And shan"t very rarely used in American English.
3. Short for am not is the form aren't(which, unlike the form ain"t, is not colloquial and informal):
I am late, aren't I? (and NOT... amn"t I?)
I'm late, right?
None of us have experienced this situation: you learn English, you know it quite well, you turn on an English film in the original and you realize... that you don’t understand anything. There can be many reasons for this, and one of them is ignorance colloquial abbreviations words known to us. In this article we will talk about the most common informal abbreviations and give examples of their use from films, TV series, cartoons and songs. You're gonna learn English today!
20 informal abbreviations in English
We immediately want to inform you: you need to know all the abbreviations below in order to understand the modern speech of foreigners, but you should use these words carefully. All abbreviations are informal, so you shouldn’t use them in negotiations, but in a conversation with a friend it’s quite possible to throw in some “I wanna cuppa tea” (read on to find out what we told you :-)).
Below you will see examples of the use of informal abbreviations from films, songs and cartoons. We would like to inform you that we are providing the official translation of the characters' phrases, so do not be surprised if it is not literal. Now let's get acquainted with the 20 most popular informal English abbreviations.
This abbreviation in oral speech can perhaps be found even more often than its full form going to. So let's learn how to use it correctly.
I'm not gonna play tennis with you. = I'm not going to play tennis with you. - I don't going to play tennis with you.
Please note: speakers in their speech most often also omit the verb to be before the word going. For example, let's look at a line from the movie From Dusk Till Dawn:

2. Gimme = give me - give/give me
This abbreviation is familiar to us all from the ABBA song of the same name “Gimme, Gimme, Gimme”. So, you can ask your friend to give you something:
Gimme your pen. = Give me your pen. - Give me your pen.
Let's listen to how ABBA's lead singers pronounce this word.
3. Lemme = let me - let me
This abbreviation is similar to the previous one, but is used less frequently. Although lemme (and all other abbreviations) can very often be found in the songs of Beyonce or Rihanna. You can use it like this:
Lemme take it. = Let me take it. - Let me take this.

4. Gotta
And this abbreviation can replace as many as two constructions:
- gotta = (have) got a - there is (something), to have (something).
Moreover, in some cases the verb have/has is placed before gotta, and in other cases it is omitted. Let's look at examples to better understand the rules for using this popular abbreviation.
You gotta note it. =You have got to note it. - You must write it down.
Has she gotta suitcase? = Has she got a suitcase? - She has There is suitcase?
It should be noted that gotta is still more often used in the first meaning - “must do something.” Let's look at an example from the movie Forrest Gump:

5. Wanna
The situation with this word is similar to the previous one: wanna has two meanings. Let's look at examples of their use.
- wanna = want to - want (to do something);
Do you wanna go home? = Do you want to go home? - You Want Go home?
- wanna = want a - want (something).
I wanna cup of tea =I want a cup of tea - I Want Cup of tea.
Excellent use case wanna words we will be served by the touching and romantic song I Wanna Grow Old with You.
Modal verb ought to apparently seemed too long to the British, and so they decided to “shorten” it to the conveniently pronounced oughta. Here's how it's used:
You oughta buy pizza for me. =You ought to buy pizza for me. - You should buy me a pizza.
But such a funny example was “provided” to us by the film “ star Wars. Episode IV: A New Hope:

7. Ain’t = am not, are not, is not, has not, have not - not (as a negative particle)
The abbreviation ain’t is the most ambiguous in the English language. First, see how many words it can replace. Secondly, you need to know this abbreviation, but it is advisable not to use it in your own speech. The fact is that some native English speakers consider it too informal and even illiterate. But authors of songs and film scripts love this word and use it quite often. Here's an example from the movie Iron Man 2:
The hero tells us this phrase:
I’d love to leave my door unlocked when I leave the house, but this ain't Canada. - I would like to leave my door unlocked when I leave the house, but this Not Canada.
In this example, ain’t replaces the combination is not. And here is an example from Bon Jovi’s song, where he sings the phrase “til we ain’t strangers anymore” (while we are not strangers yet).
In this example, ain’t replaces construction are not. Be careful and look at the context to understand what is being said.
A very popular abbreviation that you will see in many films. You can use it in your own speech like this:
I have a lotta books at home. = I have a lot of books at home. = I have lotsa books at home. = I have lots of books at home. - In my house a lot of books.
We found a wonderful example of the use of two abbreviated forms of the word “a lot” in the fourth part of “The Fast and the Furious”.

