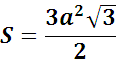The lateral faces of an arbitrary prism are parallelograms, and therefore the area of these faces is calculated according to known rules. The lateral surface area of a prism is the sum of the areas of all its lateral faces. In order to write a formula expressing the area of the lateral surface of a prism (generally speaking, inclined), consider the normal section of the prism (Fig. 382). Since the normal section plane is, by definition, perpendicular to the edges of the prism, the segments along which it intersects the lateral faces of the prism serve as the heights of these faces if the edges of the prism are taken as their bases. The areas of individual faces will be expressed by the equalities
Adding all these equalities term by term and taking them out of brackets we find
or, taking into account that the sum in parentheses is the perimeter of the normal section, we finally obtain
![]()
The lateral surface of a prism is equal to the product of its lateral edge and the perimeter of the normal section.
In the case of a straight prism, this formulation is simplified. The lateral surface of a straight prism is equal to the product of the lateral edge and the perimeter of the base of the prism.
Task. A regular straight trihedral prism with a base edge equal to a is truncated by an inclined plane. The lengths of the lateral edges of a truncated prism are . Find the area of the lateral surface of the truncated prism.
Solution. The lateral faces of a truncated prism are trapezoids (rectangular). Let us apply the formula for the area of a trapezoid to each of them. We find
and the lateral surface area is .
Section 3 Geometry
Topic 3.2. Polyhedra
Practical work No. 2 “Finding the elements of a prism, its surface area”
Types of student independent work: according to the conditions of the problem, find the area of the lateral, full surface of the prism
Goals:
consolidate the concepts of prism, parallelepiped, rectangular parallelepiped, linear dimensions, diagonal, lateral and total surface area of a prism;
to develop skills in finding a prism among other spatial figures and its elements;
continue to develop skills in applying formulas for finding the area of the lateral and total surface of a prism in solving practical problems;
continue to develop interest in subject knowledge and the application of knowledge in solving practical problems;
Guidelines
Study theoretical knowledge about prisms using lecture material and material proposed in the work.
Answer security questions.
Study the course of practical work, answer control questions.
Carry out independent work on the proposed option using the sample design.
Theoretical knowledge
Prism- a polyhedron, two faces of which are polygons lying in parallel planes, and the remaining faces are parallelograms having common sides with these polygons.
Types of prisms.
A prism whose base is a parallelogram is called parallelepiped.
Rectangular parallelepiped- is a parallelepiped, all faces of which are rectangles
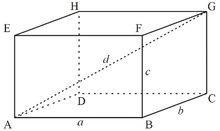
Right parallelepiped is a parallelepiped with 4 rectangular sides
Cube is a rectangular parallelepiped, all of whose faces are squares.
Straight prism is a prism whose side ribs are perpendicular to the plane of the base.
Other prisms are called inclined.
Correct prism is a right prism whose base is a regular polygon. The lateral faces of a regular prism are equal rectangles.
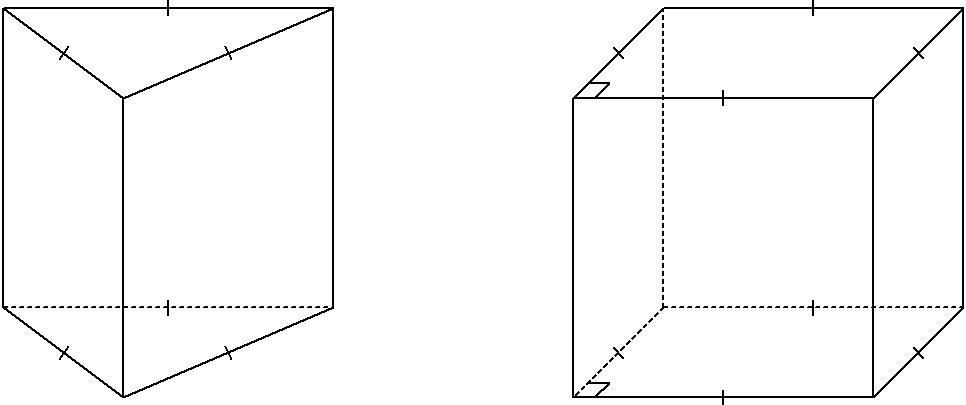
The base of the prism can be a polyhedron with any number of sides. The name of the prism depends on the number of sides .
Prism properties:
The bases of the prism are equal polygons.
The lateral faces of the prism are parallelograms.
The lateral edges of the prism are parallel and equal.
Lateral surface area of a straight prism
S b.p. = P H
where P is the perimeter of the base of the prism (the sum of all sides of the base), H is the height of the prism. The height of the straight prism coincides with the side edge.
Total surface area of the prism equal to the sum of the area of its lateral surface and twice the area of the base
S p.p. = P H +2 S basic
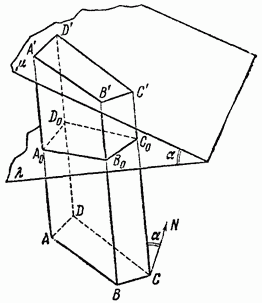
The square of the diagonal of a rectangular parallelepiped is equal to the sum of the squares of its three linear dimensions: d 2
= a 2
+b 2
+c 2
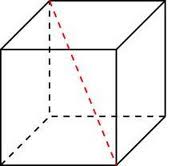
Control questions
Among the bodies depicted, select those that
are polyhedra. Which ones are prisms?
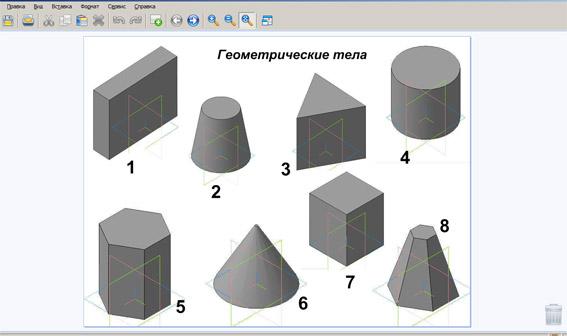
Show for a prism:
a) tops b) bases c) faces d) edges
What polyhedra lie at the base of the prism? In what planes do the bases of the prisms lie?
What segments are the lateral edges of the prism?
What kind of polygons are all the faces of a parallelepiped?
How many dimensions does a rectangular parallelepiped have?
What polygons are the bases and side faces of a rectangular prism (quadrangular, pentagonal)? How many faces does a triangular (quadrangular, pentagonal) prism have?
What surfaces does the lateral surface area of the prism and the total surface area of the prism consist of?
Write down the formula for finding the area of the lateral and total surface of a rectangular parallelepiped.
Write down the formula to find the diagonal of a rectangular parallelepiped.
Assignment for practical work: using these models, find the area of the lateral, full surface of the prism
Example: Find the area of the lateral, full surface of the prism.
Progress
1. To find the area of the lateral surface of the prism, you need to measure the following elements of the prism with a ruler: sides of the base, height. Substitute the values into the formula to find the area (if the prism is straight)
2. To find the area of the total surface of the prism, you need to find the area of the base of the prism (area of a triangle, rectangle, rhombus)
The total surface area of the prism is found as the sum of the areas of the lateral surface and the two bases.
Registration of work:
|
| Given:АВСС 1 В 1 А 1 triangular prism, straight, regular AB=BC=AC = 5 cm, H = 10 cm Find: S b.p. , S p.p. Solution: S b.p. = P H P=5+5+5=15(cm), H=10cm S b.p.= 15 10 = 150 (cm 2) Heron's formula allows you to calculate the area of a triangle (S) based on its sides a, b, c: S basic = √р(р-а)(р-в)(р-с) where p is the semi-perimeter of the triangle: p = (a+b+c):2 р= 15:2 =7.5(cm) S p.p. = P H +2 S base, = 150 + 2 7.7 = 164.4 (cm 2) |
| Solving a practical problem | The collector ordered an aquarium in the shape of a regular hexagonal prism. How many square meters of glass are needed to make an aquarium if the side of the base is 0.5 m and the height is 1.2 m? Round your answer to the nearest hundredth. First we find the area of the base. Since the base is a regular hexagon, we find the area of the base using the formula: 2. Find the area of the lateral surface: 0.5∙1.2∙6= 3.6(m²) 3. Find the total surface area using the formula: S=Sside+Smain=3.6+2∙0.6495=4.899(m2) Answer: 4.90 m² Control questions |
| What measurements are needed to calculate the lateral and total surface area of a prism? How to calculate the perimeter of the base of a prism? Write down the formulas for calculating the area of the lateral and total surface of a prism? What changes will occur when calculating the area of the lateral and total surface of a regular quadrangular, pentagonal, hexagonal prism. Tasks for independent work: Option 1 |
|
1 . How many edges does a hexagonal prism have?
Answer: a)18, b)24, c)12.
2 .Choose the correct statement.
a) a prism is called regular if its bases are regular polygons;
b) a triangular prism has two diagonals;
c) the height of the prism is equal to its lateral edge;
3.Task Find the lateral and total surface area of a rectangular parallelepiped if its dimensions are 2m, 3m, 5m.
4 . Task. The collector ordered an aquarium in the shape of a regular quadrangular prism. How many square meters of glass are needed to make an aquarium if the side of the base is 70 cm and the height is 60 cm?
Option 2
1 .How many faces does a hexagonal prism have?