9. Kinda = kind of - to some extent, like, somewhat, partly
And also kind of something - kind/type of something.
This abbreviation is used often in speech, and Americans especially love it, so let's find out how to use it. Here are simple examples:
She kinda loves him. = She kind of loves him. - She like loves him.
What kinda person are you? = What kind of person are you? - What kind of person are you? (Which one are you type person?)
Now let's look at an example from the famous song Crazy by Aerosmith. In the short passage, the abbreviation kinda is used three times to mean “kind of something,” “type of something.”
This abbreviation is also very popular. It can be used like this:
I'm sorta excited about the trip. = I'm sort of excited about the trip. - I A little / to a certain degree excited about the trip.
Consider an example from the movie “No Country for Old Men”:

Another similar reduction: the British again “ate” the preposition of. It's very easy to use:
I wanna cuppa tea = I want a cup of tea - I want cup tea.
We found an example in famous film"The King speaks." As you remember, speech therapist Lionel was from Australia, and Australians love such abbreviations as much as Americans. Lionel said this:

You probably noticed the analogy between the last words: in all of them the preposition of is added to the previous word, only changed to -ta. We can use this abbreviation as follows:
We have just come outta library. = We have just come out of library. - We just arrived from libraries.
A wonderful example was given to us by the equally wonderful film “Leon”. By the way, there is also the one you already know, gonna.

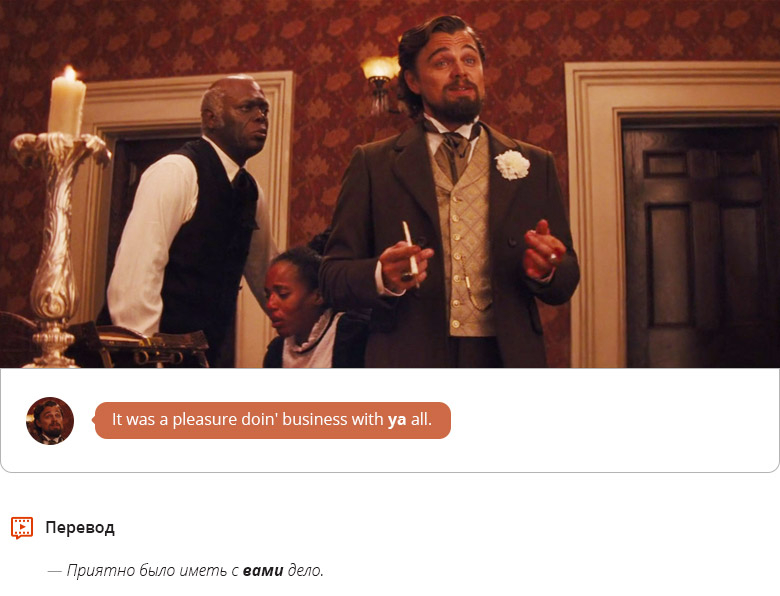
13. Ya = y’ = you - you, you, you
It would seem, why abbreviate a word that already consists of three letters? Apparently, the pace of life of English-speaking people is so high that they “shorten” the pronoun you (you, you, you) to two letters - ya or even to one - y’. You can use this shorthand like this:
Thank you ya y' for the flowers and cake! = Thank you you for the flowers and cake! - Thank you you for flowers and cake!
I must say that in films, in the speech of the characters, you will hear ya more often than you. These are the examples we found in the Django Unchained feed:

And this word often raises questions among people who have not yet studied informal English abbreviations: dunno combines three words at once - do not know. Here's how it's used.
What is John's favorite color?
-I dunno. =I don't know.
-What is John's favorite color?
- I Don't know.
We found an excellent example in the film “Shutter Island”:

15. C’mon = come on - okay, come on; let's go
The English decided to shorten the phrasal verb come on to one word. It can be used both as a verb “let’s go” and as an exclamation “come on”, “oh well”.
C'mon, don’t be so captious! She is a loyal friend. = Come on, don’t be so captious! - Come on, don't be so picky! She is a true friend.
We found a good example in the film “The Curious Case of Benjamin Button”:

The English “made fun of” the word “because” the most: in informal speech they pronounce it any way they like, but not as in the dictionary. Here's an example:
I don't like these candies ‘cos/'coz/'cause/cuz they are too sweet. = I don’t like these candies because they are too sweet. - I don't like these candies because they are too sweet.
And here’s an example you can hear in the comedy “The Hangover”:

This abbreviation has many "brothers" in different times and forms: didn'tcha = didn't you, wontcha = won't you, whatcha = what are you, whatcha = what have you, gotcha = got you, betcha = bet you, etc. Let's give a simple example of use of this abbreviation:
Whatcha doing here? = What are you doing here? - What you what are you doing here?
There is an excellent example in the film “Dark Areas”:

18. Shoulda = should have
This English abbreviation also has many “brothers”: coulda = could have, woulda = would have, mighta = might have, musta = must have, coulda = couldn't have, shouldna = shouldn't have, woulda = wouldn't have, she' da = she would have, he'da = he would have, I'da = I would have, they'da = they would have, you'da = you would have. As you already understood, the word have is replaced by one letter a, and the negative particle not is replaced by the letter n, and then these letters are attached to the word in front. Here's an example:
You shoulda told me about the rules. =You should have told me about the rules. - You should have tell me about the rules.
Here's an example we found in the movie "Avengers: Age of Ultron":

19. Didja = did you
This word continues the “tradition” of the previous two: similar contractions are used with different words and in all of them you changes to ja. For example: couldja = could you, wouldja = would you, howdja = how did you, whadaya = whataya = what do you, wheredja = where did you, whadja = what did you. Here's a simple example:
Didja buy salt yesterday? = Did you buy salt yesterday? - Did you buy salt yesterday?
A best example Adam Lambert's song Whataya Want from Me will use similar abbreviations.
20. Tell 'em = tell them - tell them
An excellent solution for those who have never learned to perfectly pronounce the sound formed by the phrase th :-) Just “swallow” complex sound and tell tell'em:
Tell'em I am going to leave at 9 p.m. = Tell them I am going to leave at 9 p.m. - Tell them, I'm going to leave at 9 pm.
A great example of using this abbreviation is Michael Jackson's song Human Nature.
In addition to these abbreviations, there are others in English, but they are used a little less frequently than those listed above. Still, you can find them in films or songs, so we present them in the table below.
| Reduction | Full phrase | Usage example |
|---|---|---|
| needa | need to | I needa leave now. =I need to leave now. - I need it now need to leave. |
| hafta/hasta | have to / has to | I hafta go, my boss is waiting for me. =I have to go, my boss is waiting for me. - I must go, my boss is waiting for me. |
| init | isn't it | It's awesome init? = It's awesome, isn't it? - It is excellent, is not it? |
| useta | used to | I useta get up early when I was a child. =I used to get up early when I was a child. - I have was a habit getting up early when I was a child. |
| supposeta | supposed to | You were supposeta buy sugar yesterday. = You were supposed to buy sugar yesterday. - You had buy sugar yesterday. |
How to correctly pronounce the above-mentioned English informal abbreviations? To find out, go to pronuncian.com and listen to the announcer say them.
Now don't forget to download our table with the most popular informal abbreviations in English.
(*.pdf, 235 Kb)
Now your vocabulary has been expanded with informal vocabulary that you can put into practice to sound natural and not old-fashioned. Be sure to study it, and then it will be easier for you to understand the phrases of movie characters or the lyrics of your favorite songs. We wish you success in improving your English!