Answer: a)6, b)8, c)10
2
a) the area of the total surface of a prism is called the sum of the areas of its lateral faces and base;
b) a triangular prism has no diagonals;
c) the height of a straight prism is equal to its lateral edge;
3 .Task. Find the lateral and total surface area of a rectangular parallelepiped if its dimensions are 3cm, 4cm, 5cm.
4. Problem It is necessary to make a box with a lid for storing potatoes in the shape of a straight prism 0.7 m high. At the base of the prism is a rectangle with sides 0.4 m and 0.6 m. How much plywood will be needed to make the box?
Option 3 (advanced level tasks)
1 .How many faces does a quadrangular prism have?
Answer: a)6, b)8, c)10
2 . Choose the correct statement.
a) An n – carbon prism has 2 n edges;
b) the area of the total surface of a prism is called the sum of the areas of its lateral faces;
c) a triangular prism has three diagonals;
3 .Task. How many sheets of 8-wave slate, 1750*1130 mm in size, are needed to cover the roof of a building 10 m long? The pediment has the shape of an isosceles right triangle with a hypotenuse of 10 m and a leg of 7 m.
4 .Task. It is necessary to cover a room with wallpaper of the “matting” type, the length of which is 6 m, width 4 m, height 3 m, the area of windows and doors is 1/5 of the total area of the walls. How many rolls of wallpaper are needed to cover a room if the length of the roll is 12 m and the width is 50 cm?
Forms of control
Timely execution. Registration of work. Correct use of formulas for calculations, absence of calculation errors.
Literature
Bashmakov M.I. Mathematics. Textbook for general education institutions beginning. and Wednesday prof. education
http://fcior.edu.ru/ - “Federal Center for Information and Educational Resources”. Modules: Regular polyhedra. Prism. Parallelepiped.
ru.wikipedia.org› Regular polyhedron. Prism. Parallelepiped.
Instructions
Understand what a prism is and what form this geometric figure can have. Please note that the word “prism” is translated from Latin as “something sawn off.” This polyhedron always has two bases, which are located in parallel planes and are equal polygons. They can be triangular, quadrangular, or n-gonal.
Remember that the number of remaining (side) faces depends on the type of base. If the base is a triangle, there will be three side faces, a quadrilateral will have four, and so on.
where a is the length of one side of this figure.
Simply put, measure one of the sides of the square and multiply this figure by the number of sides, that is, by 4. In our case, the perimeter is 16 cm (4 * 4).
Rectangle and rhombus. For these two figures, only the sides parallel to each other are equal, so the perimeter is determined as follows:
where a and b are the touching sides. Thus, in our example, the perimeter of the rectangle is 24 cm (2*(8+4)).
Triangle. Since triangles can be completely different - isosceles, irregular, with right angles, the only correct way to determine the perimeter of such a figure is the formula:
That is, to calculate the perimeter of a triangle, simply measure the lengths of all three sides and add the resulting numbers. In our case, the perimeter of the triangle is 10.7 cm (2+5+3.7).
Circle . The perimeter of a circle is called the circumference, which is calculated using a special formula:
where d is the diameter of the circle, and 3.14 is the number “pi”, which was specially derived by scientists to determine the perimeter of a given geometric figure. Our circle (see figure) has a diameter of 3 cm, that is, the perimeter of the circle is 9.42 cm (3 * 3.14).
Sources:
- how to find the circumference of a circle
Perimeter triangle, like any other flat geometric figure, is the sum of the lengths of the segments limiting it. Therefore, to calculate the length of the perimeter, you need to know the lengths of its sides. But due to the fact that the lengths of the sides in geometric figures are related by certain relationships to the values of the angles, knowledge of only one or two sides and one or two angles may be sufficient.
Instructions
Add up all the side lengths triangle(A, B, C), if they are known, is the simplest possible way to find the length of the perimeter (P): P=A+B+C.
If the values of two angles are known triangle(β and γ) and the length of the side between them (A), then, based on the theorem of sines, you can find out the lengths of the other two sides. Each of them will be equal to the quotient of the division operation, where the dividend will be the product of the length of the known side and the sine of the angle between the known and the desired sides, and the divisor will be the sine of the angle equal to the difference between 180° and the sum of two known angles. That is, the unknown side B will be calculated using the formula B=A∗sin(β)/sin(180°-α-β), and the unknown side C - using the formula C=A∗sin(γ)/sin(180°- α-β). Then the length of the perimeter (P) can be determined by adding these two expressions to the length of the known side A: P = A + A∗sin(β)/sin(180°-α-β) + A∗sin(γ)/sin(180 °-α-β) = A∗(1 + sin(β)/sin(180°-α-β) + sin(γ)/sin(180°-α-β)).